Fatty liver was completely reversed using one simple, cheap supplement, in a fascinating study.
(🧵1/8)

(🧵1/8)

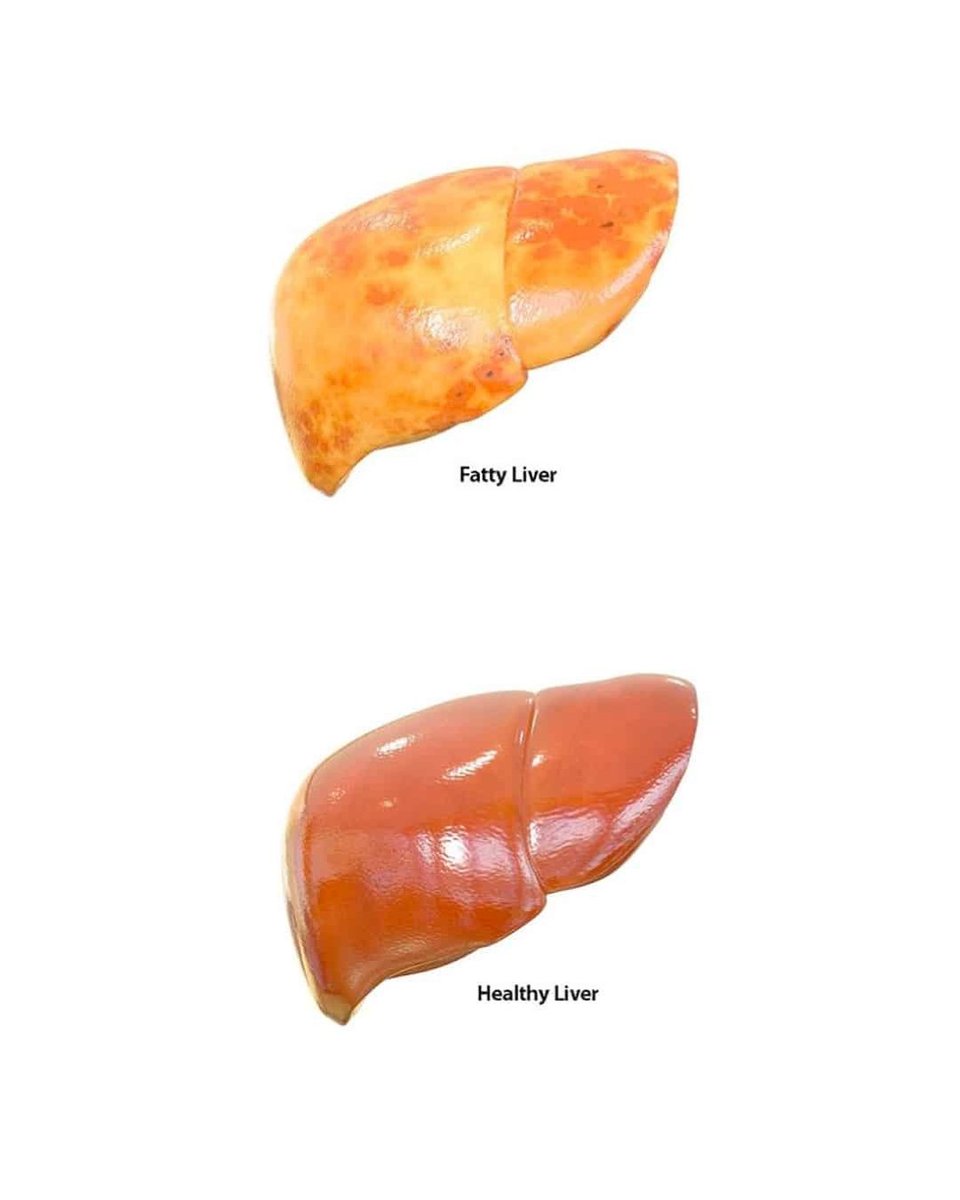
This was a small experiment done in the late 90s, and somehow it's never been investigated since clinically.
They gave children 2-6g of taurine per day for several months, in some cases over a year.
(2/8)
They gave children 2-6g of taurine per day for several months, in some cases over a year.
(2/8)
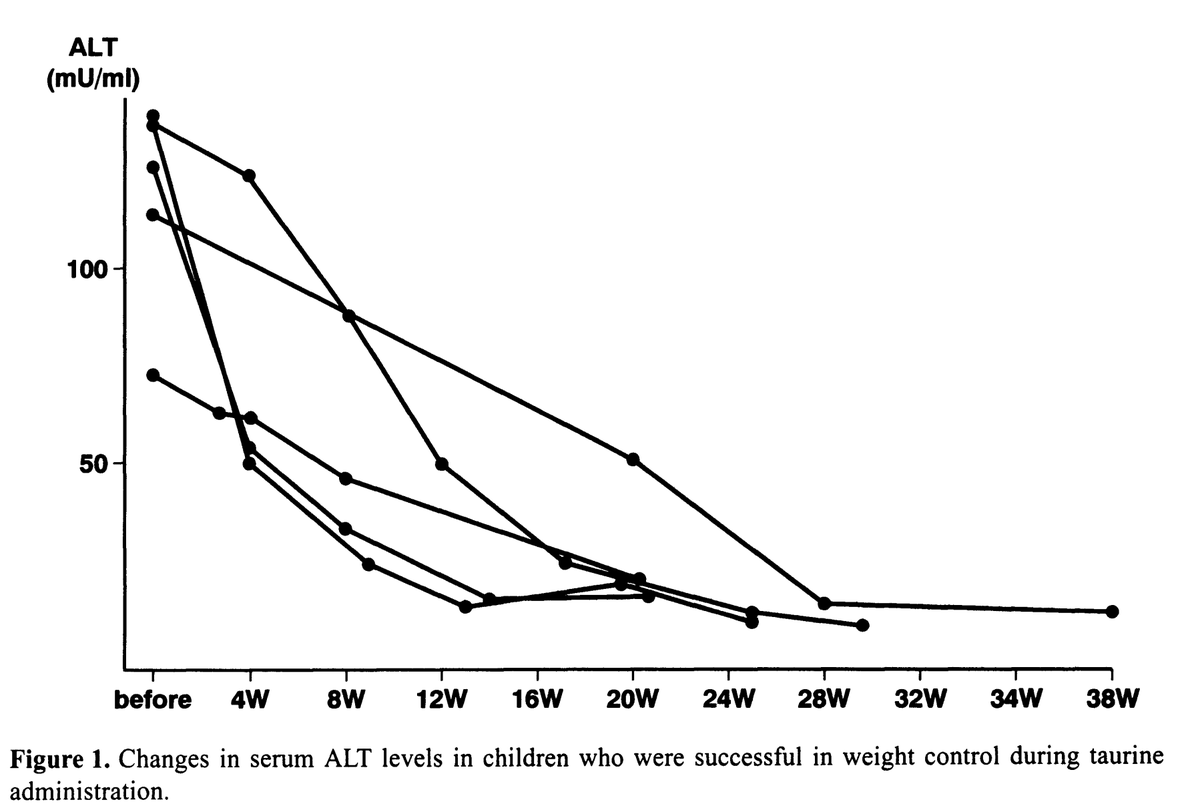
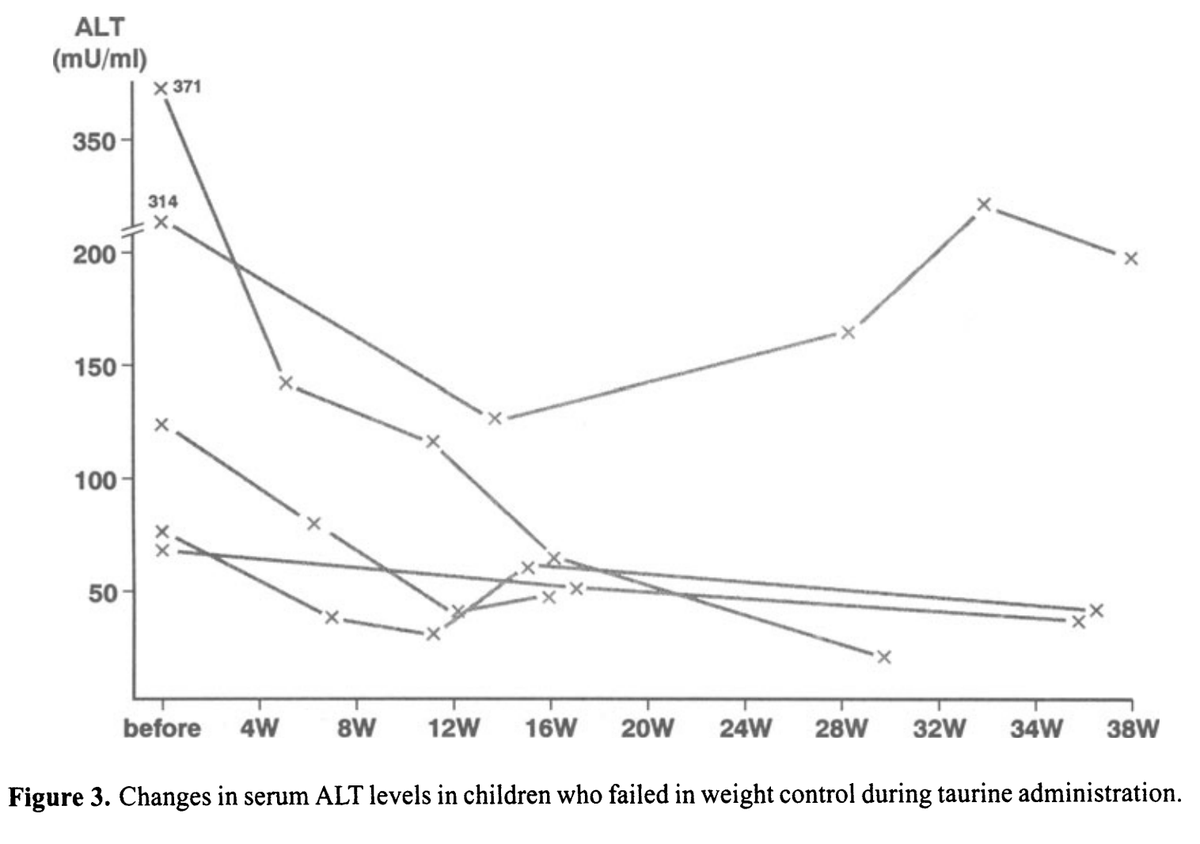
Taurine quickly reduced markers of liver damage.
The levels of ALT dropped dramatically - a key blood marker of liver damage.
This was true whether or not the children lost weight along the way.
(3/8)

The levels of ALT dropped dramatically - a key blood marker of liver damage.
This was true whether or not the children lost weight along the way.
(3/8)
Taurine normalized nearly all lab measures of liver / metabolic health, even without weight loss.
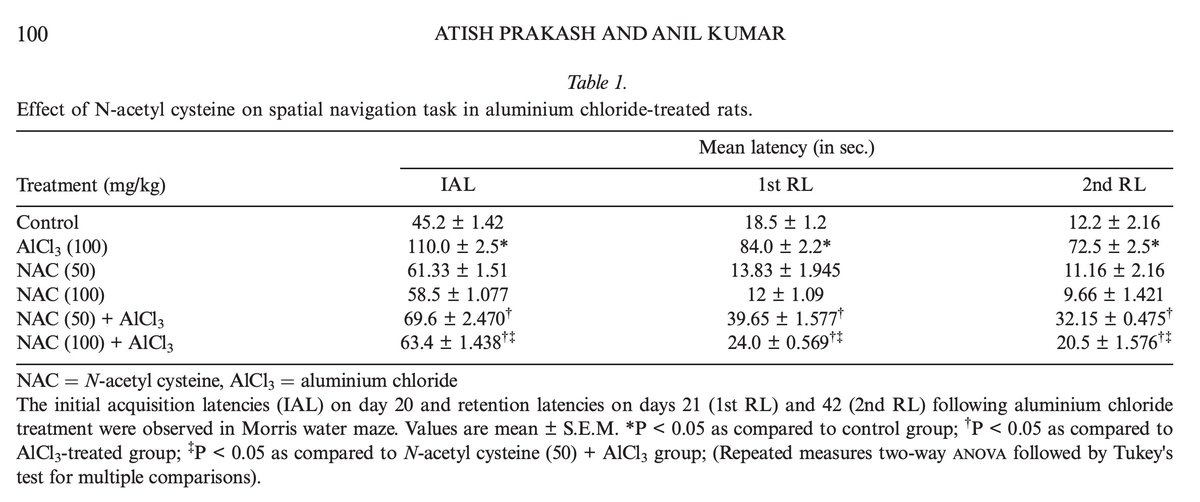
This was one case - after 12 weeks (prior to weight loss):
AST: ↓ ~49% → less general liver injury
ALT: ↓ ~63% → major reduction in liver-specific damage
γ-GTP: ↓ ~48% → reduced bile duct stress & oxidative burden
Ch-E: ↓ ~22% → normalized liver synthetic activity
Total Cholesterol: ↓ ~24% → improved cholesterol metabolism
HDL-Cholesterol: ↑ ~75% → protective “good” cholesterol boosted
Triglycerides: ↓ ~80% → massive drop in fat buildup
Phospholipids: ↓ ~42% → better lipid transport & balance
CT number (liver): 0 → 56 HU → fat cleared from liver
Liver/Spleen ratio: 0 → 1.1 → normalized density
(4/8)
This was one case - after 12 weeks (prior to weight loss):
AST: ↓ ~49% → less general liver injury
ALT: ↓ ~63% → major reduction in liver-specific damage
γ-GTP: ↓ ~48% → reduced bile duct stress & oxidative burden
Ch-E: ↓ ~22% → normalized liver synthetic activity
Total Cholesterol: ↓ ~24% → improved cholesterol metabolism
HDL-Cholesterol: ↑ ~75% → protective “good” cholesterol boosted
Triglycerides: ↓ ~80% → massive drop in fat buildup
Phospholipids: ↓ ~42% → better lipid transport & balance
CT number (liver): 0 → 56 HU → fat cleared from liver
Liver/Spleen ratio: 0 → 1.1 → normalized density
(4/8)
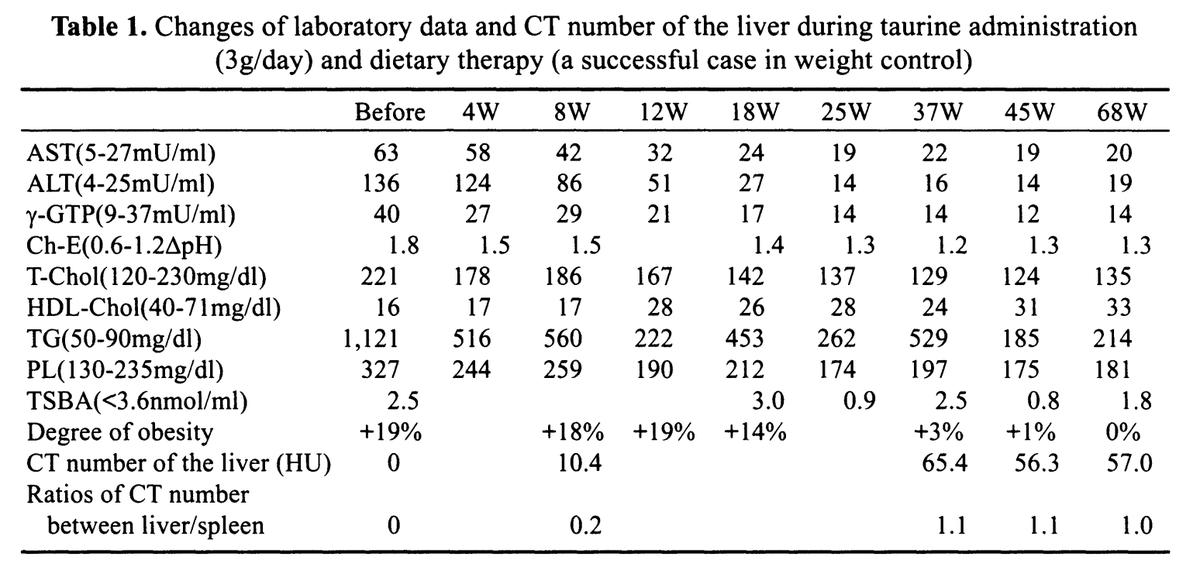
Here is a visualization of how taurine reduced liver fat.
Darker = less density, indicative of more fat and less functional tissue (lower HU).
Brighter areas are healthier with more density (higher HU) and less fat.
(5/8)
Darker = less density, indicative of more fat and less functional tissue (lower HU).
Brighter areas are healthier with more density (higher HU) and less fat.
(5/8)
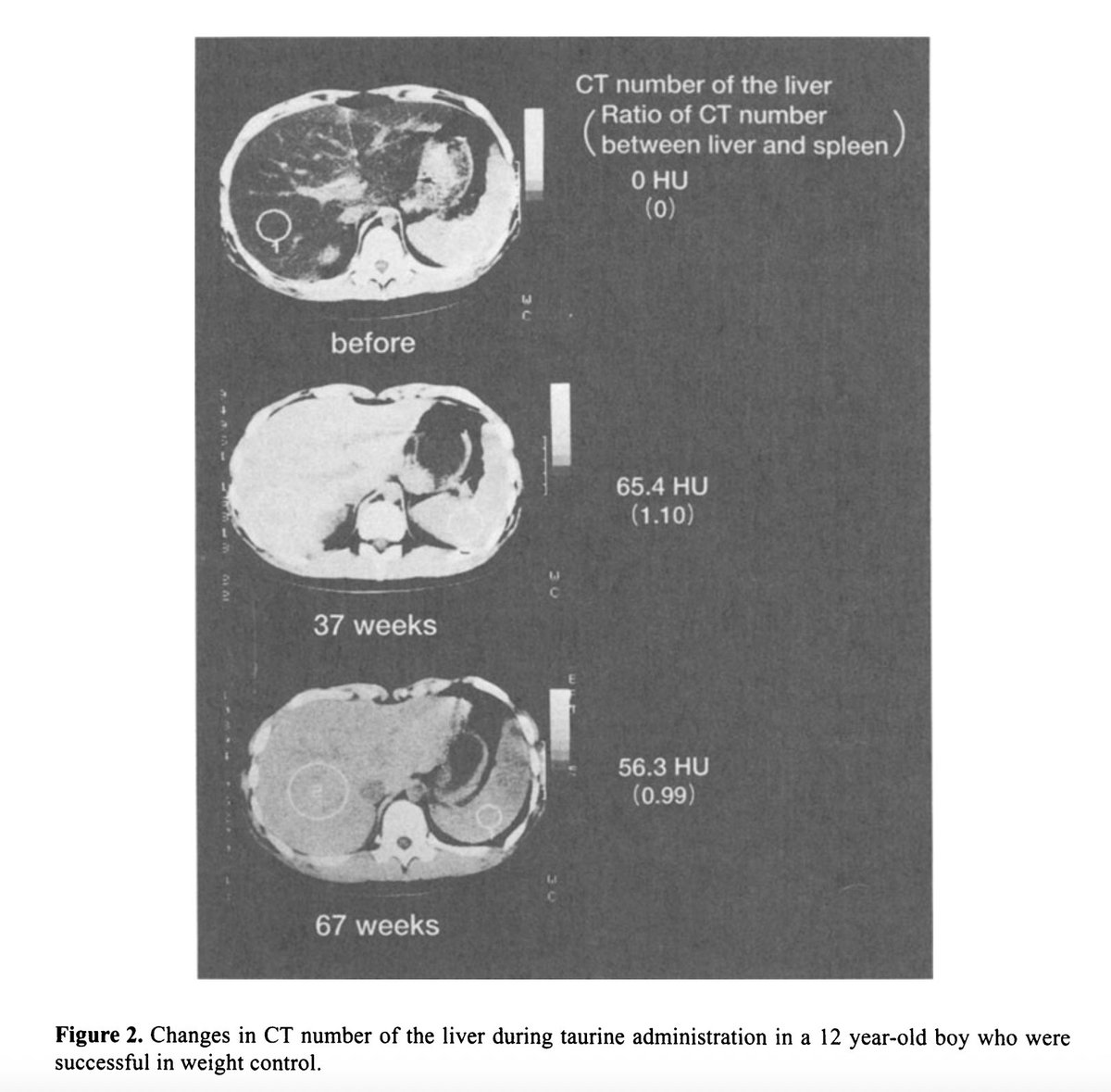
Here's another example.
This child did not lose any weight.
Taurine alone was responsible for a significant improvement in liver fat, you can see how much brighter it got.
(6/8)
This child did not lose any weight.
Taurine alone was responsible for a significant improvement in liver fat, you can see how much brighter it got.
(6/8)
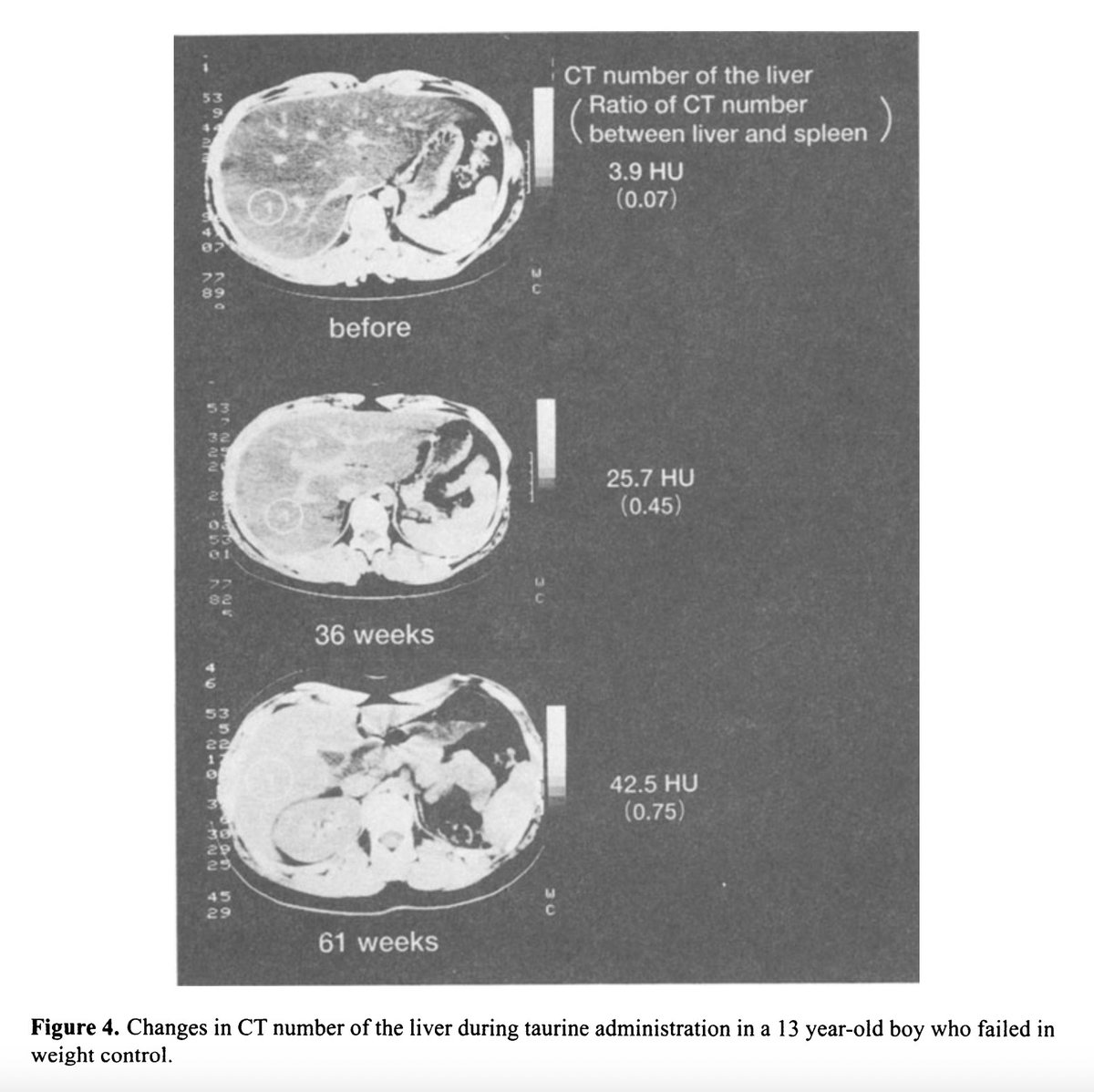
Taurine substantially reduced liver fat in all children.
The CT number ratio between liver + spleen is a normalized measure of how healthy the liver is, how little fat it has.
Every single one improved.
(7/8)
The CT number ratio between liver + spleen is a normalized measure of how healthy the liver is, how little fat it has.
Every single one improved.
(7/8)
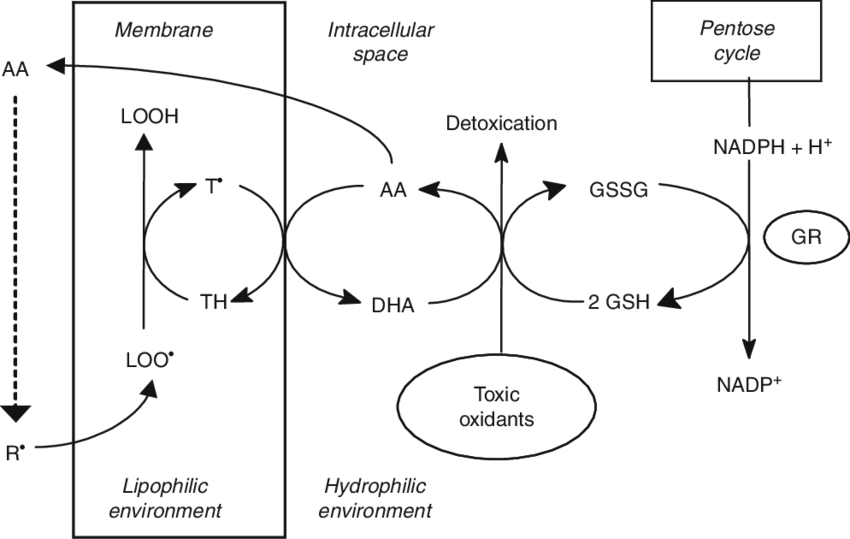
Why is taurine so healthy for the liver?
Well, it's hard to even count the reasons, but I'll try.
☆ Antioxidant (HOCl/HOBr) → quenches toxic halogen oxidants by converting them into TauCl/TauBr, protecting hepatocytes from collateral immune damage.
☆ Osmoregulation → buffers water/electrolyte shifts so liver cells don’t swell or shrink under metabolic stress.
☆ ER Stress → aids protein folding and reduces unfolded protein response, easing pressure on hepatocytes.
☆ Mitochondrial protection → stabilizes membranes, supports ATP production, and prevents Ca²⁺ overload, preserving energy metabolism.
☆ pH buffer → fine-tunes local proton balance in mitochondria/ER, keeping enzymes and gradients functional. Prevents acidosis.
☆ Prevents apoptosis → blocks cell death pathways triggered by Ca²⁺ dysregulation or oxidative stress.
☆ Improves glycogen storage → enhances the liver’s ability to store and release glucose, stabilizing blood sugar.
☆ Inhibits triglyceride synthesis → suppresses fat buildup in hepatocytes, preventing fatty liver.
☆ Membrane fluidity → maintains optimal balance in lipid bilayers, protecting integrity and signaling.
☆ Conjugates bile acids → detoxifies bile acids, making them more soluble and less damaging to membranes.
☆ Anti-inflammatory → TauCl/TauBr dampen NF-κB and cytokines, reducing chronic liver inflammation.
☆ Stimulates glucose metabolism → promotes glycolysis and oxidative use of glucose, reducing reliance on fat storage.
☆ Calcium buffer → Inhibiting excitotoxic cell death
I could go on, but I think you get the point.
Even just in the mitochondria alone, taurine exerts a ton of benefits.
Truly a special amino acid - it's unfortunate it doesn't get the love it deserves.
(8/8)
Well, it's hard to even count the reasons, but I'll try.
☆ Antioxidant (HOCl/HOBr) → quenches toxic halogen oxidants by converting them into TauCl/TauBr, protecting hepatocytes from collateral immune damage.
☆ Osmoregulation → buffers water/electrolyte shifts so liver cells don’t swell or shrink under metabolic stress.
☆ ER Stress → aids protein folding and reduces unfolded protein response, easing pressure on hepatocytes.
☆ Mitochondrial protection → stabilizes membranes, supports ATP production, and prevents Ca²⁺ overload, preserving energy metabolism.
☆ pH buffer → fine-tunes local proton balance in mitochondria/ER, keeping enzymes and gradients functional. Prevents acidosis.
☆ Prevents apoptosis → blocks cell death pathways triggered by Ca²⁺ dysregulation or oxidative stress.
☆ Improves glycogen storage → enhances the liver’s ability to store and release glucose, stabilizing blood sugar.
☆ Inhibits triglyceride synthesis → suppresses fat buildup in hepatocytes, preventing fatty liver.
☆ Membrane fluidity → maintains optimal balance in lipid bilayers, protecting integrity and signaling.
☆ Conjugates bile acids → detoxifies bile acids, making them more soluble and less damaging to membranes.
☆ Anti-inflammatory → TauCl/TauBr dampen NF-κB and cytokines, reducing chronic liver inflammation.
☆ Stimulates glucose metabolism → promotes glycolysis and oxidative use of glucose, reducing reliance on fat storage.
☆ Calcium buffer → Inhibiting excitotoxic cell death
I could go on, but I think you get the point.
Even just in the mitochondria alone, taurine exerts a ton of benefits.
Truly a special amino acid - it's unfortunate it doesn't get the love it deserves.
(8/8)

Taurine is awesome and can be a part of a personalized plan to optimize your health.
If you'd like some help with that, book a free call with us here and we'll get you the guidance you need: go.prism.miami/consultation
If you'd like some help with that, book a free call with us here and we'll get you the guidance you need: go.prism.miami/consultation
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh