
@HarvardHBS Prof, #ManagingTheFutureOfWork initiative ... Bama native, not digitally native. GIFT OF GLOBAL TALENT (https://t.co/TzkYx8bdzs).
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 Before 2004, all foreign students could bank on getting an #H1B visa at graduation ... these guarantees evaporated, however, when the cap reverted 65,000 due to sunset clauses … except that specific agreements exempted students from five countries
Before 2004, all foreign students could bank on getting an #H1B visa at graduation ... these guarantees evaporated, however, when the cap reverted 65,000 due to sunset clauses … except that specific agreements exempted students from five countries 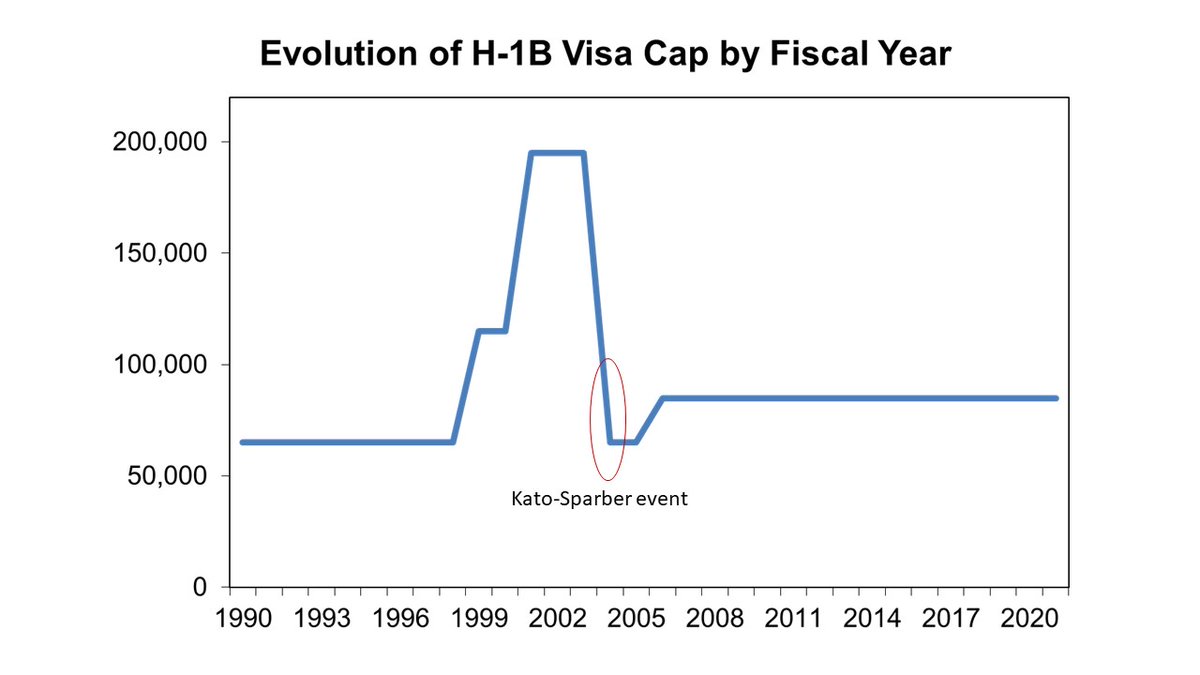

 After a semester of work, students felt both optimistic and pessimistic about the future of work. Exponential growth of technology allows for unimaginable innovation - but linear change in our ability to adapt to that growth means institutions (and people) will be left behind.
After a semester of work, students felt both optimistic and pessimistic about the future of work. Exponential growth of technology allows for unimaginable innovation - but linear change in our ability to adapt to that growth means institutions (and people) will be left behind.

 MS' Golden Triangle Region holds a rich manufacturing history, but plant shutdowns and job losses hit GTR hard from the 1980s thru early 2000s.
MS' Golden Triangle Region holds a rich manufacturing history, but plant shutdowns and job losses hit GTR hard from the 1980s thru early 2000s. 



 CEWD is a non-profit industry consortium born in 2006 to combat emerging industry-wide skills gaps (the "silver tsunami"). It has since developed innovation guides for energy companies to use to develop better talent pipelines and ensure up-to-date skills development.
CEWD is a non-profit industry consortium born in 2006 to combat emerging industry-wide skills gaps (the "silver tsunami"). It has since developed innovation guides for energy companies to use to develop better talent pipelines and ensure up-to-date skills development. 

 Their plan is to invest $100bn into basic R&D in middle America cities to spur breakthrough innovations, attracting talented people and unlocking growth
Their plan is to invest $100bn into basic R&D in middle America cities to spur breakthrough innovations, attracting talented people and unlocking growth

 A recent report coauthored by @JosephBFuller and @Burning_Glass estimate 3m or more jobs in the US could benefit thru apprenticeships and provide holders greater upward mobility… While apprenticeships are popular in Europe, the models need to be fit to the US context to work
A recent report coauthored by @JosephBFuller and @Burning_Glass estimate 3m or more jobs in the US could benefit thru apprenticeships and provide holders greater upward mobility… While apprenticeships are popular in Europe, the models need to be fit to the US context to work 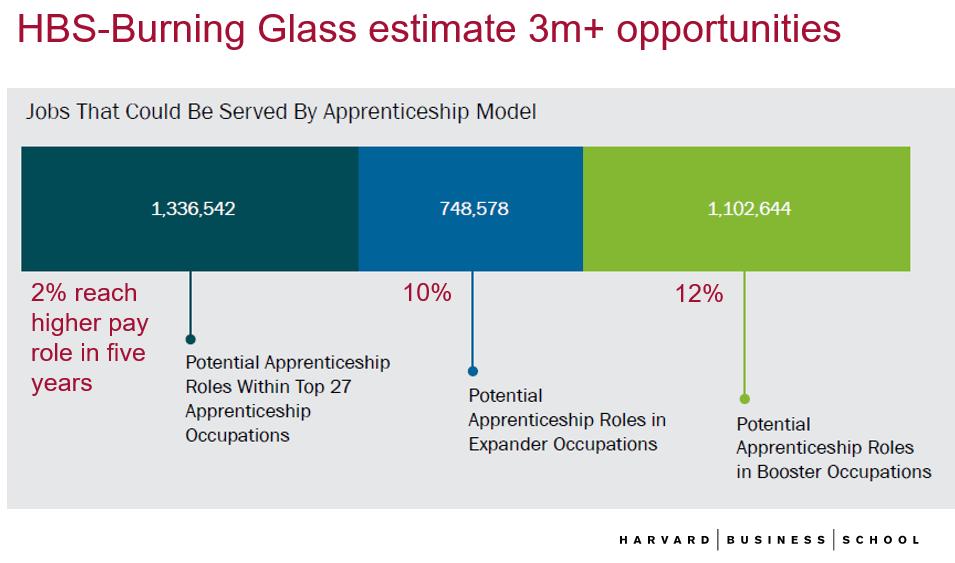

 Bad middle skills pipelines are costly: attrition costs colleges $16bn & bad hiring costs employers $150bn. There are many reasons:
Bad middle skills pipelines are costly: attrition costs colleges $16bn & bad hiring costs employers $150bn. There are many reasons:

 With tech reshaping the economy, policies like UBI & a federal job guarantee have become popular as ways to boost the safety net & handle change. Class considered three key features of these policies: whether they are universal, means-tested / targeted support, or work-connected.
With tech reshaping the economy, policies like UBI & a federal job guarantee have become popular as ways to boost the safety net & handle change. Class considered three key features of these policies: whether they are universal, means-tested / targeted support, or work-connected. 

 @rex_change uses AI to match home buyers to sellers & offer a lower fee. It's working to allocate tasks - eg use agents or gig workers to show homes? Class also wondered: is lower cost REX's selling point or is its matching tech what brings the real value?
@rex_change uses AI to match home buyers to sellers & offer a lower fee. It's working to allocate tasks - eg use agents or gig workers to show homes? Class also wondered: is lower cost REX's selling point or is its matching tech what brings the real value?
 Businesses often create their own problem: by imposing unnecessary barriers to employment (eg, degree inflation, not having "care culture"), they drive up the cost of their own labor.
Businesses often create their own problem: by imposing unnecessary barriers to employment (eg, degree inflation, not having "care culture"), they drive up the cost of their own labor.

 Workers' prospects have diminished over the past 50 or so years, particularly at the middle-skill level:
Workers' prospects have diminished over the past 50 or so years, particularly at the middle-skill level:

 Based in Columbus OH, Hot Chicken Takeover makes delicious Nashville Hot Chicken… yummy, esp with Miss B's banana pudding to follow!
Based in Columbus OH, Hot Chicken Takeover makes delicious Nashville Hot Chicken… yummy, esp with Miss B's banana pudding to follow! 

 Originally targeting NFL QBs, STRIVR now provides VR training for Walmart's frontline workers. It made this pivot because the prep process is the same: replicate setting, minimize cost of failure, & practice makes perfect. All translate to *anyone* improving work performance.
Originally targeting NFL QBs, STRIVR now provides VR training for Walmart's frontline workers. It made this pivot because the prep process is the same: replicate setting, minimize cost of failure, & practice makes perfect. All translate to *anyone* improving work performance. 

 Union membership has steadily declined over the past 50 years, but the majority of class predicted union ranks would hold steady or grow by 2030. Why? 1) Unions could provide training for skills acquisition, which is vital to future of work…
Union membership has steadily declined over the past 50 years, but the majority of class predicted union ranks would hold steady or grow by 2030. Why? 1) Unions could provide training for skills acquisition, which is vital to future of work… 

 1: @conveyiq's candidate management system. Well-positioned in the market, ConveyIQ sees automated text & video interview analysis as a big growth area. Class worked on requirements for tech performance & whether recruiters would feel augmented or replaced
1: @conveyiq's candidate management system. Well-positioned in the market, ConveyIQ sees automated text & video interview analysis as a big growth area. Class worked on requirements for tech performance & whether recruiters would feel augmented or replaced
 The Great Recession hammered lower-skill workers: even in the recovery, employment numbers have been lagging. Walmart, the US' largest private employer, employs a significant proportion of lower-skilled workers - changes it makes have national impact.
The Great Recession hammered lower-skill workers: even in the recovery, employment numbers have been lagging. Walmart, the US' largest private employer, employs a significant proportion of lower-skilled workers - changes it makes have national impact. 

 Demographic trends have reshaped the economy. Rising women's LFPR was the largest driver of US GDP growth since the 60s, but this force has plateaued and the population is rapidly aging. The Care Economy is vital for keeping the workforce strong in numbers and productivity.
Demographic trends have reshaped the economy. Rising women's LFPR was the largest driver of US GDP growth since the 60s, but this force has plateaued and the population is rapidly aging. The Care Economy is vital for keeping the workforce strong in numbers and productivity. 

 TVCs (temps, vendors, contractors) make up ~50% of Google's workforce. TVCs recently protested that they deserve similar benefits (healthcare, paid vacations) & information (they're excluded from town hall meetings & other internal communications) as FT workers they work beside.
TVCs (temps, vendors, contractors) make up ~50% of Google's workforce. TVCs recently protested that they deserve similar benefits (healthcare, paid vacations) & information (they're excluded from town hall meetings & other internal communications) as FT workers they work beside. 

 Co-CEO @BiedermanRob discussed how Catalant provides access to scarce skills through gig work, especially for firms outside talent clusters, and the infrastructure to support project-based work.
Co-CEO @BiedermanRob discussed how Catalant provides access to scarce skills through gig work, especially for firms outside talent clusters, and the infrastructure to support project-based work.
 The Big Shift, by @jhagel, @jseelybrown & @langdavison, argues that quality access to flows of knowledge are now more important than accumulated stocks. After vigorous debate, the class agreed with a recipe of 80% flow / 20% stock for today's businesses.
The Big Shift, by @jhagel, @jseelybrown & @langdavison, argues that quality access to flows of knowledge are now more important than accumulated stocks. After vigorous debate, the class agreed with a recipe of 80% flow / 20% stock for today's businesses.