
Our goal is to make concise reviews of orthopedic topics.
Check out our past reviews at: https://t.co/FMMTD8Tj3j
Founder: @CSMorford
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

 Most tibial pilon fractures result from high-energy axial loading through the talus.
Most tibial pilon fractures result from high-energy axial loading through the talus. 

 First off, what is an eponym fracture?
First off, what is an eponym fracture?
 The humeral shaft is defined as the area distal to the surgical neck and proximal to the epicondyles.
The humeral shaft is defined as the area distal to the surgical neck and proximal to the epicondyles. 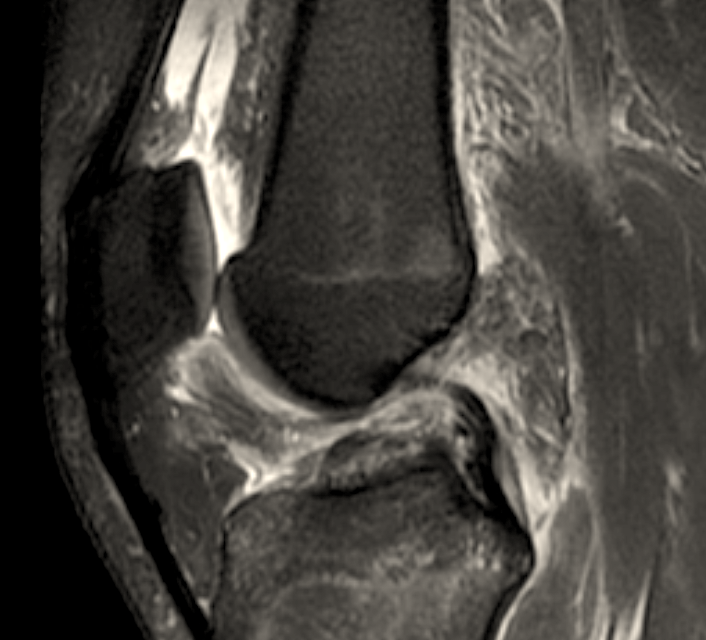
 The ACL is the primary restraint to anterior tibial translation and also plays a role in rotary stability
The ACL is the primary restraint to anterior tibial translation and also plays a role in rotary stability
 Proximal humerus fractures are common, accounting for around 5% of all fractures with increasing frequency with age.
Proximal humerus fractures are common, accounting for around 5% of all fractures with increasing frequency with age. 
 Clavicle fractures are typically the result of a fall onto the shoulder and are one of the most common fractures in children.
Clavicle fractures are typically the result of a fall onto the shoulder and are one of the most common fractures in children.
 Basicervical femoral neck, intertrochanteric (IT), and subtrochanteric (ST) hip fractures are different from femoral neck fractures in that they are extracapsular.
Basicervical femoral neck, intertrochanteric (IT), and subtrochanteric (ST) hip fractures are different from femoral neck fractures in that they are extracapsular.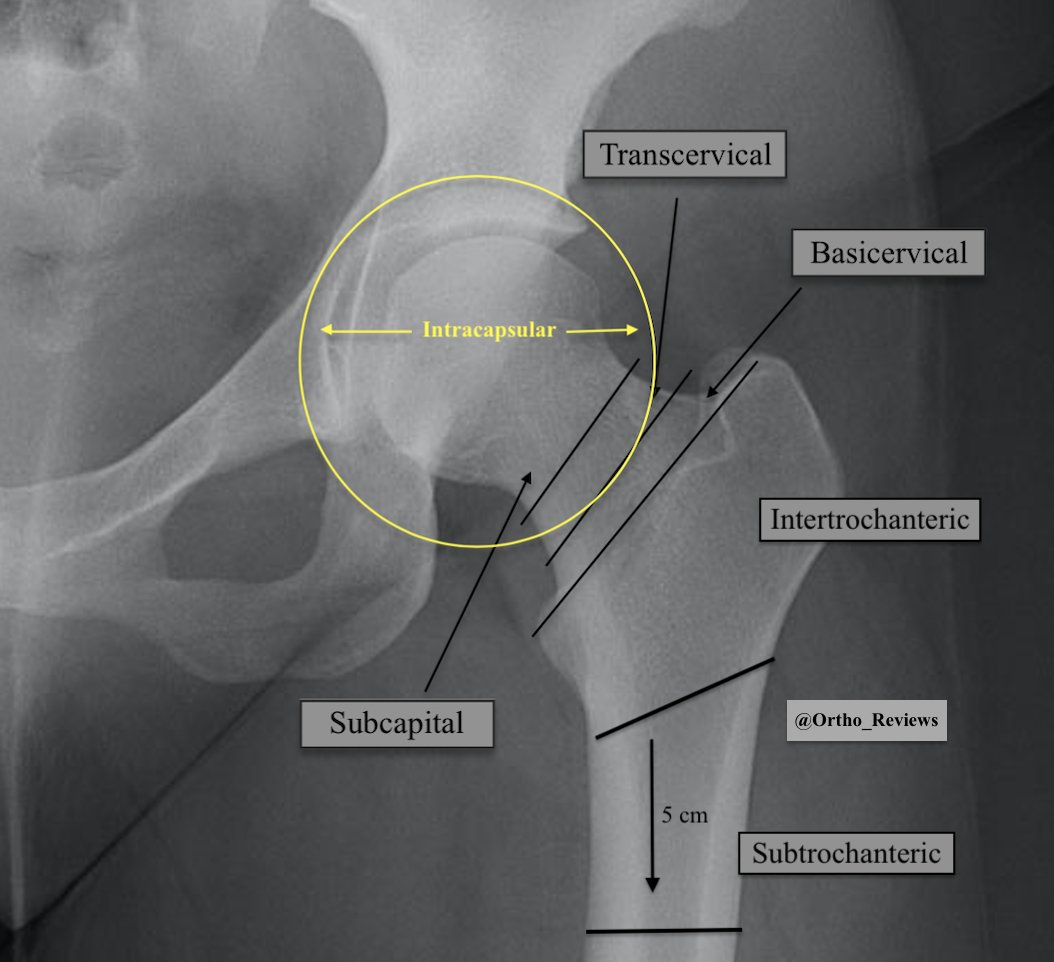

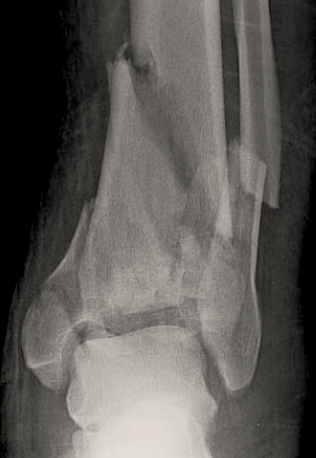
 The ankle is a complex hinge joint comprised of the tibial plafond, talar dome, and distal fibula.
The ankle is a complex hinge joint comprised of the tibial plafond, talar dome, and distal fibula.
 Pediatric femoral shaft (PFS) fractures constitute a small portion of pediatric fractures roughly 1-2% with a bimodal age distribution
Pediatric femoral shaft (PFS) fractures constitute a small portion of pediatric fractures roughly 1-2% with a bimodal age distribution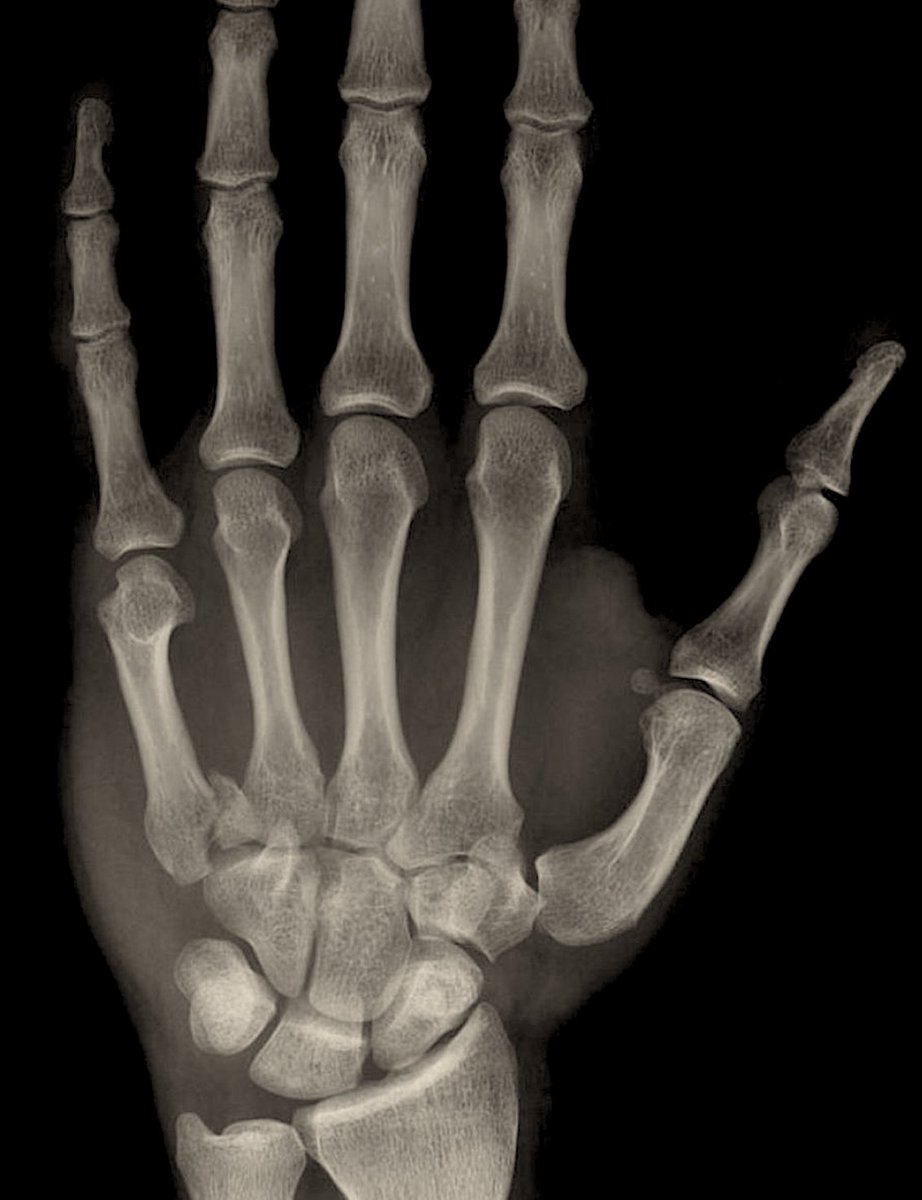
 This patient is presenting with an intraarticular fx of the 5th metacarpal base.
This patient is presenting with an intraarticular fx of the 5th metacarpal base.

 SCFE’s are an adolescent hip pathology with an average age of onset of 11-12.
SCFE’s are an adolescent hip pathology with an average age of onset of 11-12. 
 The distal humerus is composed of two columns, a medial and lateral column that are connected by the trochlea forming a triangular shape.
The distal humerus is composed of two columns, a medial and lateral column that are connected by the trochlea forming a triangular shape.

 Distal radius (DR) fractures have a bimodal age distribution. “accounting for around 25% of fractures in the pediatric population and up to 18% of all fractures in the elderly age group.” (2)
Distal radius (DR) fractures have a bimodal age distribution. “accounting for around 25% of fractures in the pediatric population and up to 18% of all fractures in the elderly age group.” (2)
 Patellar maltracking is the most common complication of primary TKA.
Patellar maltracking is the most common complication of primary TKA. 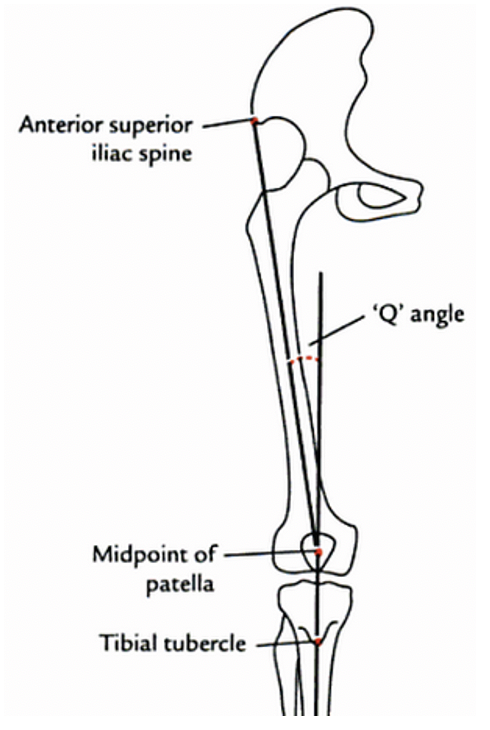

 The meniscus function is two-fold. It increases stability by deepening the tibial surface and it aids in force transmission by increasing the contact area to spread force over a larger surface area. The meniscus is responsible for 50% of load transmission across the knee. (1)
The meniscus function is two-fold. It increases stability by deepening the tibial surface and it aids in force transmission by increasing the contact area to spread force over a larger surface area. The meniscus is responsible for 50% of load transmission across the knee. (1)