1/Is trying to understand peripheral nerve injury getting on your last nerve? Is the brachial plexus breaking you?
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you understand, recognize & remember the classification of peripheral nerve injuries
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #neurorad #neurotwitter
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you understand, recognize & remember the classification of peripheral nerve injuries
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #neurorad #neurotwitter

2/Normally the peripheral nerve is protected by surrounding myelin & connective tissue.
Think of the nerve like a hot dog. It is wrapped nice & cozy: first, by toppings right up against the hot dog (myelin) & then a bun holding it all in (connective tissue)
Think of the nerve like a hot dog. It is wrapped nice & cozy: first, by toppings right up against the hot dog (myelin) & then a bun holding it all in (connective tissue)

3/Although nerve injury can be compressive or stretch or even from radiation, it is easiest to think of it like a punch to the face. Imaging that sort of injury hits the nerve, like a fist to your face 

4/Type of injury you get depends on how hard you were hit.
At its mildest, a punch gives you a bruise or black eye. This is the mildest nerve injury, neuropraxia.
Myelin is injured, so you get a conductive deficit, but it heals—just like you’ll eventually open that eye again
At its mildest, a punch gives you a bruise or black eye. This is the mildest nerve injury, neuropraxia.
Myelin is injured, so you get a conductive deficit, but it heals—just like you’ll eventually open that eye again

5/If the hit is harder, you don’t just get soft tissue injury, you break a bone. This is degree of nerve injury is called axonotmesis
The axon is disrupted, but the connective tissue is intact. So it can regenerate, like a fracture forms callus to fill the defect
The axon is disrupted, but the connective tissue is intact. So it can regenerate, like a fracture forms callus to fill the defect

6/Finally, the hardest hit is decapitation. This is the most severe injury—neurotmesis--axon & connective tissue are both disrupted.
Nerve is essentially severed. Like decapitation, the nerve can’t recover from this. Although, unlike decapitation, surgery can help this injury
Nerve is essentially severed. Like decapitation, the nerve can’t recover from this. Although, unlike decapitation, surgery can help this injury

7/This is the Seddon classification of injury.
But it’s missing something—bc it groups all nerve “fractures” or axonotmesis as the same.
But not all fractures are equal. There’s a big difference between a nasal fx & a LeFort. Sunderland classification makes this distinction
But it’s missing something—bc it groups all nerve “fractures” or axonotmesis as the same.
But not all fractures are equal. There’s a big difference between a nasal fx & a LeFort. Sunderland classification makes this distinction

8/Sunderland classification divides the nerve “fractures” into different severities—depending on how much of the axon/connective tissue is disrupted
Sunderland class 2/3 are like mild fx’s that can heal on their own, while class 4 are the facial smash fractures that need surgery
Sunderland class 2/3 are like mild fx’s that can heal on their own, while class 4 are the facial smash fractures that need surgery

9/Think of the connective tissue like scaffolding—if it's intact, nerve can use the scaffolding to rebuild
If only the axon is injured, scaffold is intact & it’ll heal
If only endoneurium is disrupted, there’s enough to rebuild
But only having perineurium is often not enough
If only the axon is injured, scaffold is intact & it’ll heal
If only endoneurium is disrupted, there’s enough to rebuild
But only having perineurium is often not enough

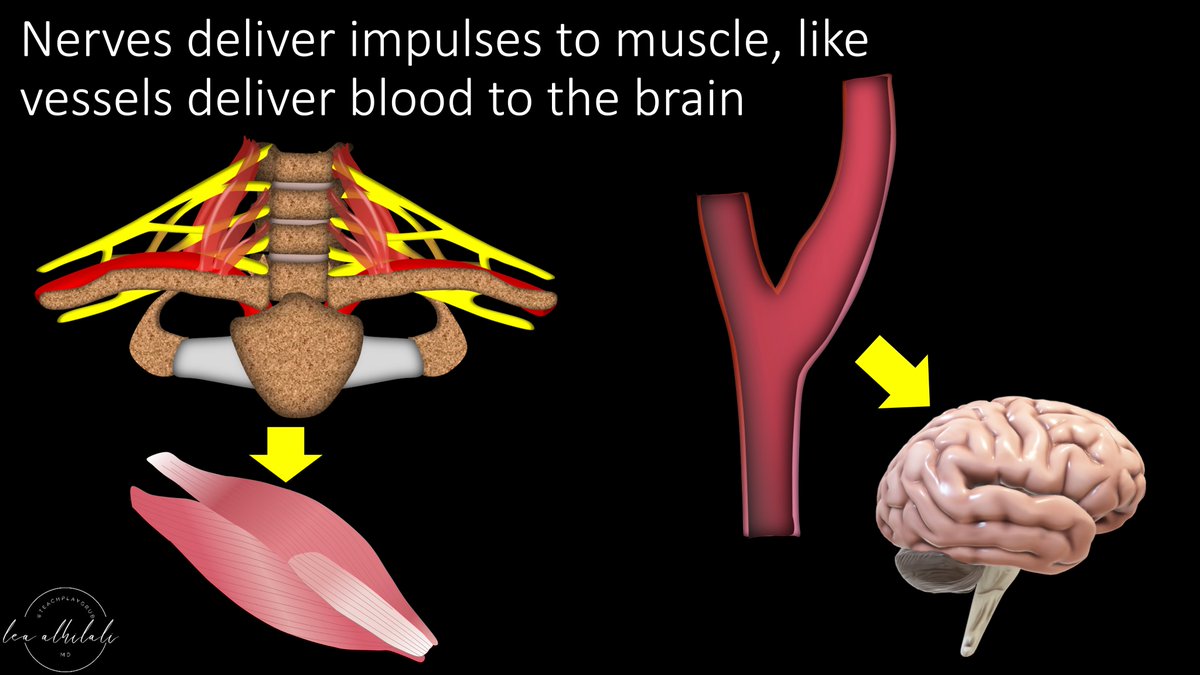
10/How do these injuries look on imaging?
Think of the nerve like a vessel.
Nerves deliver information to muscles the way your carotids deliver blood/oxygen to your brain.
Muscles are the end organ for nerves the way your brain is the end organ for your carotid
Think of the nerve like a vessel.
Nerves deliver information to muscles the way your carotids deliver blood/oxygen to your brain.
Muscles are the end organ for nerves the way your brain is the end organ for your carotid
11/How much damage you do the nerve is like how much stenosis there is in the carotid.
The worse the stenosis, the more likely you are to have a stroke.
Similarly, the worse the nerve injury, the more likely you are to have denervation changes in the muscle
The worse the stenosis, the more likely you are to have a stroke.
Similarly, the worse the nerve injury, the more likely you are to have denervation changes in the muscle

12/Class 1 or nerve bruise is like mild calcified plaque you see in the carotid everyday. It does mean there’s been endothelial injury, but it’s not severe enough to cause any stroke.
So the nerve is bright on imaging from the injury, but the muscle is normal
So the nerve is bright on imaging from the injury, but the muscle is normal

13/Here is an example of a Class 1 injury—this is a patient with right jaw paresthesias after a right mandibular tooth extraction. You can see that the right inferior alveolar nerve is bright compared to the left—but no muscle signal 

14/Class 2/3 or mild nerve fracture is like a dissection. Part of the wall is disrupted like a dissection, but part is intact
Vessel is often enlarged in dissection. Nerve is too enlarged
Also, dissections throw emboli causing end organ damage—so have muscle signal here too
Vessel is often enlarged in dissection. Nerve is too enlarged
Also, dissections throw emboli causing end organ damage—so have muscle signal here too

15/Here’s an example of class 2/3 injury. Nerves of the brachial plexus are enlarged, like a vessel w/a false lumen added to it, but there’s no discontinuity.
You can’t see the difference between axon & endoneurium disruption on imaging, so they’re grouped together
You can’t see the difference between axon & endoneurium disruption on imaging, so they’re grouped together

16/In class 4 injury (serious fx) only perineurium remains.
It’s like a contained nerve rupture—like a pseudoaneurysm is like a contained vessel rupture. So it’s focally enlarged (neuroma) like a vessel is focally enlarged at a pseudoaneurysm
It’s like a contained nerve rupture—like a pseudoaneurysm is like a contained vessel rupture. So it’s focally enlarged (neuroma) like a vessel is focally enlarged at a pseudoaneurysm

17/Class 5 injury is nerve decapitation—it’s like thrombosis of an artery, nothing gets through
And just like how thrombosis is associated w/stroke, these injuries have muscle denervation.
But unlike real decapitation, some of these injuries may be amenable to microsurgery
And just like how thrombosis is associated w/stroke, these injuries have muscle denervation.
But unlike real decapitation, some of these injuries may be amenable to microsurgery

18/Here is an example of class 5 injury. Nerves of the brachial plexus are focally disrupted, and there is fluid in the gap, just like how there would be thrombus in the gap of a thrombosed vessel or squirting blood in the gap of a decapitated head 😳 

19/So now you understand the pathology behind peripheral nerve injuries, how they are classified, and how to recognize them on imaging
Hopefully, now you can approach these injuries without being nervous!
Hopefully, now you can approach these injuries without being nervous!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















