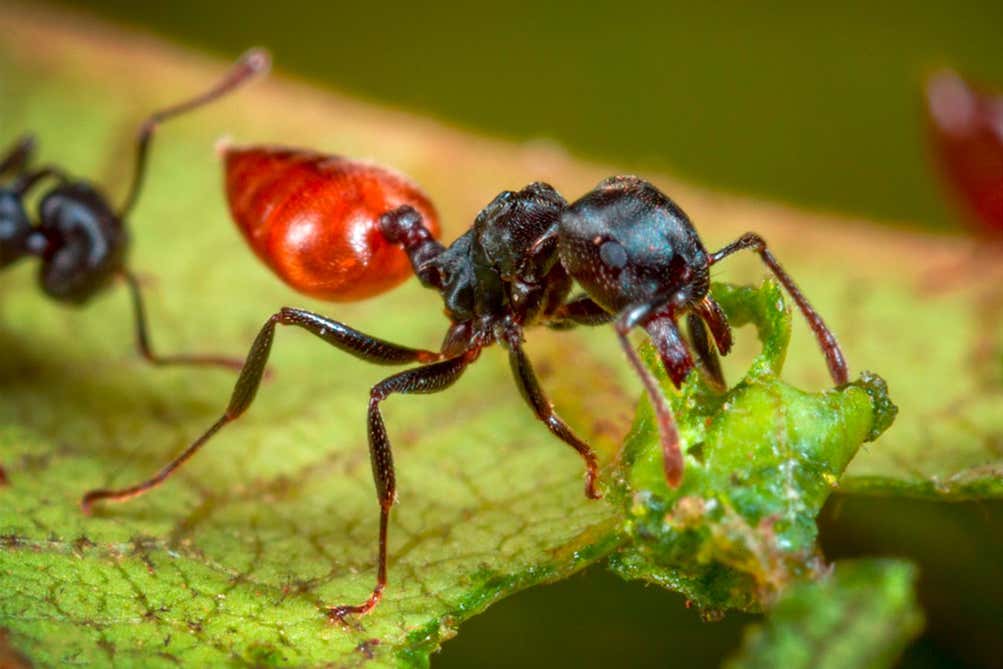
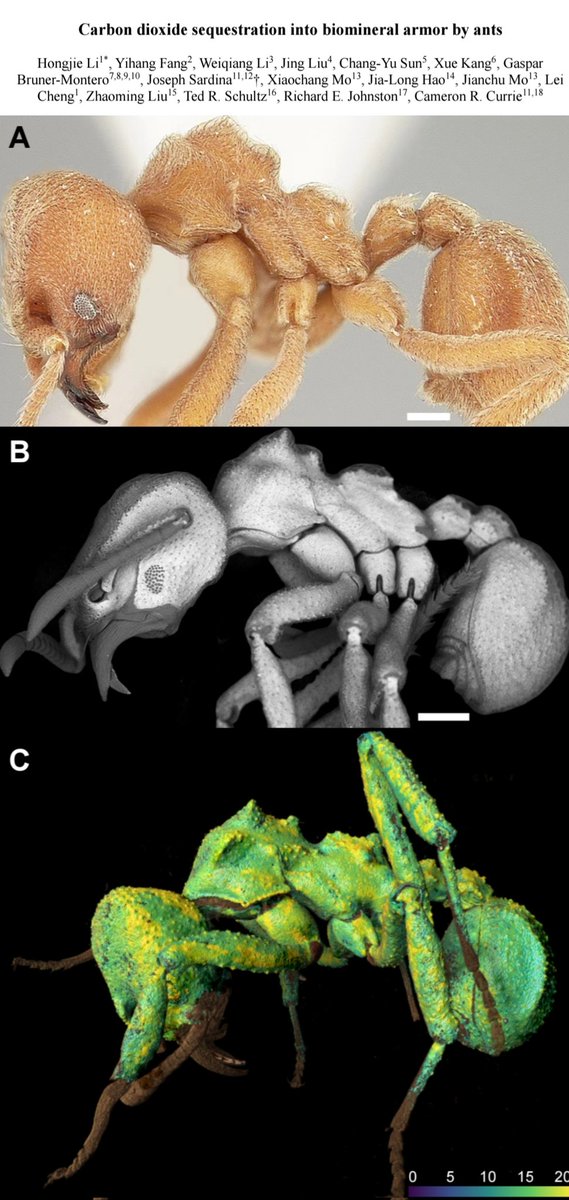
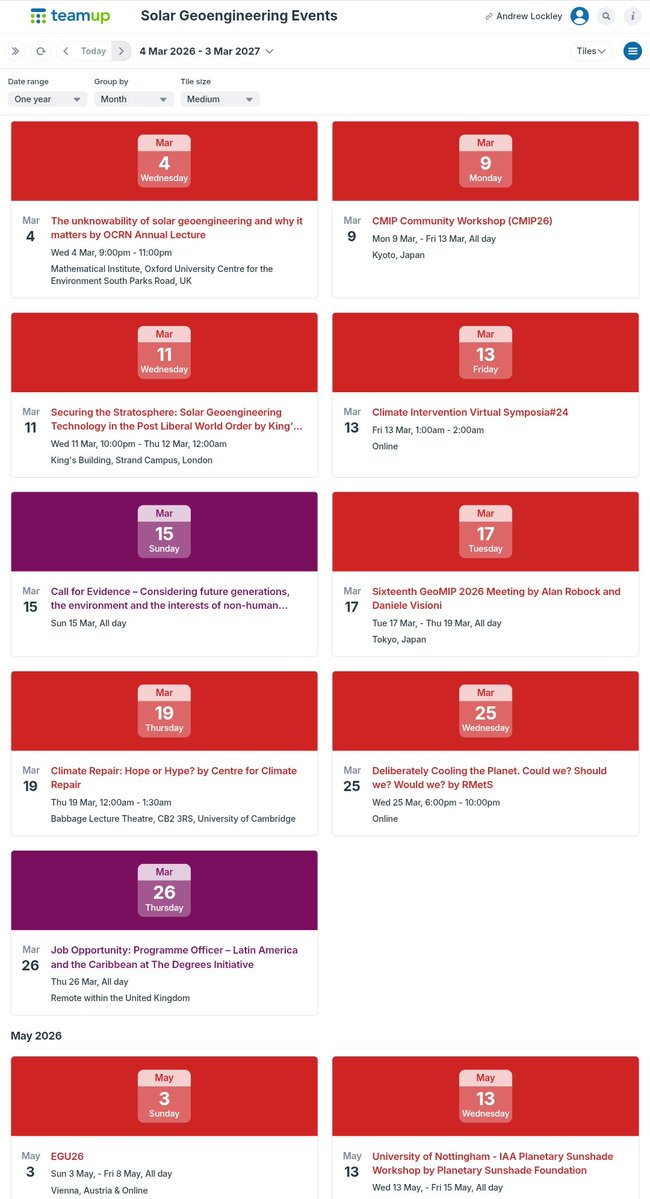
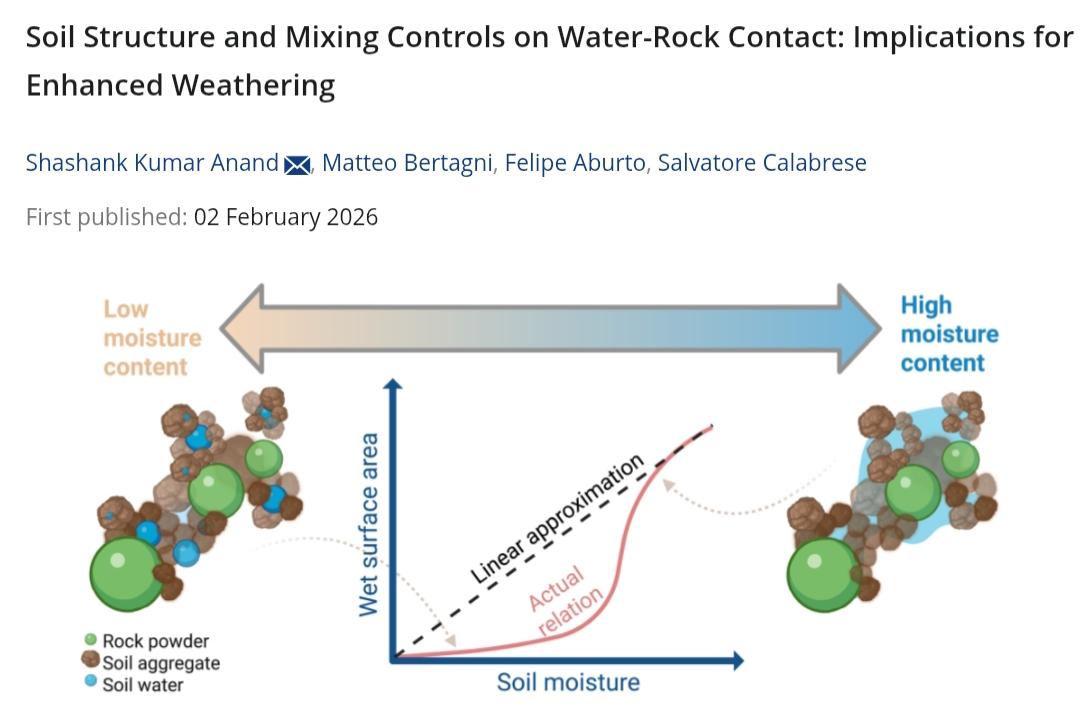
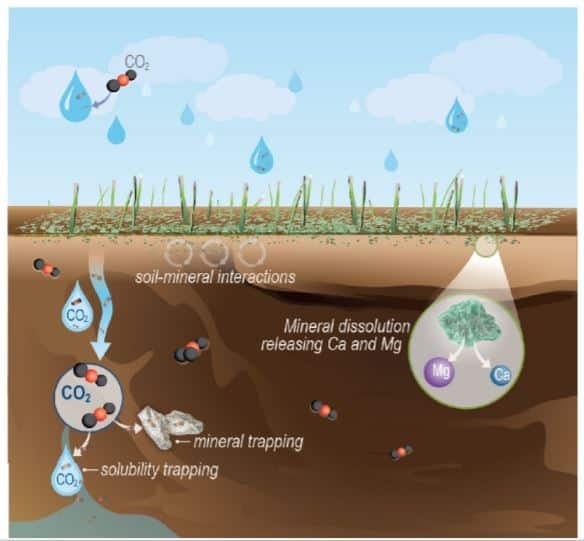
🚨NEW STUDY🚨
"Six models are used in a recent study to analyze the climatic, environmental & socio-economic consequences of #overshooting a C budget consistent with the 1.5°C temp target along the cause-effect chain from emissions & #CarbonRemovals to climate risks & impact."
🧵
"Six models are used in a recent study to analyze the climatic, environmental & socio-economic consequences of #overshooting a C budget consistent with the 1.5°C temp target along the cause-effect chain from emissions & #CarbonRemovals to climate risks & impact."
🧵

"Global climatic indicators such as CO2-concentration and mean temperature closely follow the #CarbonBudget #overshoot with mid-century peaks of 50 ppmv and 0.35°C, respectively."
2/10
2/10
Findings of this study highlight that "investigating #overshoot scenarios requires temporally and spatially differentiated analysis of climate, environmental and socioeconomic systems."
3/10
3/10
Researchers find "persistent and spatially heterogeneous differences in the distribution of #carbon across various pools, ocean heat content, sea-level rise as well as #economic damages."
4/10

4/10


"Moreover, it was find in the study that key impacts, including degradation of marine ecosystem, heat wave exposure & economic damages, are more severe in equatorial areas than in higher latitudes, although absolute #temperature changes are stronger in higher latitudes."
5/10
5/10

"The detrimental effects of a 1.5 °C warming and the additional effects due to #overshoots are strongest in non-OECD countries (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development)."
6/10
6/10

"Constraining the overshoot inflates CO2 prices, thus shifting #CarbonRemoval towards early #afforestation while reducing the total cumulative deployment only slightly, while mitigation costs increase sharply in #DevelopingCountries."
7/10
7/10

"Thus, scenarios with C budget overshoots can reverse global mean temp increase but imply more persistent & geographically heterogeneous impacts. Overall, the decision about #overshooting implies more severe trade-offs btw #mitigation & impacts in #DevelopingCountries."
8/10

8/10


Read the study led by @NB_pik entitled: "Exploring risks and benefits of overshooting a 1.5 °C carbon budget over space and time" here ⬇️
iopscience.iop.org/article/10.108…
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
#Overshoot
9/10
iopscience.iop.org/article/10.108…
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
#Overshoot
9/10

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh