
Bioethicist | Doctor | Own views, with data | Personal account @_euzebiusz_
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

https://twitter.com/StraightStats/status/1640860479689052160
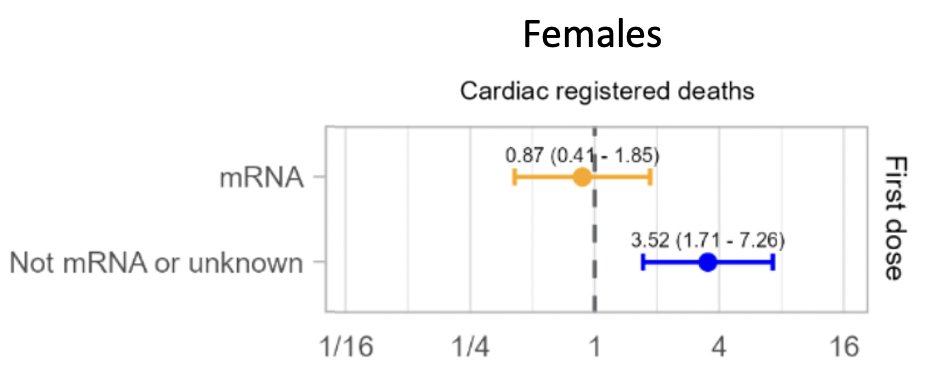
 Second key finding regarding cardiac deaths after covid19 vaccines
Second key finding regarding cardiac deaths after covid19 vaccines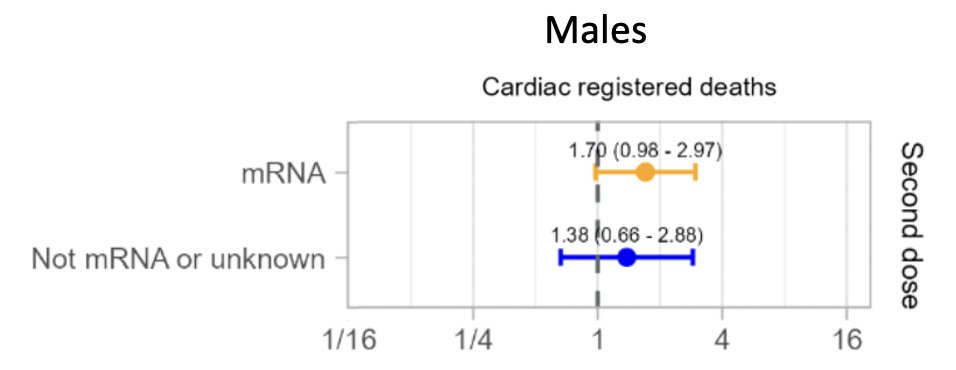



 2/ Covid heterodoxy in three layers by @pgodfreysmith @Sydney_Uni
2/ Covid heterodoxy in three layers by @pgodfreysmith @Sydney_Uni https://twitter.com/BallouxFrancois/status/14755676045049733182. Post-vaccination infections (and re-infections) will help to:
https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1422395572888096770?s=20

https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1416870155070545925
 In northern summer 2021, I called this:
In northern summer 2021, I called this:https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1416870155070545925?s=20

 According to the article below, this 1830s quote is the first English use of the term "moral panic" in its modern sense (although note that it was quoting a French physician)
According to the article below, this 1830s quote is the first English use of the term "moral panic" in its modern sense (although note that it was quoting a French physician)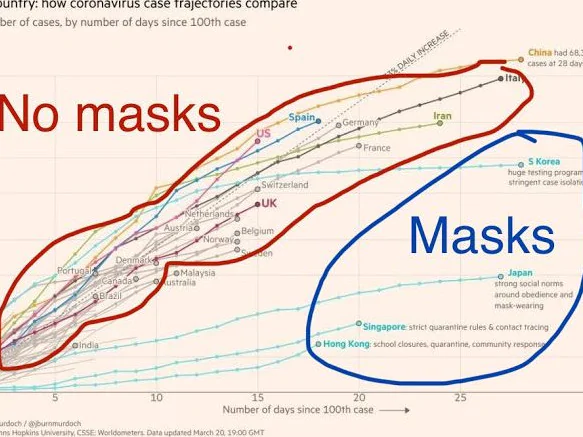
https://twitter.com/BallouxFrancois/status/14251819335506411602/ The standard idea of clinical equipoise is that research (or an RCT) is ethical when there is “no consensus within the expert clinical community about the comparative merits of the alternatives being tested”
https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1300691735719243776?s=20
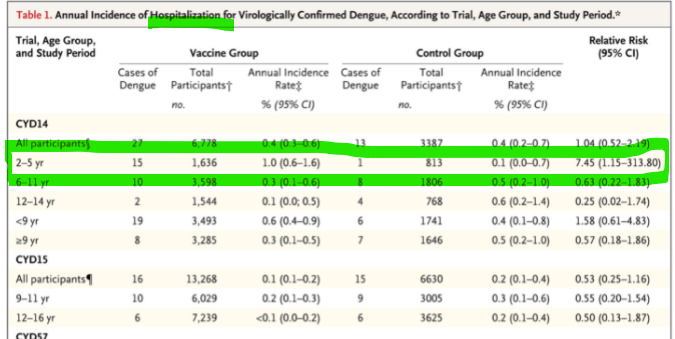
https://twitter.com/RepThomasMassie/status/1406944837383954446?s=20
https://twitter.com/COVID_questions/status/1402189106105389074To take the most obvious example, multiple high-income country regulators have restricted the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in children and young adults
https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1380291174137667584?s=20
https://twitter.com/TheEliKlein/status/1402042007711895552One response, as below, is that we should mix vaccinated and unvaccinated in order to reduce the probability of infection in the latter (i.e., indirect protection or herd immunity)
https://twitter.com/greg_boes1/status/1402088718190665740?s=20

https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1288287682389393408?s=20@COVID_questions @bergerbell @pgodfreysmith @NahasNewman @WesPegden It is a tragedy, in the sense of the "remorseless working" of well-understood factors underlying public health in general, e.g. poverty

 2/ Previous reviews of American Infectious Diseases Guidelines found that only 14% of recommendations were based on the highest level of evidence
2/ Previous reviews of American Infectious Diseases Guidelines found that only 14% of recommendations were based on the highest level of evidence
https://twitter.com/ID_ethics/status/1351718128942678024
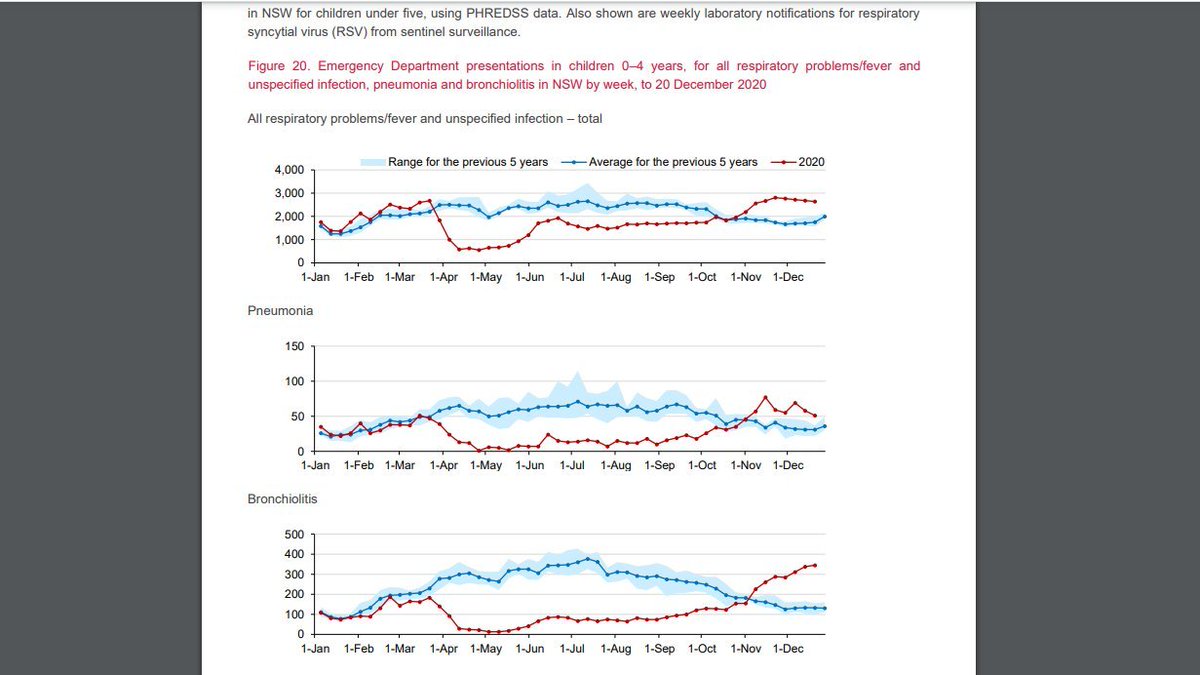
 To get a sense of #RSV vs. #covid19 in children:
To get a sense of #RSV vs. #covid19 in children:
 The above is an example of how scientists and journal editors could better communicate findings and risks
The above is an example of how scientists and journal editors could better communicate findings and risks