1\ My thoughts on the Chinese APT contractor leak 🇨🇳
Specifically, I want to talk about the leaked
- iOS Spyware
- Physical implantable devices
- Email surveillance system
Let's consider detection and how these would be installed.
Specifically, I want to talk about the leaked
- iOS Spyware
- Physical implantable devices
- Email surveillance system
Let's consider detection and how these would be installed.
https://twitter.com/AzakaSekai_/status/1759326049262019025
2\ The iOS spyware requires no jailbreak.
This should not "scare" you at all.
The capabilities of the leaked Chinese APT contractor "iOS Spyware" are accessing:
- basic mobile phone data
- GPS location
- Contacts
- Photos / multimedia files
- Recording sounds
If this sounds familiar, it should. These are settings accessible...Accessible ANY application requesting these permissions on a phone :)
This means, the delivery for the "spyware" would likely (my guess) be in the form of an application that the user installs on their device and must approve these permissions. If you've ever done mobile forensics, this is almost one of the first things you would check.
This should not "scare" you at all.
The capabilities of the leaked Chinese APT contractor "iOS Spyware" are accessing:
- basic mobile phone data
- GPS location
- Contacts
- Photos / multimedia files
- Recording sounds
If this sounds familiar, it should. These are settings accessible...Accessible ANY application requesting these permissions on a phone :)
This means, the delivery for the "spyware" would likely (my guess) be in the form of an application that the user installs on their device and must approve these permissions. If you've ever done mobile forensics, this is almost one of the first things you would check.

3\ The implantable devices are very similar in concept to the Hak5 devices.
This is not a new attack vector and NOT novel.
However, this should serve as a push for businesses to consider their threat models and playbooks for this kind of event.
Specifically the vendor's devices are disguised as:
- A power strip
- A power adapter
The way they work (as per the document) is:
1. Cracks WiFi password, sets up socks proxy
3. Cracks routing device
4. Self destruction to clear all system data
From an ops standpoint this targets a weak point of most businesses as most orgs do not have the best logging set up for their peripheral devices. It's why a lot nation states target edge devices for initial access (EDR blindspot / logging blindspot and difficulty of analysis for blue teamers).
However, once they pivot onto a vulnerable device or onto the network... the work of the detection team stays the same, it may just be difficult (in the absence of logs) to piece together what occurred.

This is not a new attack vector and NOT novel.
However, this should serve as a push for businesses to consider their threat models and playbooks for this kind of event.
Specifically the vendor's devices are disguised as:
- A power strip
- A power adapter
The way they work (as per the document) is:
1. Cracks WiFi password, sets up socks proxy
3. Cracks routing device
4. Self destruction to clear all system data
From an ops standpoint this targets a weak point of most businesses as most orgs do not have the best logging set up for their peripheral devices. It's why a lot nation states target edge devices for initial access (EDR blindspot / logging blindspot and difficulty of analysis for blue teamers).
However, once they pivot onto a vulnerable device or onto the network... the work of the detection team stays the same, it may just be difficult (in the absence of logs) to piece together what occurred.


4\ Finally the email analysis system is a platform allowing the operator to search and look through gathered emails and intelligence.
From an IR/blue team standpoint, the key point of interest is HOW do they gather this information.
In this paragraph they wrote there is an "execution link". This then grants "permissions".
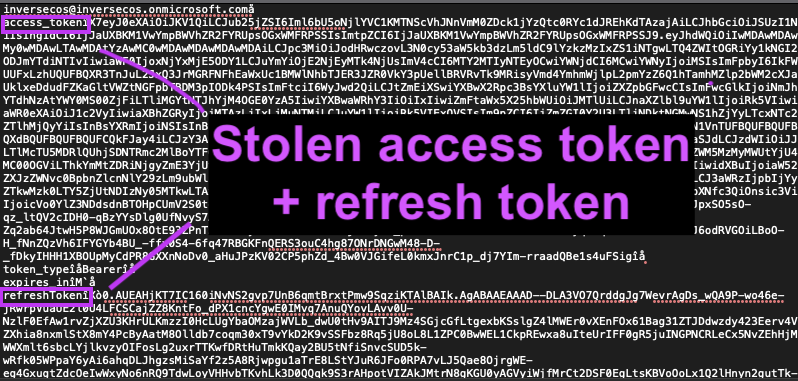
It sounds a lot like an initial access vector of phishing and fetching an access token :D
Not too bad hey?
From an IR/blue team standpoint, the key point of interest is HOW do they gather this information.
In this paragraph they wrote there is an "execution link". This then grants "permissions".
It sounds a lot like an initial access vector of phishing and fetching an access token :D
Not too bad hey?

5\ Given that this vendor contracts to APTs, the two questions in my mind for orgs would be something like:
1. Physical implants are used and purchased by APT groups, do we have playbooks? How do we deal with these threats?
2. Peripheral devices are targeted. How much visibility do we have over these devices? (This also includes work issued mobile devices)
1. Physical implants are used and purchased by APT groups, do we have playbooks? How do we deal with these threats?
2. Peripheral devices are targeted. How much visibility do we have over these devices? (This also includes work issued mobile devices)
6\ I rarely ever tweet but I’m glad this pulled me away from working and let me procrastinate for a bit hehe xD
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh