
One of the most important diagnostic tests in Cardiology to interpret is the EKG.
Here are my thoughts and notes. Will continue to this thread. Let me know what you think!
Thread #8: Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
#arjuncardiology #medtwitter #CardioTwitter #MedEd #IMG
Here are my thoughts and notes. Will continue to this thread. Let me know what you think!
Thread #8: Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
#arjuncardiology #medtwitter #CardioTwitter #MedEd #IMG
Ventricular Conduction:
- Normal electrical stimulus reaches ventricles from the atria through the AV node & His-Purkinje systems
- First part of heart to be depolarized is the left-side of the septum; then spreads to RV and LV by right & left bundles
- Normal QRS < 0.10 sec
- Normal electrical stimulus reaches ventricles from the atria through the AV node & His-Purkinje systems
- First part of heart to be depolarized is the left-side of the septum; then spreads to RV and LV by right & left bundles
- Normal QRS < 0.10 sec

RBBB:
- 1st phase of depolarization: Left side of septum is stimulated first (branch of left bundle); on a normal ECG produces a septal r-wave in V1 and small septal q-wave in V6. No impact with RBBB.
- 2nd phase: Simultaneous depolarization of LV and RV. No impact with RBBB.
- 1st phase of depolarization: Left side of septum is stimulated first (branch of left bundle); on a normal ECG produces a septal r-wave in V1 and small septal q-wave in V6. No impact with RBBB.
- 2nd phase: Simultaneous depolarization of LV and RV. No impact with RBBB.

RBBB:
- 3rd phase: Delayed RV depolarization produces a third phase of ventricular stimulation. V1 (right-sided chest leads) records this phase of ventricular stimulation as a (+) wide deflection (R' wave).
- Will see a wide negative S-wave deflection in left-sided chest leads
- 3rd phase: Delayed RV depolarization produces a third phase of ventricular stimulation. V1 (right-sided chest leads) records this phase of ventricular stimulation as a (+) wide deflection (R' wave).
- Will see a wide negative S-wave deflection in left-sided chest leads
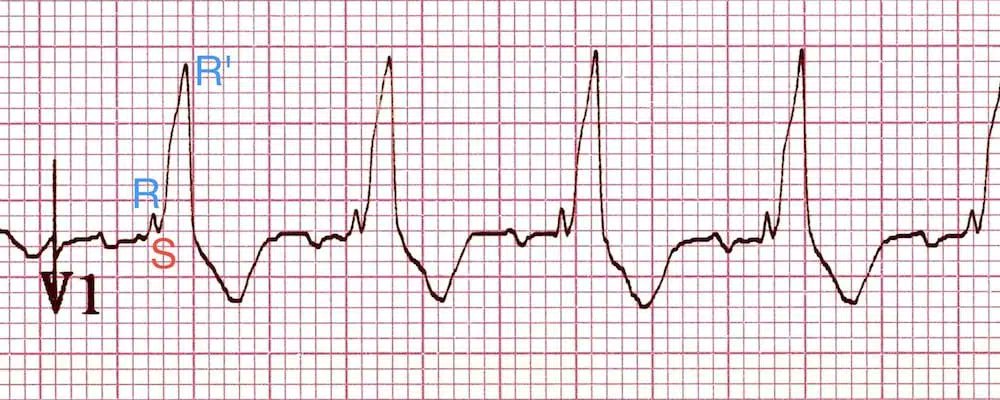
Complete and Incomplete RBBB:
- Complete: QRS > 0.12 seconds in duration w/ rSR' in lead V1 and qRS in V6
- Incomplete: Same QRS patterns, but duration is between 0.10 - 0.12 seconds
- Complete: QRS > 0.12 seconds in duration w/ rSR' in lead V1 and qRS in V6
- Incomplete: Same QRS patterns, but duration is between 0.10 - 0.12 seconds
RBBB:
- May not have underlying heart disorder
- Can be seen with ASD, COPD with pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary stenosis, cardiomyopathy, and CAD
- No specific treatment, can be permanent or transient
- May not have underlying heart disorder
- Can be seen with ASD, COPD with pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary stenosis, cardiomyopathy, and CAD
- No specific treatment, can be permanent or transient
Thank you to this amazing website for the graphics: litfl.com/right-bundle-b…
Also this is another great video:
Let me know what you think and stay tuned for left bundle branch block next!
Also this is another great video:
Let me know what you think and stay tuned for left bundle branch block next!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh














