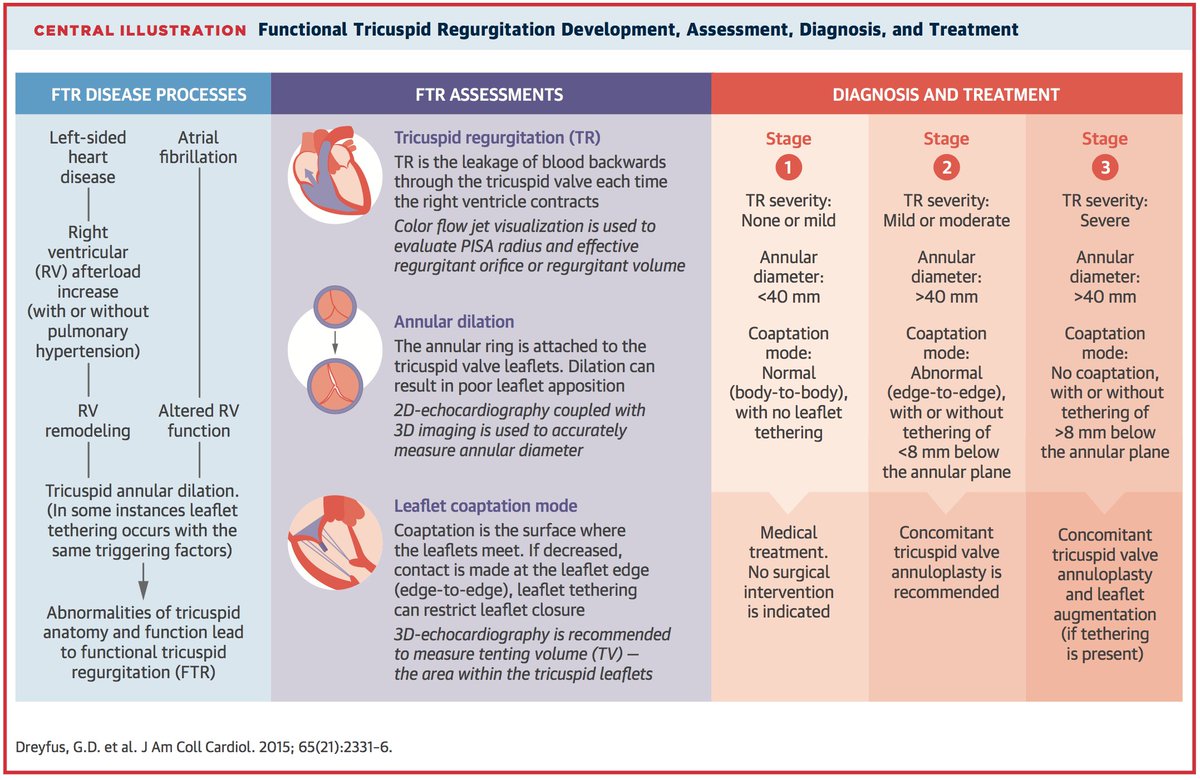
1⃣&2⃣ - Applications
3⃣ , 4⃣ , 5⃣ & 6⃣ - Data: Pressures, PCWP Waveform, CO & Shunts
7⃣ - Complications
Take home: RHC = useful diagnostic tool. Safe & effective use depends on thoughtful placement and data intepretation

1⃣ - Applications
Accurate assessment of hemodynamics and etiology of shock
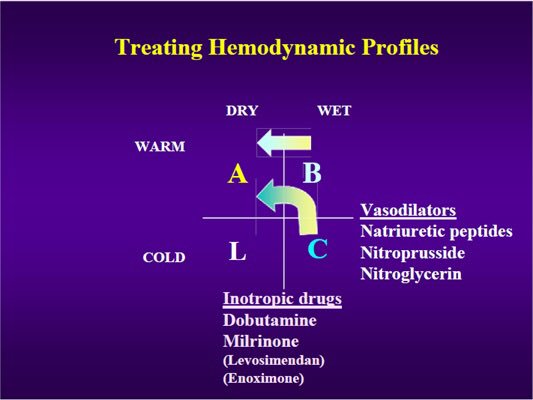
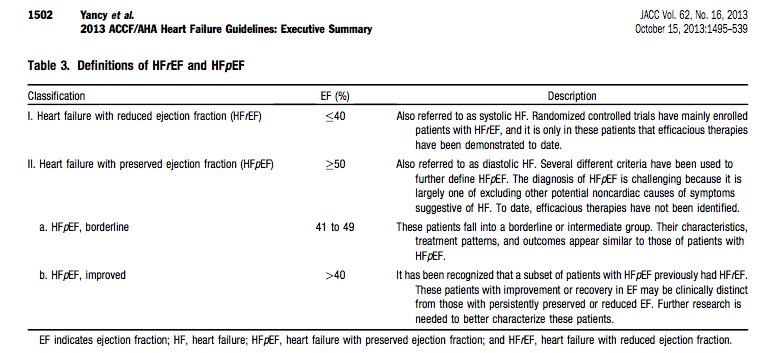
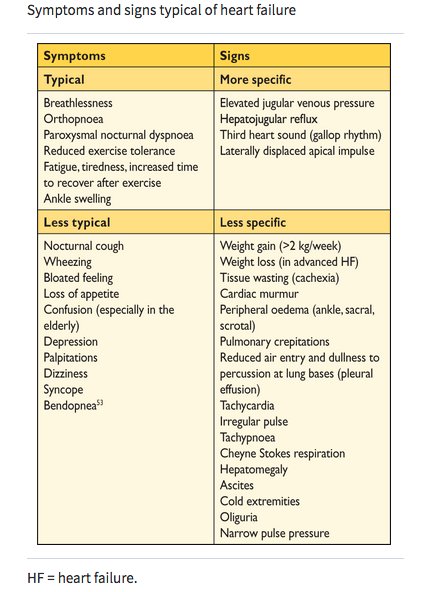
Assessment and management of severe HF e.g. "tailored therapy"
Evaluations of intracardiac shunts, valvular lesions
Perioperative management of severe HF
2⃣ - Applications
Risk stratification for patients considered for ❤️ Xplant
Establishing dx of PAH vs. secondary PH
Ddx: ❤️ vs non-❤️ cause of pulm edema (*caveat: RHC not indicated for routine mgmt of pulm edema or CHF)
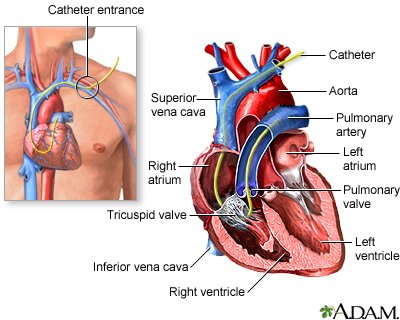
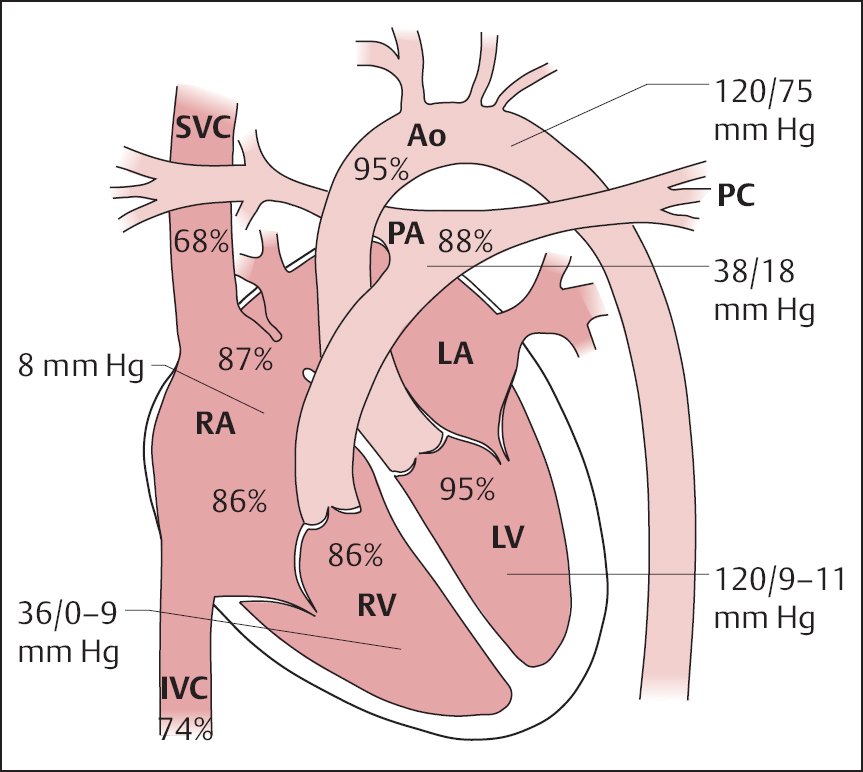
3⃣ - Data: Pressures
Allows for measurement of 1. CVP/RAP, 2. PASP, PAd, mPAP, 3. PAOP/PCWP
Absolute numbers and morpholopy of pressure waveforms assist with diagnosis and management of disease processes
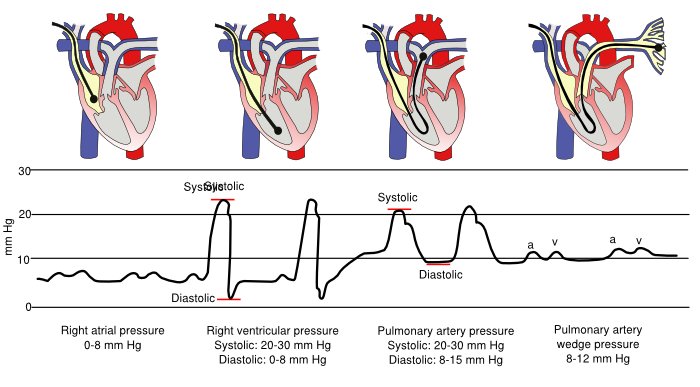
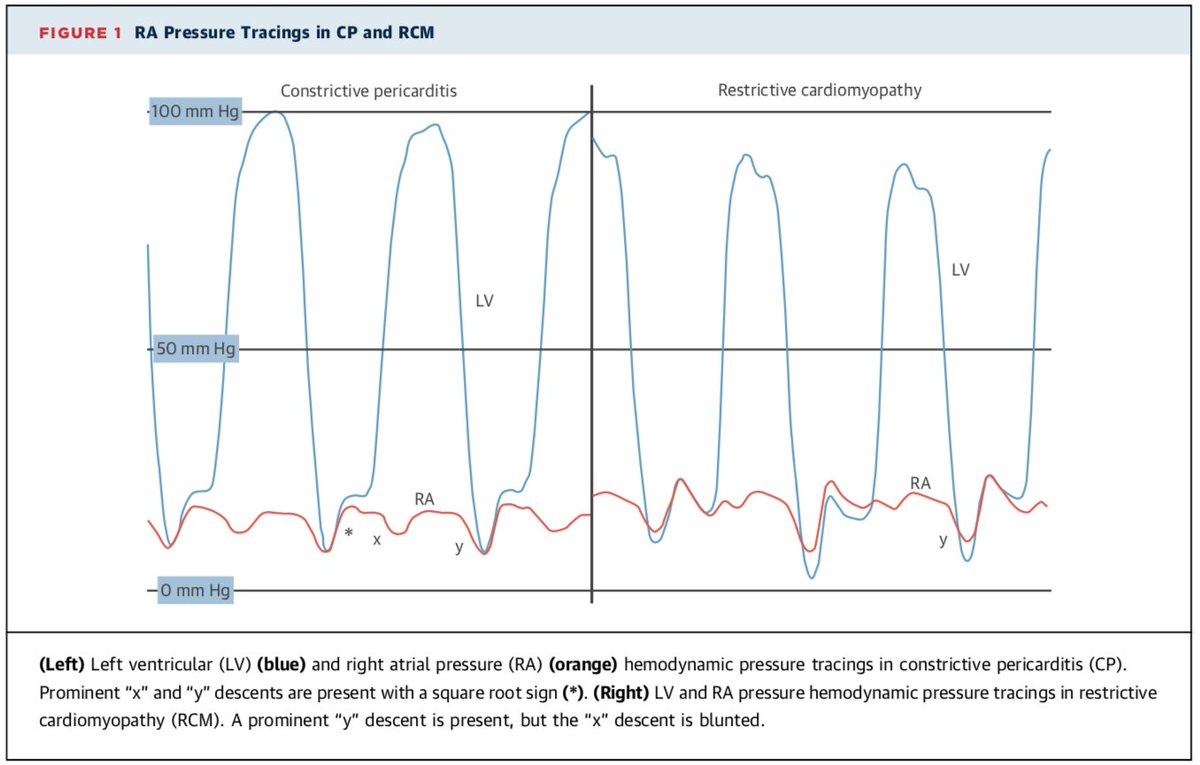
4⃣ - Data: RAP/PCWP Waveforms
PCWP estimates LAP. Use end-diastolic wedge pressure to estimate LVEDP (assuming no intervening pathology). Measure @ end-expiration when intrathoracic P ~ 0 regardless of whether patient is vented.
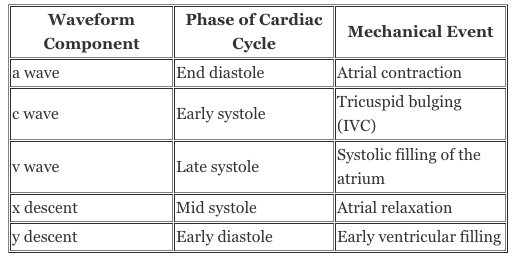
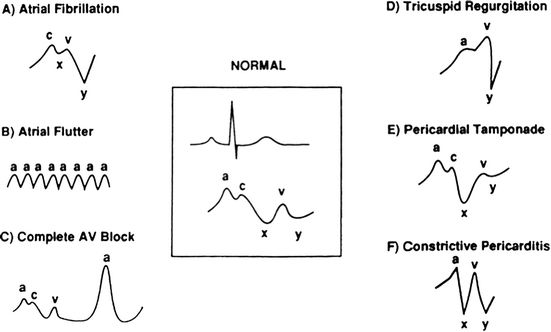
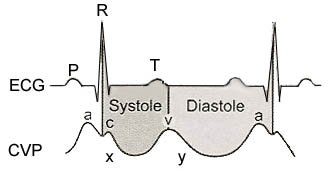
5⃣ - Data: CO
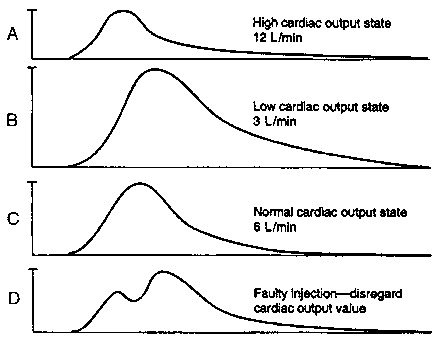
Allows for measurement of Fick and thermodilution (TD) CO.
For Fick, VO2 can be measured in closed breathing circuit or estimated (3cc/kg/min)
TD uses cold saline to calculate CO via 🔺 blood temp / time

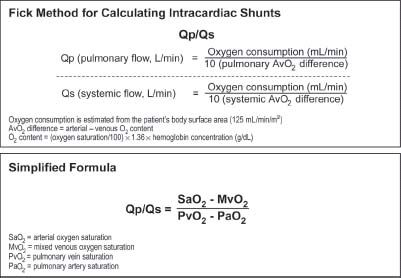
6⃣ - Data: Shunts
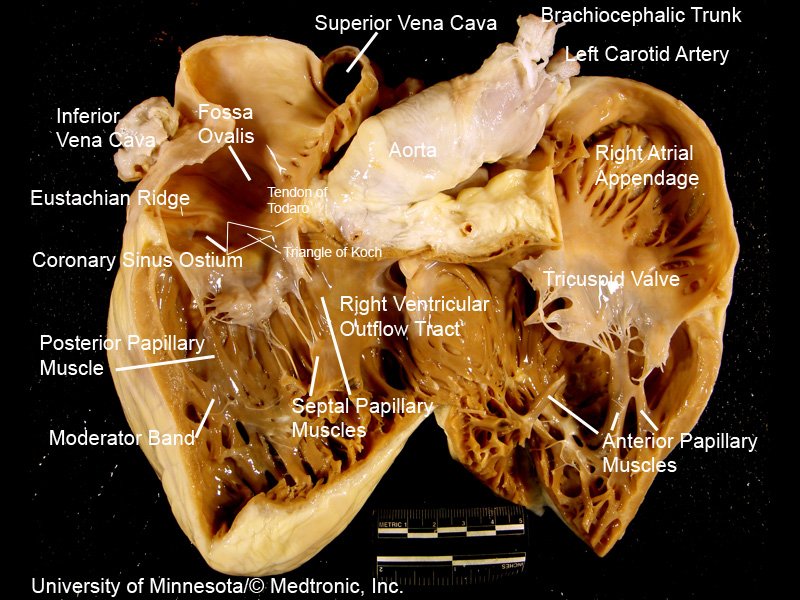
RHC (+simultaneous LHC) allows for detection of intracardiac shunts via differential O2 sats.
Mere detection of L ➡️ R shunt can be done w RHC alone via "step-up" in sats.
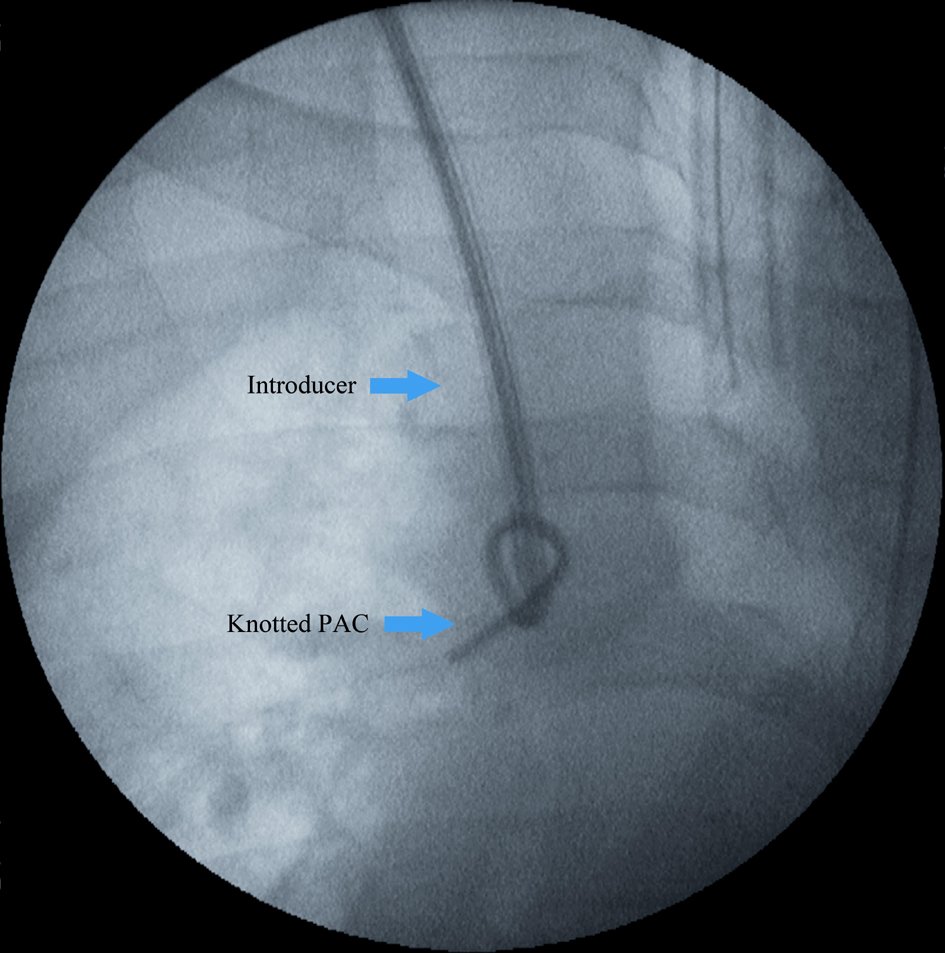
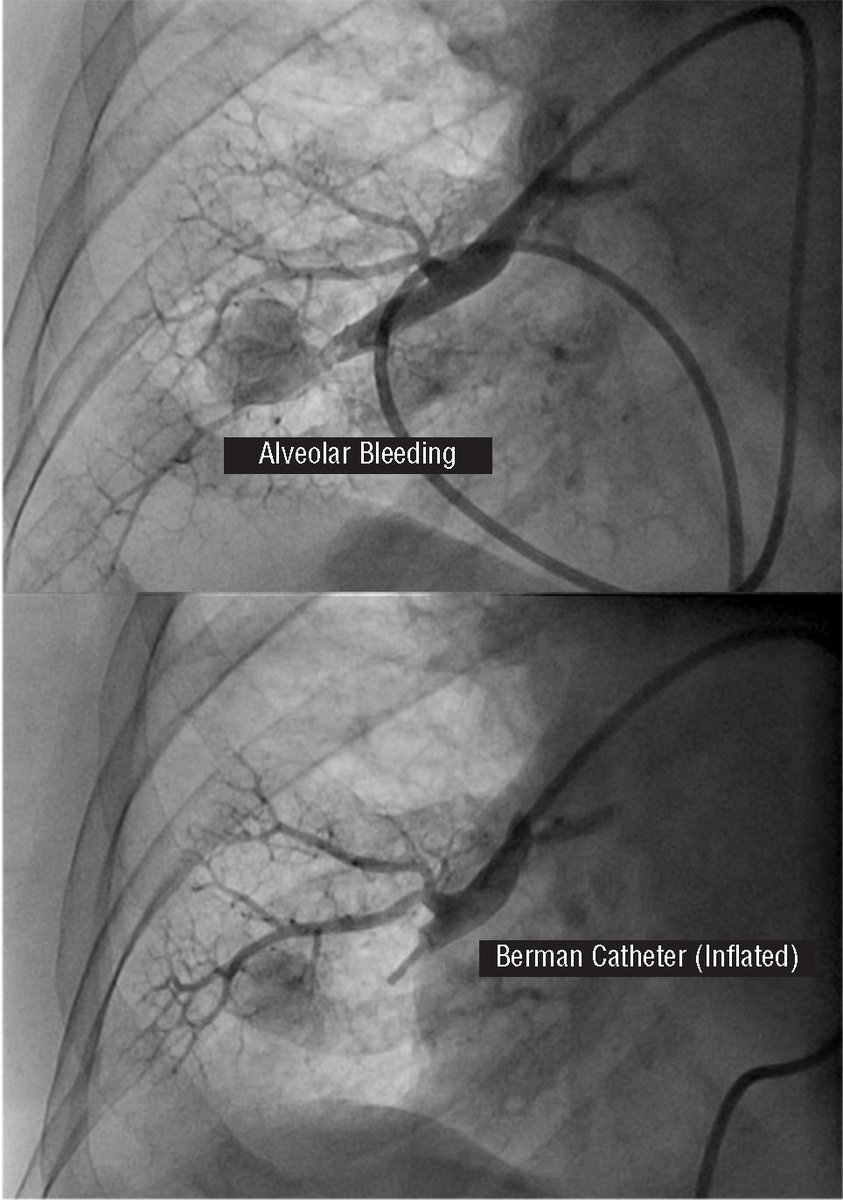
7⃣ - Complications
Broadly, 2/2 attainment of vasc access, catheter manipulation, and catheter residence.
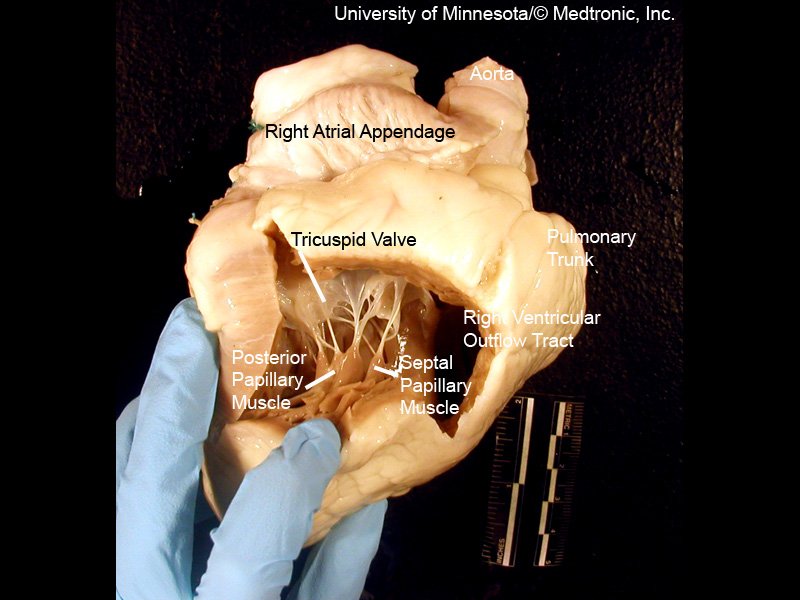
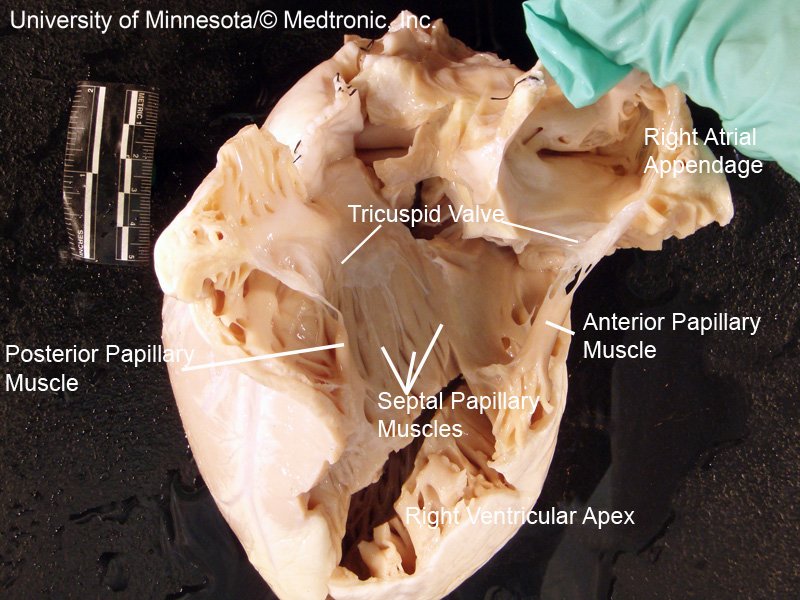
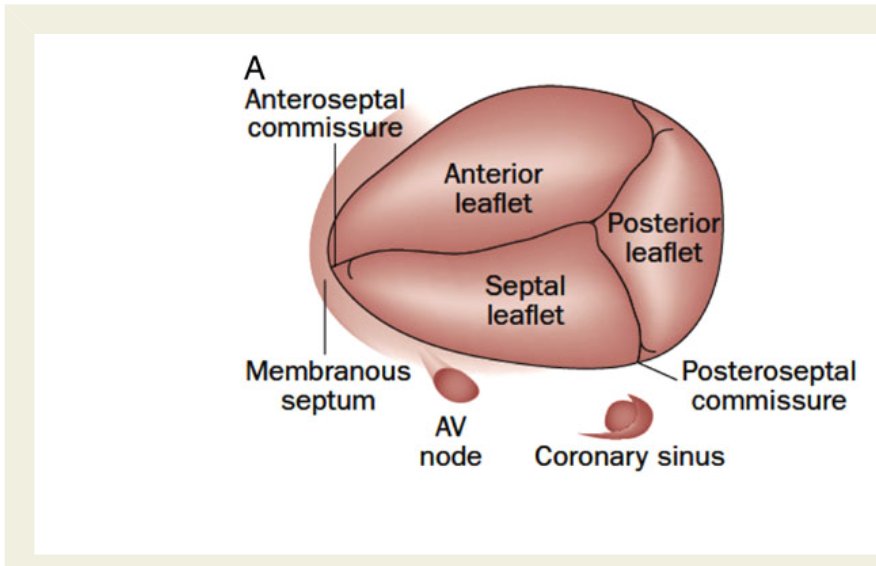
➡️ Arterial puncture, bleeding, nerve injury, PTX, thrombus/embolus, arrhythmias, TV chord damage, PA rupture, line infxn