🚨📝NEW PAPER 📝🚨
Recent study present an analysis of “the gap between the CO2 storage required to meet net zero targets and the slow maturation of regional storage resources.”
#NetZero
#EuropeanGreenDeal
#CarbonDioxideStorage
#EnergyTransition
🧵 1/12

Recent study present an analysis of “the gap between the CO2 storage required to meet net zero targets and the slow maturation of regional storage resources.”
#NetZero
#EuropeanGreenDeal
#CarbonDioxideStorage
#EnergyTransition
🧵 1/12
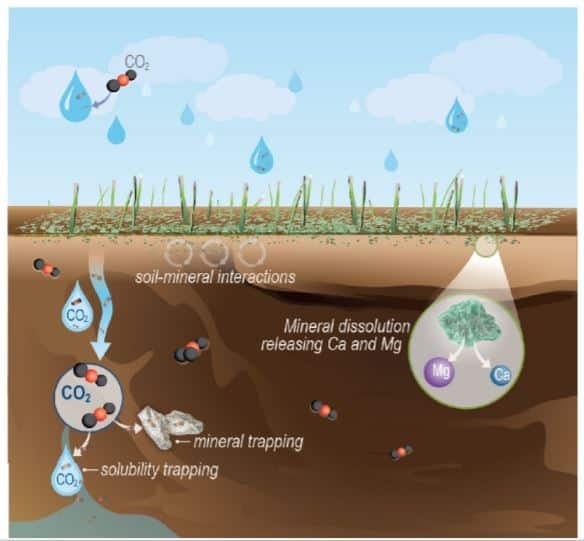
Researchers estimate that “European storage rates need to boost 30-100x by 2030 to meet #NetZero by 2050. 🇨🇳 & North America face a similar challenge. The slow global progress of #CarbonStorage undermines the latest IPCC, IEA & EU transition pathways to net zero by 2050.”
2/12
2/12

“These pathways imply a radically in teased demand for carbon capture and storage & #NegativeEmissionTechnologies (#NETs), contributing 500 of 700 megatonnes of #CarbonDioxideRemoval annually by 2050.”
3/12
3/12

Here, scientists of this study investigate “if sufficient #storage can be developed in time. China 🇨🇳 (30%), (15%) and Europe 🇪🇺(10%) dominate global #emissions.”
In this study, “Europe was chosen as a data-rich exemplar.”
4/12
In this study, “Europe was chosen as a data-rich exemplar.”
4/12
“Assuming #NetZero in 2050, researchers back-calculate the #storage required under 3️⃣ scenarios of low, medium, and high #CCS demand.”
5/12
5/12
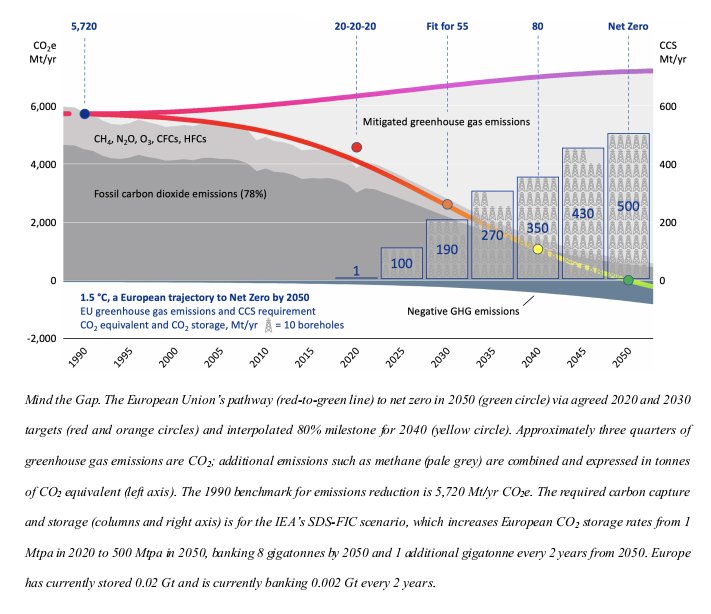
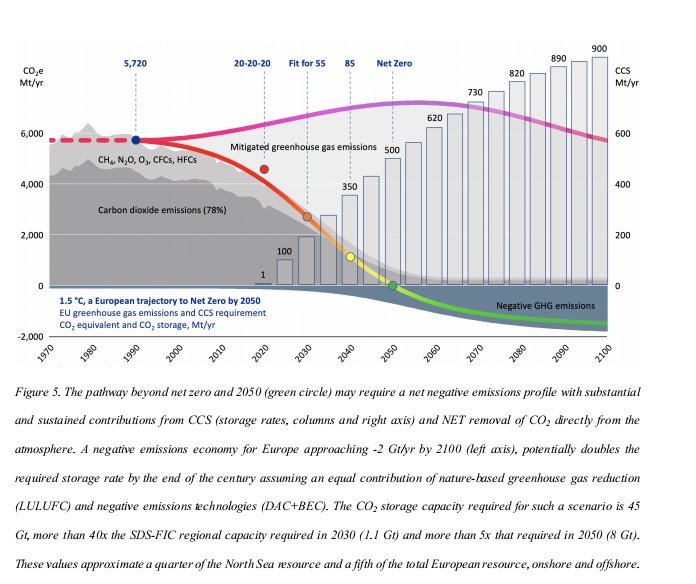
“Even the low demand scenario requires 0.2 Gt of #storage by 2030, increasing to 1.3 Gt by 2050. The moderate & high demand scenarios require 5-8 Gt by 2050. The current #CarbonStorage rate in #Europe is 0.001 Gt/yr.”
6/12
6/12

So, “there is a huge gap btw policy demand & #storage supply. Adaptation of existing #hydrocarbon tech has the potential to close this gap, with CCS for the entire EU requiring less than half the historic rate of HC exploration & development in UK North Sea from 1980-2010.”
7/12
7/12

“Counter to expectation, #storage cannot be delivered by exponential growth but requires an early & sustained investment of 30-50 boreholes per year starting before 2030 to build sufficient capacity,” researchers affirmed.
8/12
8/12

“A 5-year lead-time to identify & mature prospects needs policy intervention before 2025. Continued policy deferral will lock Europe into a low CCS pathway that restricts the contribution of #NETs at a potential cost of €100 billion for every gigatonne delayed beyond 2050.”
9/12
9/12

According to this research, “North America & China require similar policy intervention to close the gap on #CarbonStorage and #NetZero.”
10/12
10/12

To get more information on the research entitled: "Mind the gap: will slow progress on carbon dioxide storage undermine net zero by 2050?" (Preprint) visit ⬇️
📖📝➡️eartharxiv.org/repository/vie…
#NetZero
#EuropeanGreenDeal
#CarbonDioxideStorage
#EnergyTransition
11/12

📖📝➡️eartharxiv.org/repository/vie…
#NetZero
#EuropeanGreenDeal
#CarbonDioxideStorage
#EnergyTransition
11/12


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh