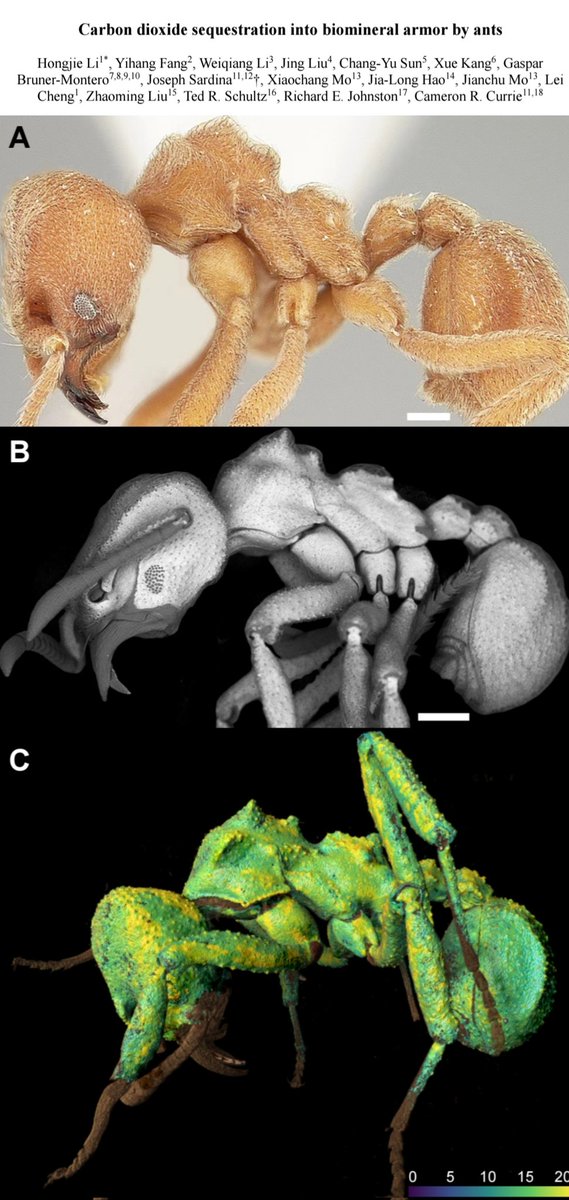
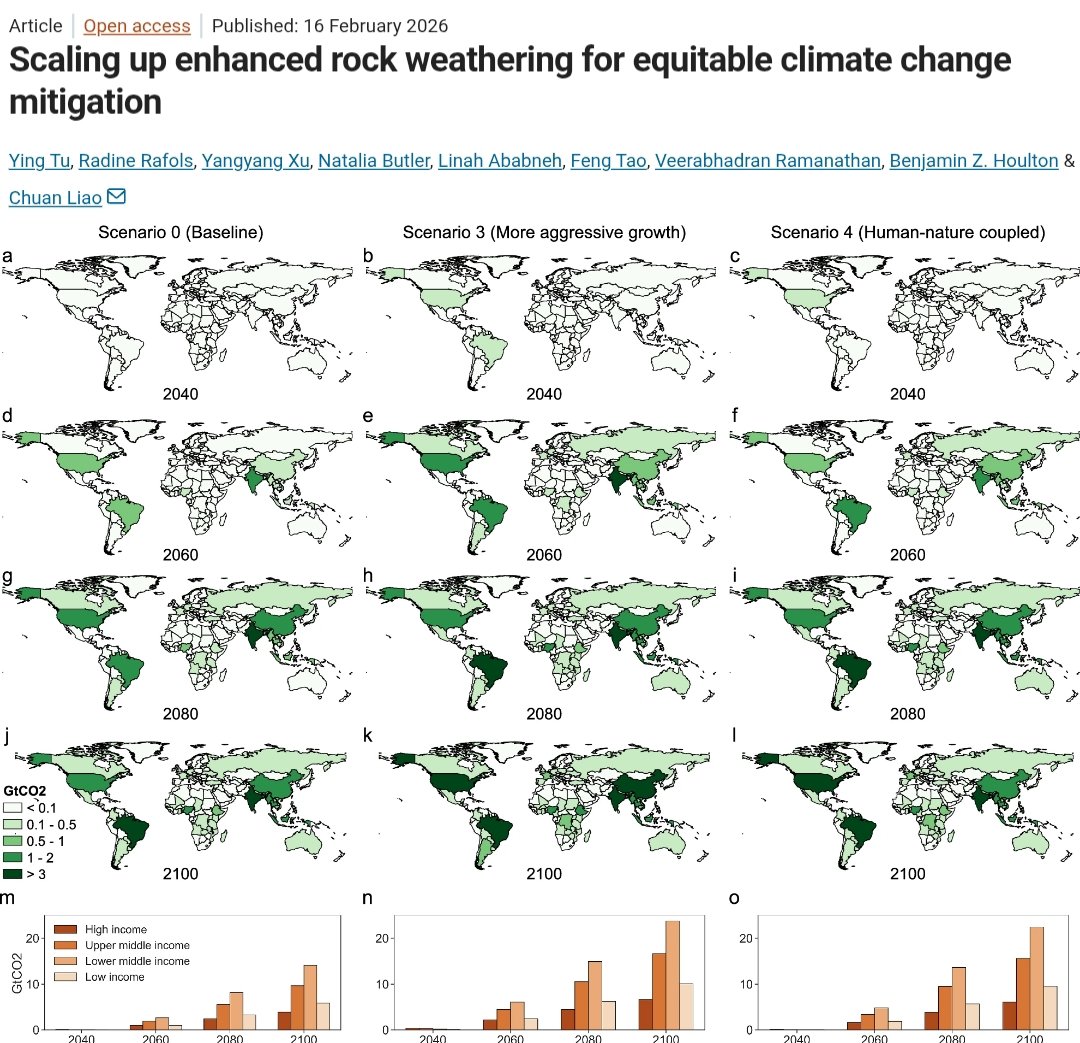
🚨✍️𝐍𝐄𝐖 𝐃𝐎𝐂𝐓𝐎𝐑𝐀𝐋 𝐓𝐇𝐄𝐒𝐈𝐒✍️🚨
"The discussion of energy consumption for cryogenic & combined #DirectAirCapture systems is explored in the newly published thesis."🎛️
Details are discussed in a🧵⬇️
1/10

"The discussion of energy consumption for cryogenic & combined #DirectAirCapture systems is explored in the newly published thesis."🎛️
Details are discussed in a🧵⬇️
1/10
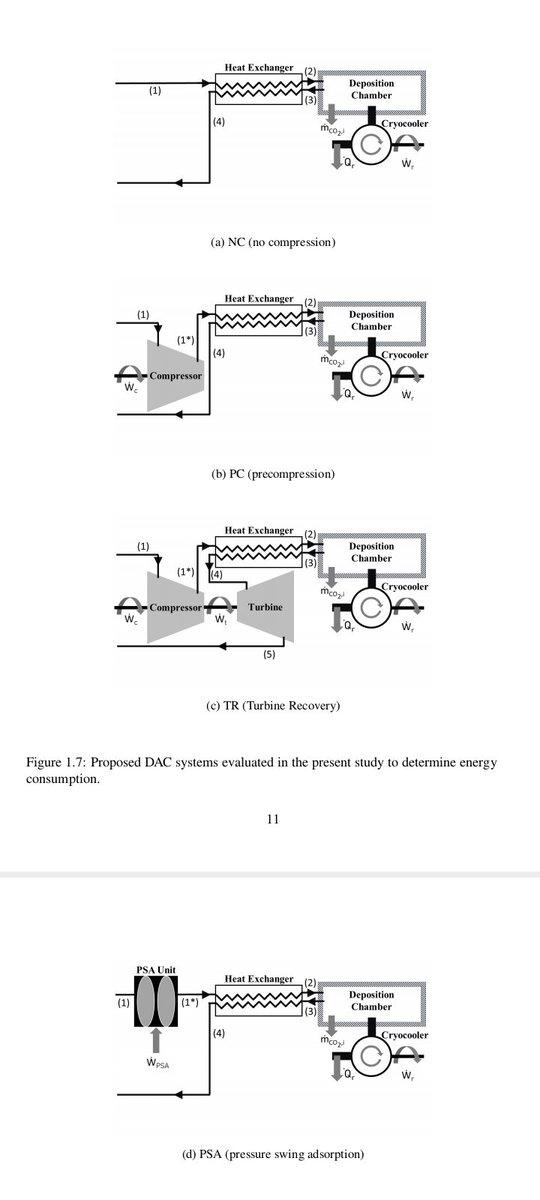

In this novel approach, "a thermodynamic model was constructed using psychometric theories to model the #desublimation of CO2 in a #DAC system. The system was modeled
to include a precooling heat exchanger & a deposition chamber where the desublimation
of CO2 occurs."
2/10
to include a precooling heat exchanger & a deposition chamber where the desublimation
of CO2 occurs."
2/10

3️⃣ base systems studied:
🔸 NC (no precompression/turbine recovery)
🔸PC (precompression only)
🔸TR (precompression & turbine recovery)
at 3️⃣ different compression ratios, n=400, 800 & 2000.
Then, a combination #DAC system, PSA, was modeled."
3/10
🔸 NC (no precompression/turbine recovery)
🔸PC (precompression only)
🔸TR (precompression & turbine recovery)
at 3️⃣ different compression ratios, n=400, 800 & 2000.
Then, a combination #DAC system, PSA, was modeled."
3/10

"A dual-column, 4️⃣-step Skarstrom Cycle PSA (pressure swing adsorption & cryogenic distillation) unit was analyzed using Extended Langmuir Models & the
ideal gas law to simulate a CO2 conc. prior to the deposition chamber. The NC & PSA systems were assessed at Tamb= -50◦C."
4/10
ideal gas law to simulate a CO2 conc. prior to the deposition chamber. The NC & PSA systems were assessed at Tamb= -50◦C."
4/10

This study finds that "while increasing the compression ratio of the system, there is no net energy benefit when capturing CO2 given the current state-of-the-art in commercial compressor & #cryocooler capabilities."
5/10
5/10

"The assessment of the efficiency of a precooler versus TR finds that it is more advantageous to utilize a heat exchanger precooler than precompression with turbine recovery in a #DAC system. Combining DAC systems may yield a more efficient system."
6/10
6/10

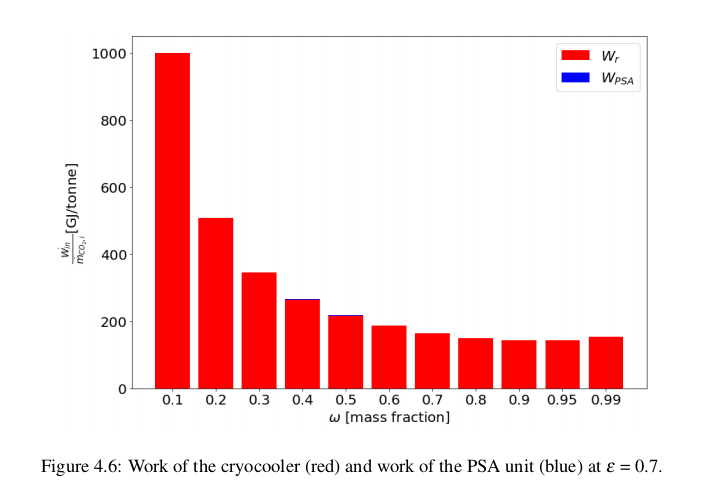
"PSA combined with cryogenic capture is less energy intensive than cryogenic capture alone. In a combined #DAC system with PSA and cryogenic distillation,
the PSA unit has a significantly lower energy consumption than the #cryocooler."
7/10

the PSA unit has a significantly lower energy consumption than the #cryocooler."
7/10


"Increasing the concentration of CO2 entering the deposition chamber significantly decreases the required energy consumption of the #cryocooler."
8/10
8/10
Read the complete #Doctoral #Thesis entitled: "Atmospheric Carbon Capture: A Review on Current Technologies and Analysis of Energy Consumption for Various Direct Air Capture (DAC) Systems" here ⬇️
commons.erau.edu/edt/728/
#DirectAirCapture
#DAC
9/10
commons.erau.edu/edt/728/
#DirectAirCapture
#DAC
9/10
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh