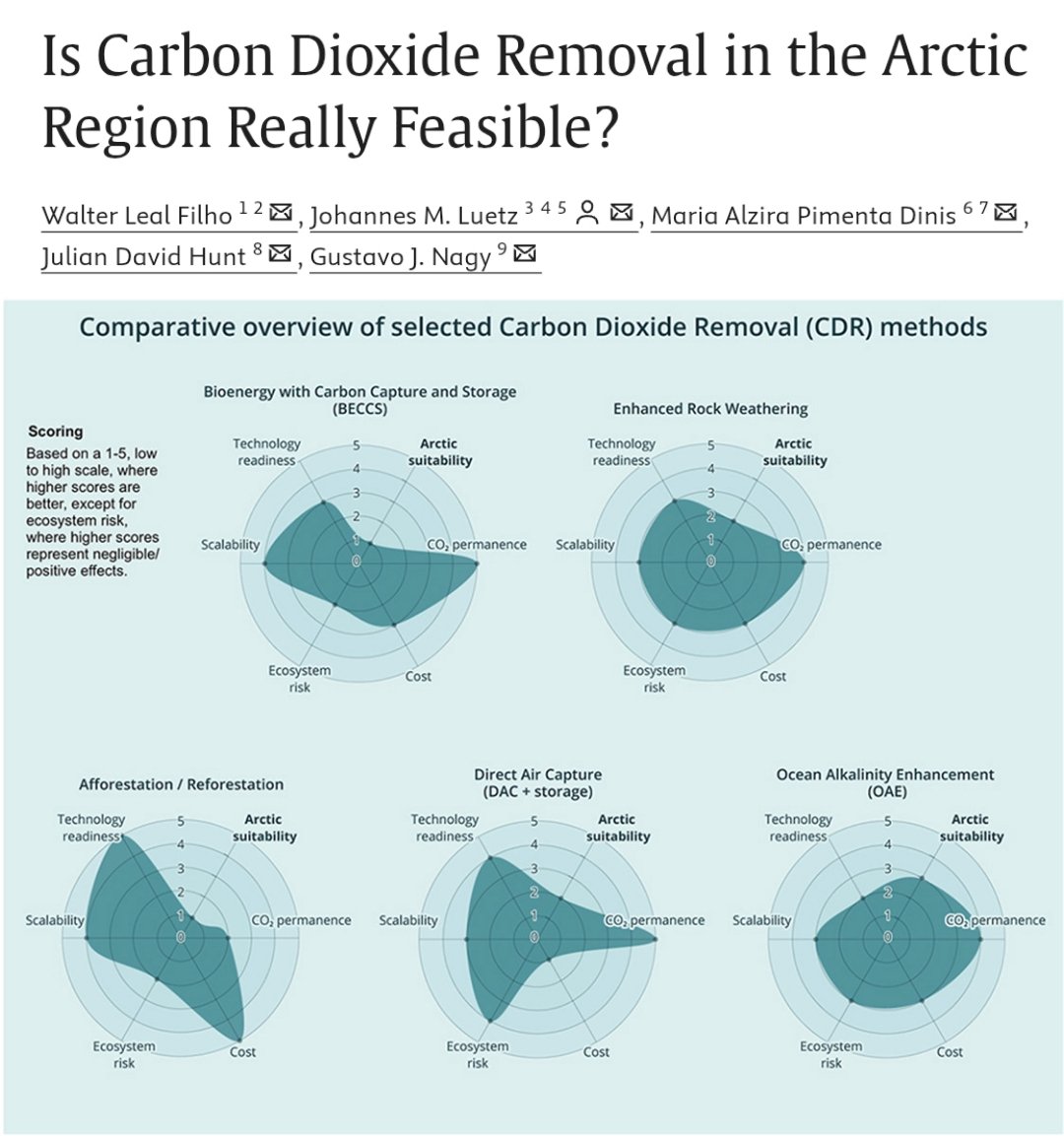
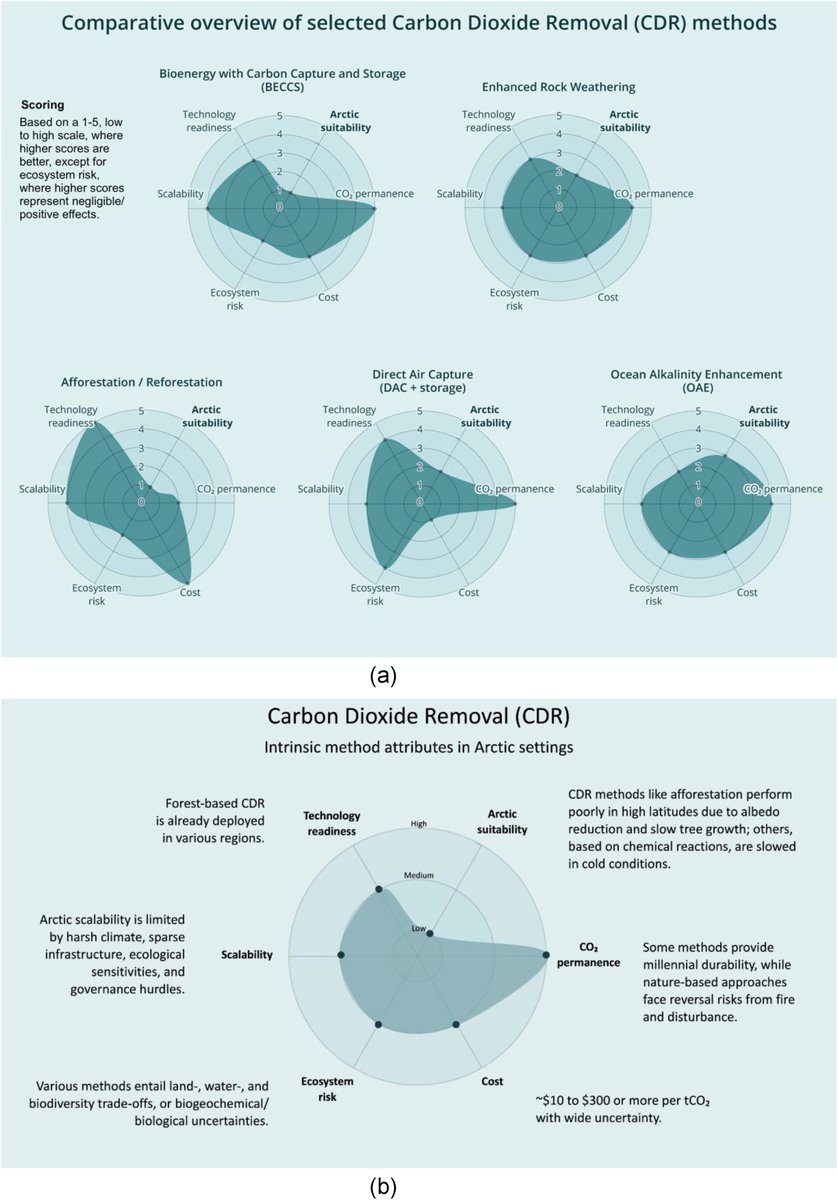
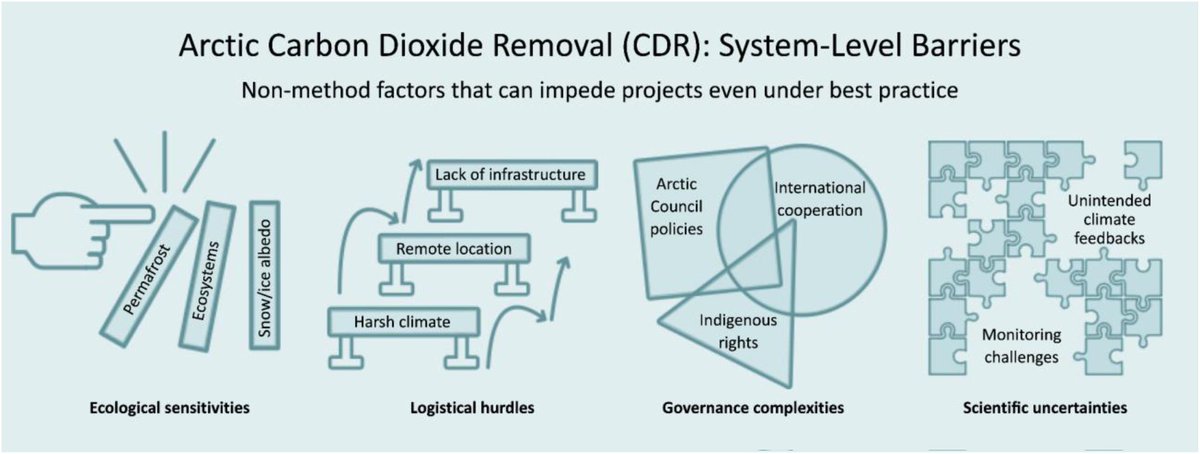
🚨🌊NEW PAPER 🌊🚨
"One of the planet’s most vital #CarbonSinks i.e. SOUTHERN OCEAN (SO) (absorbs ~40% of C) is revealing its secrets as tiny organisms in the SO play an outsized role in moderating Earth’s #climate."
Details from the recent research are discussed in a🧵⬇️
1/8
"One of the planet’s most vital #CarbonSinks i.e. SOUTHERN OCEAN (SO) (absorbs ~40% of C) is revealing its secrets as tiny organisms in the SO play an outsized role in moderating Earth’s #climate."
Details from the recent research are discussed in a🧵⬇️
1/8

"Based on 107 independent observations of the seasonal cycle from 63 #biogeochemical profiling floats, new study conducted by scientists from #NOAA & University of Hawai'i provide the basin-scale estimate of distinct biogenic #CarbonPool production at Southern Ocean."
2/8
2/8

Researchers find "significant meridional variability with enhanced #ParticulateOrganicCarbon production in the subantarctic & polar Antarctic sectors & enhanced #DissolvedOrganicCarbon production in the subtropical & sea-ice-dominated sectors."
3/8
3/8

"#ParticulateInorganicCarbon production peaks between 47°S and 57°S near the “great calcite belt.” Relative to an abiotic Southern Ocean (SO), organic C production enhances CO2 uptake by 2.80 ± 0.28 Pg C y−1, while PIC production reduces CO2 uptake by 0.27 ± 0.21 Pg C y−1."
4/8
4/8

"Without organic C production, the SO would be a CO2 source to the atm. The findings of this study emphasize the importance of #DOC & #PIC production, in addition to the well-recognized role of #POC production, in shaping the influence of C export on air–sea CO2 exchange."
5/8
5/8

IN SIMPLE WORDS ⬇️
🌊 "Researchers discovered that if the amount of #carbon produced by tiny organisms in Southern Ocean decreased by 30%, the Southern Ocean would release carbon dioxide instead of #absorbing it, which could worsen the #GreenhouseEffect on our planet."
6/8
🌊 "Researchers discovered that if the amount of #carbon produced by tiny organisms in Southern Ocean decreased by 30%, the Southern Ocean would release carbon dioxide instead of #absorbing it, which could worsen the #GreenhouseEffect on our planet."
6/8

Read the open-access paper entitled: "Biogenic carbon pool production maintains the Southern Ocean carbon sink" here ⬇️
pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pn…
#CarbonSink
7/8
pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pn…
#CarbonSink
7/8
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh