Tale of forgotten "#Panchatantra Tales".
Bhartiya parents used to impart moral education to their child's very early through stories of Panchtantra, also known as the "Five Moral Conduct," is all about.
It originated in India 5000 yrs ago and spread in the world.
1/20
Bhartiya parents used to impart moral education to their child's very early through stories of Panchtantra, also known as the "Five Moral Conduct," is all about.
It originated in India 5000 yrs ago and spread in the world.
1/20

The earliest of Panchtantra tales is found from the potteries excavated in Lothal. It has stories of crows, fox and pigeons. The potteries dates at least 4500 years old when it was baked in a kiln. It survived somehow.
#Archaeology IAR-Lothal
2/20
#Archaeology IAR-Lothal
2/20
https://twitter.com/GemsOfINDOLOGY/status/1605805744418590720

The original Panchatantra composed in Sanskrit has been lost. The earliest written surviving Pahlavi version was composed before 570 CE, while the present translation has been reconstructed from the Arabic and Syrian version
3/20

3/20


It is said that that Sanskrit Panchatantra was written by Vishnu Sharman (1300bce-300ce) to teach Arthshastra to 3 fool son of a king called Amarashakti of Mahilaropa, Vishnu wrote five core stories.
This ver. was translated transmitted to Persia, Egypt, Syria and Europe.
4/20
This ver. was translated transmitted to Persia, Egypt, Syria and Europe.
4/20

The first translation from the original Sanskrit text into Pahlavi (Middle Persian) was that of a Persian court physician named Borzui (Burzuyeh or Burzoe, 531–579). His translation, which he named Karataka and Damanaka
5/20

5/20


Ibn al-Muqaffa Zoroastrian convert to lslam (720– c.757) expanded the moral aspect by adding the story of Dimna’s crimes, his trial, and his punishment, which were widely illustrated.
6/20



6/20
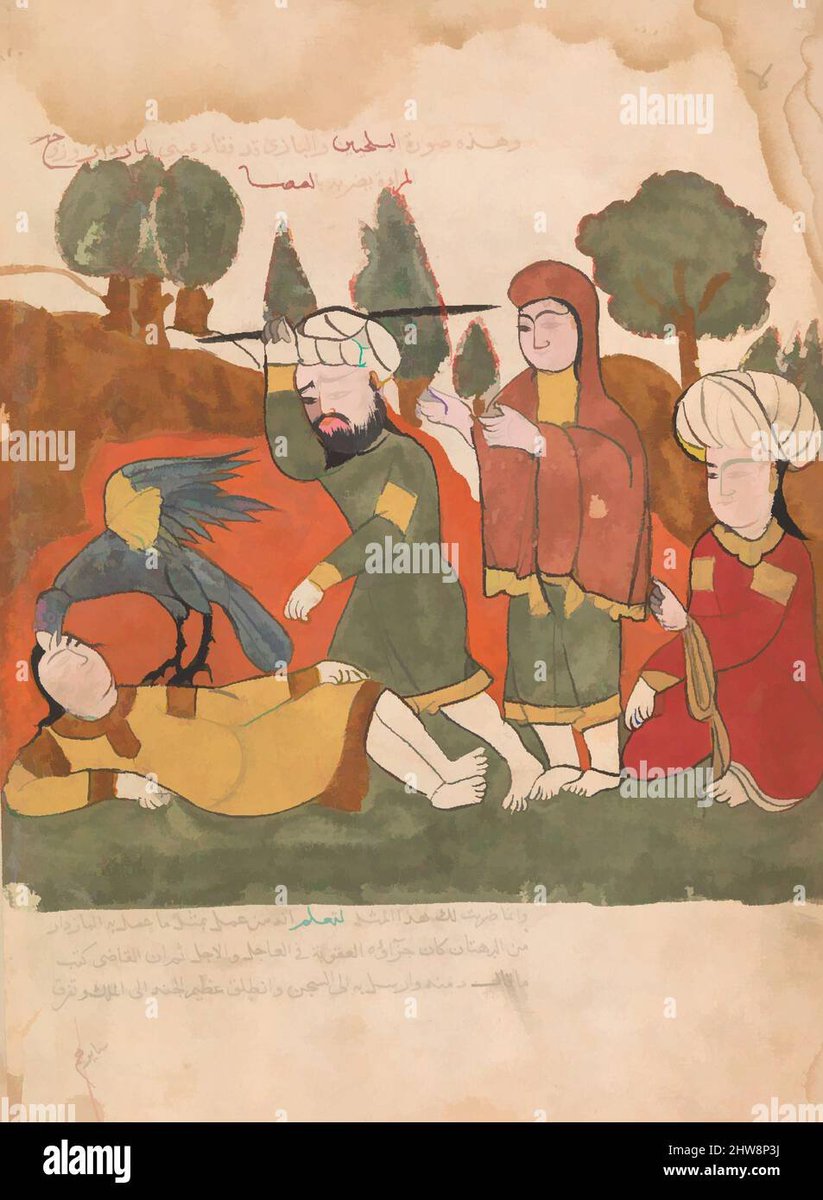




Durgasimha’s Panchatantra (c. 1025–31 CE ) written in Kannada, the dialect native to Karnataka, and the Sanskrit Tantropakhyana (before 1200 CE ), spread to Thailand, Laos, and Indonesia. Eighteen of the stories known in India are also found in Indonesia
8/20
8/20

Within South and East Asia, the Panchatantra was translated into the Newari language of Nepal and it is claimed that it was translated into Chinese by the last decade of the fifth century CE
9/20
9/20

The Panchtantra tales can be found on artefacts from 2500 bce to 200 bce and on temple walls from 7 th century.
This one from a Chandraketugarh vase. A Monkey is seen riding a Crocodile.
2nd century CE.
Credit @Shubh31209361
#Archaeology #Hindutva #हिंदुत्व
10/20
This one from a Chandraketugarh vase. A Monkey is seen riding a Crocodile.
2nd century CE.
Credit @Shubh31209361
#Archaeology #Hindutva #हिंदुत्व
10/20

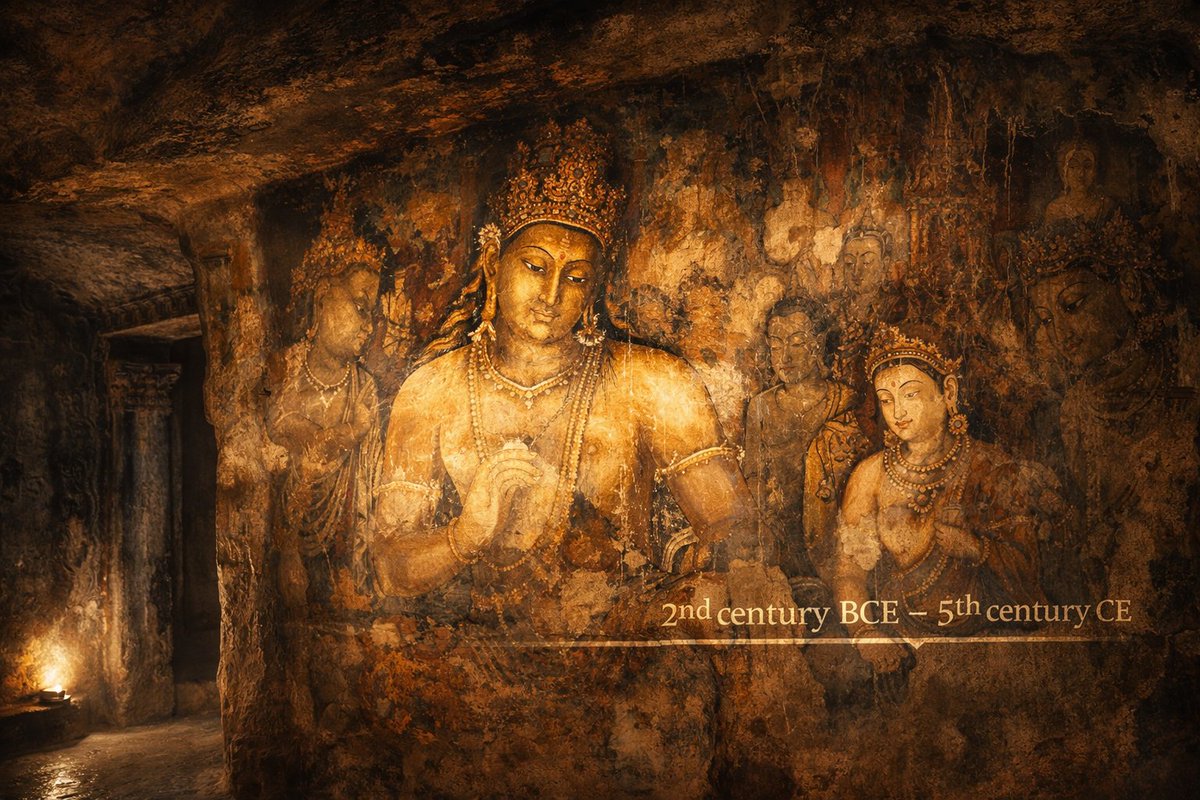
In this Tantri tale, the turtle is escaping from hunters thanks to two geese, who bear him aloft on a stick. Turtle opens its jaw to brag and falls to death
Tantri Tale. Nalanda. 7th century ce
11/20
Tantri Tale. Nalanda. 7th century ce
11/20

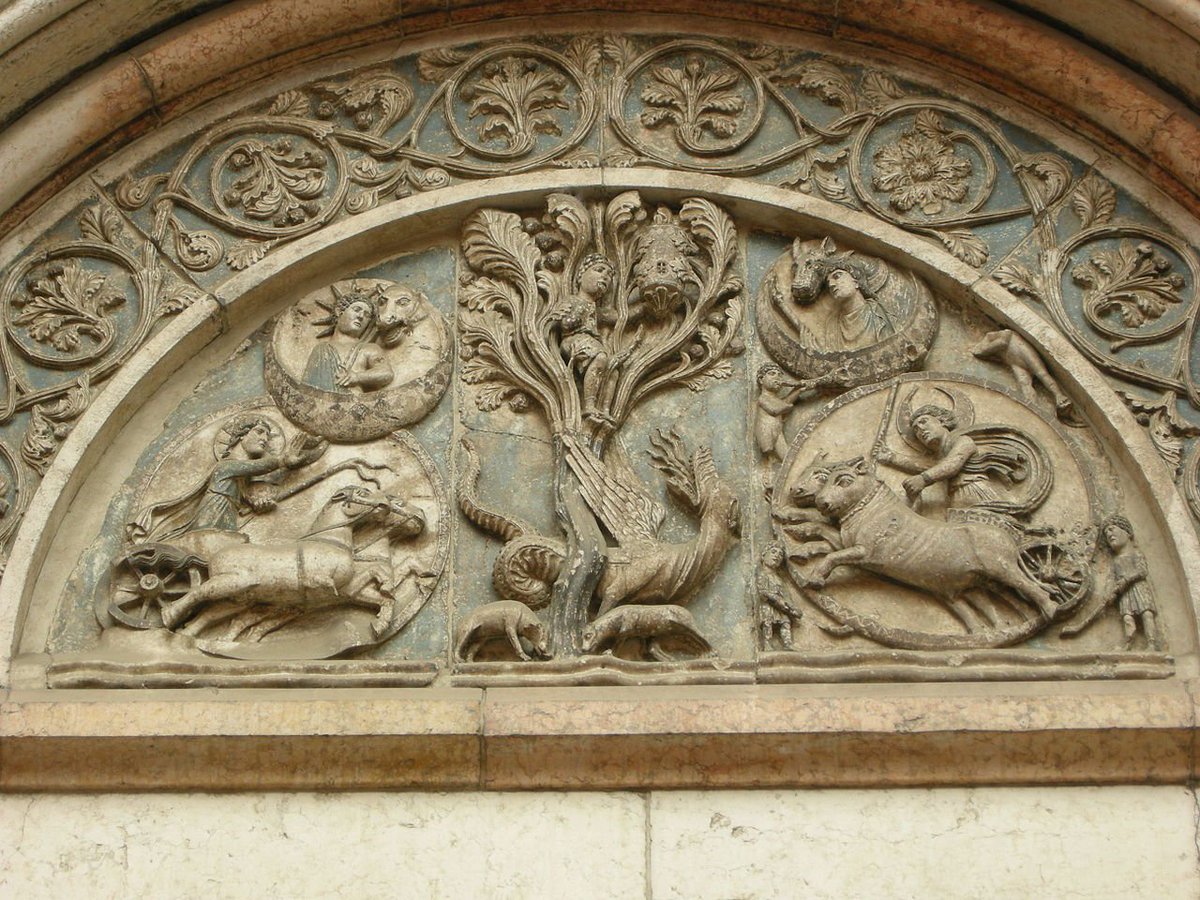
8th century #Panchatantra legends panels at Virupaksha Shaivism temple, Pattadakal Hindu monuments Karnataka
12/20


12/20



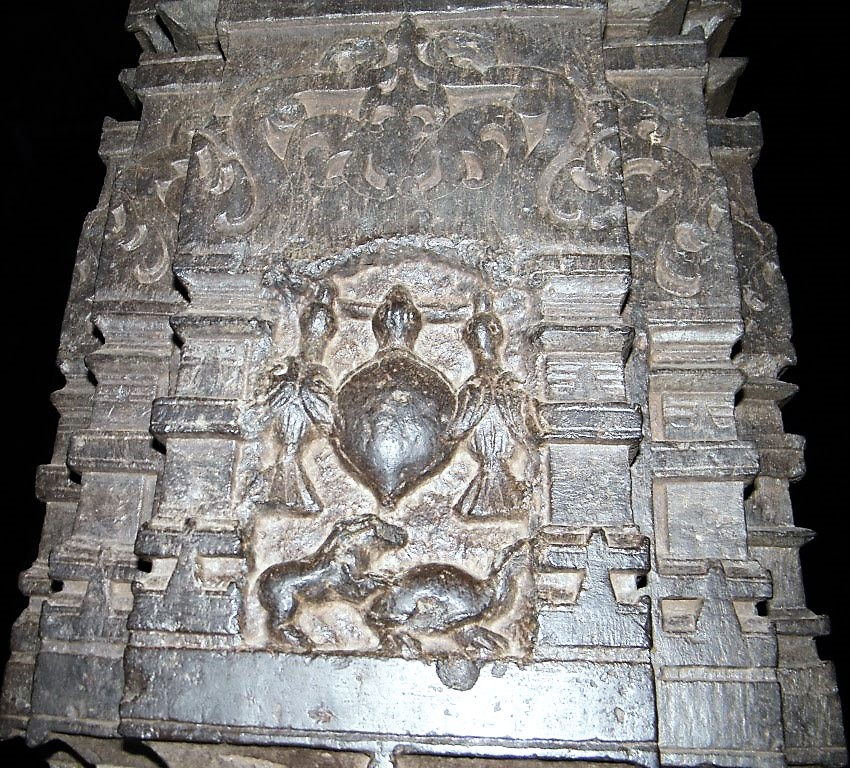
The monkey crocodile friendship story ( Panchatantra written by Vishnu Sharma ) carved on the temple wall of mukteshwar , Bhubaneswar
14/20
14/20

Panchtantra Panels on Tripurantaka Temple (Tripurantakesvara or Tripurantakeshwara) was built around c. 1070 CE by the Western Chalukyas
1. Crow & Pitcher
2. Tortoise and two geese.
3. Monkey and a crocodile
This temple is in dialipilated condition now thanks 2 @ASIGoI
16/20



1. Crow & Pitcher
2. Tortoise and two geese.
3. Monkey and a crocodile
This temple is in dialipilated condition now thanks 2 @ASIGoI
16/20




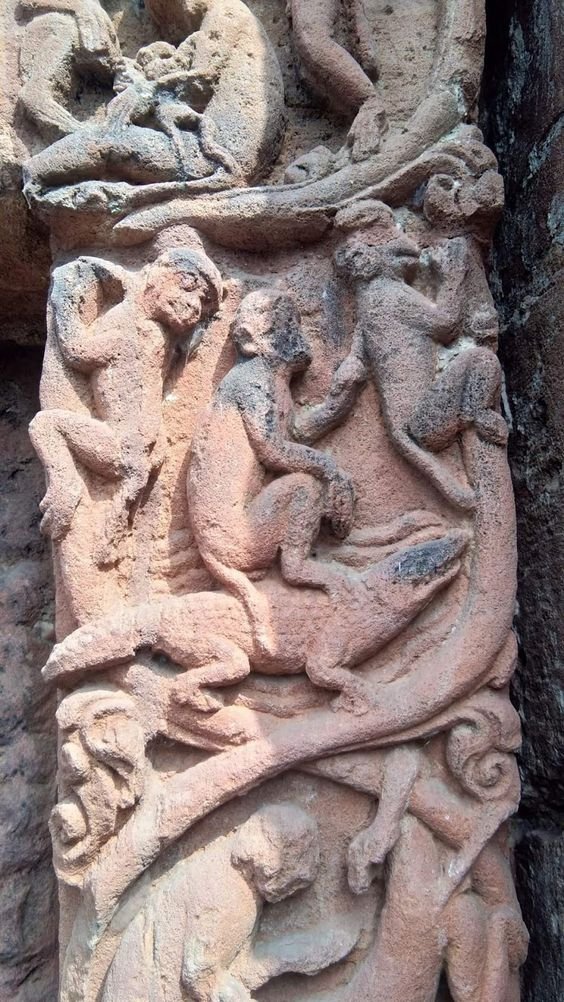
Panchatantra relief at the Mendut temple, Central Java, Indonesia
A Yogi Torgoise and a Crab can be seen in this relief
17/20
A Yogi Torgoise and a Crab can be seen in this relief
17/20
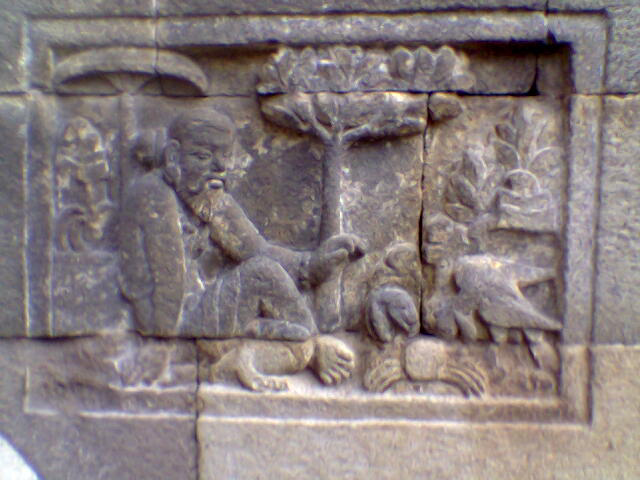

"Guide for Human Life" "Dectorium humanae vite" inspired by Giovanni, da Capua, active 13th century Compiler was published in Strasbourg in 1489.
loc.gov/resource/gdcwd…
18/20
loc.gov/resource/gdcwd…
18/20

Meeting of the jackal and the bull (Damanaka and Sanjivaka).
Executed in 1610 for Tana Sahib, the last Rajah of Golconda
The British Museum (Add. MS., 18,579)."
19/20
Executed in 1610 for Tana Sahib, the last Rajah of Golconda
The British Museum (Add. MS., 18,579)."
19/20

An 18th-century Pancatantra manuscript page in Braj ("The Talkative Turtle")
philamuseum.org/collections/re…
20/20

philamuseum.org/collections/re…
20/20


I remember "Moral Science" used to be impartd to primary students till 1980s. What happened later god knows?
So an essential Moral Education "Panchtantra" is now on verge of extinction and so does the Moral values.
jstor.org/stable/4850543…
researchgate.net/publication/33…
So an essential Moral Education "Panchtantra" is now on verge of extinction and so does the Moral values.
jstor.org/stable/4850543…
researchgate.net/publication/33…
I hope you've found this thread helpful.
Follow me @GemsOfINDOLOGY for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
Follow me @GemsOfINDOLOGY for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
https://twitter.com/GemsOfINDOLOGY/status/1662436006602375168
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh