1⃣ Anatomy
2⃣ Etiologies
3⃣ Classification
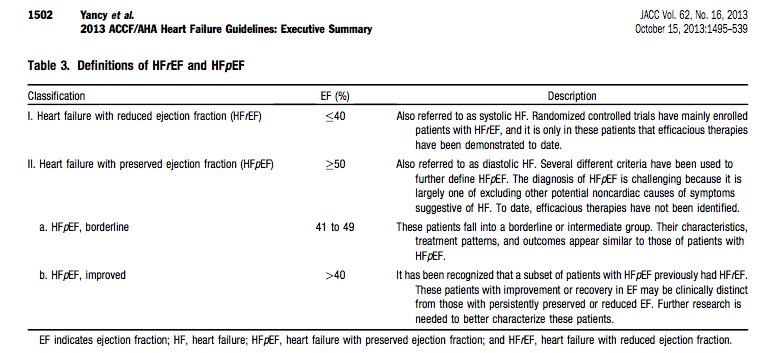
4⃣ Diagnosis
5⃣ Treatment
Resources: @ASE360 @JACCJournals @CircAHA @ACCCardioEd @UMNews @Medtronic
1/10
cc: @dr_chirumamilla
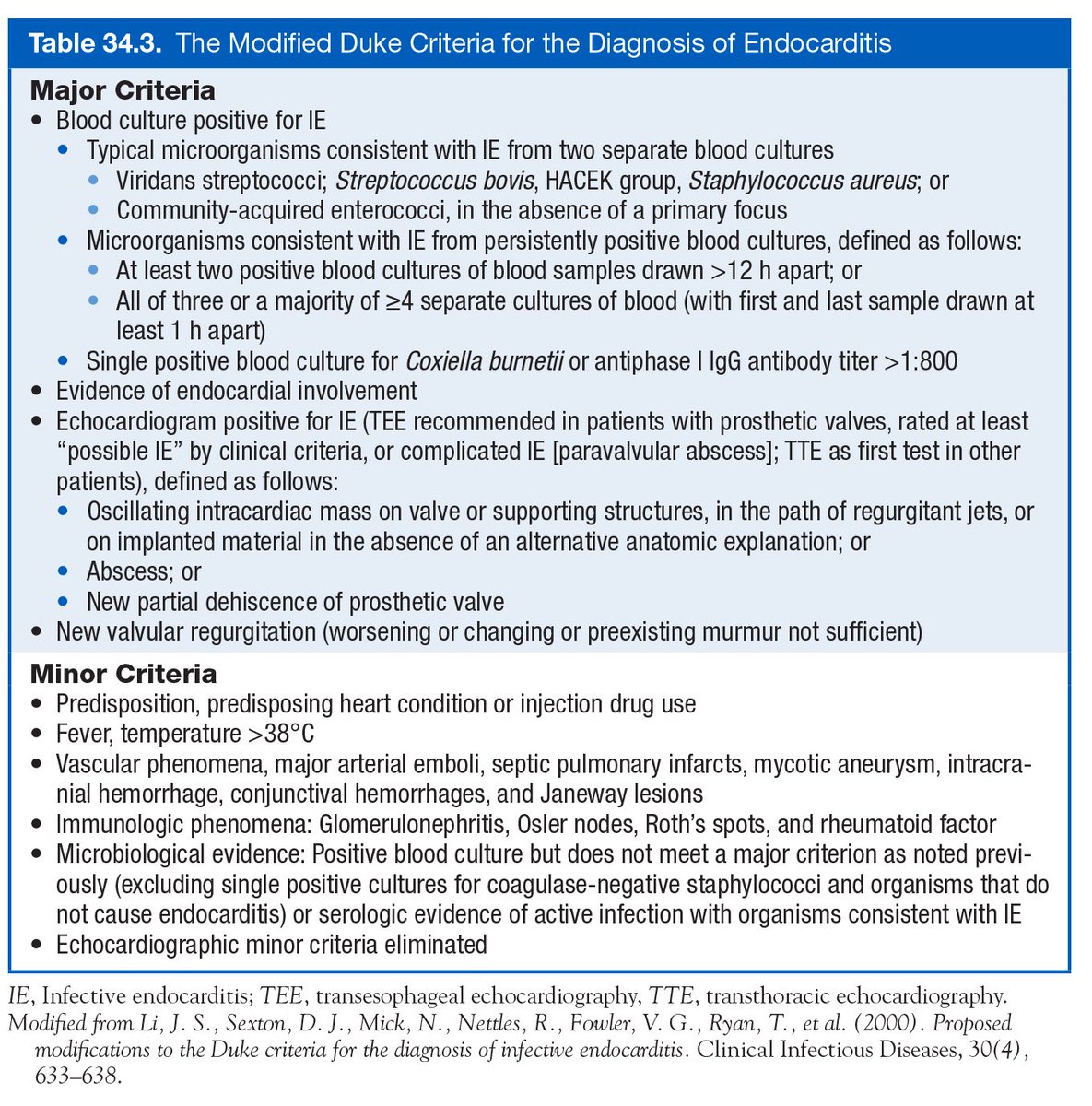
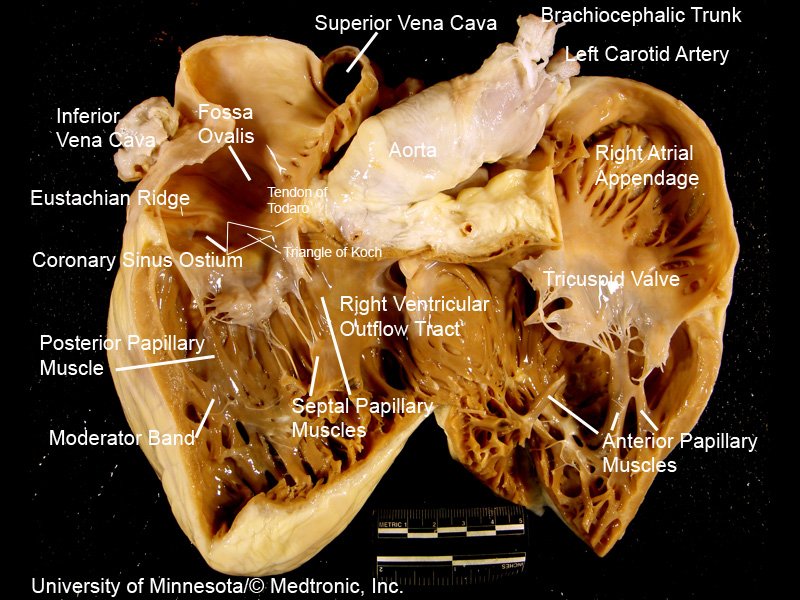
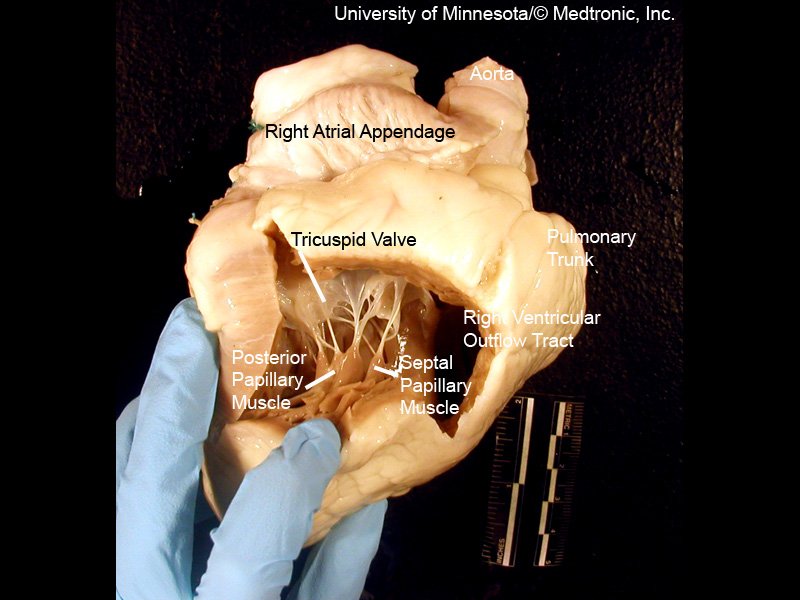
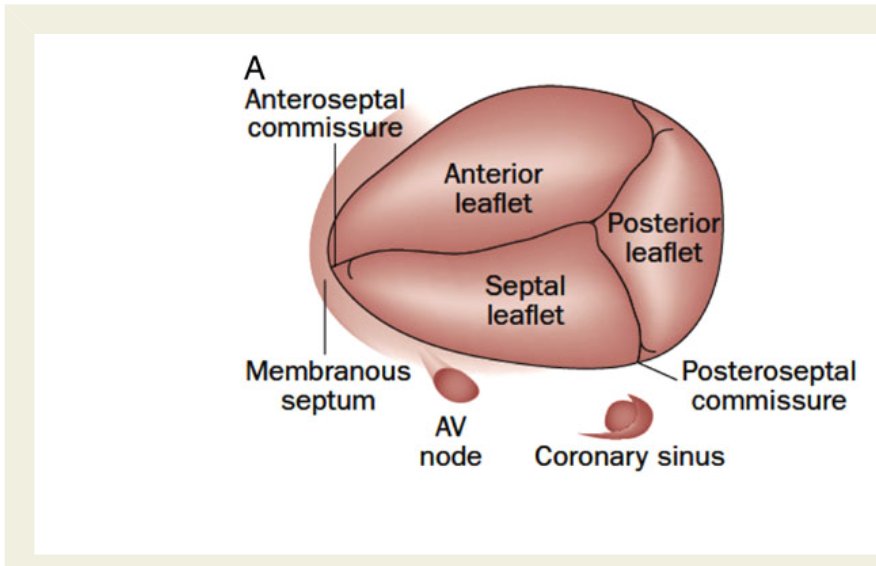
3 leaflets ⬇️ + fibrous annulus + 2 papillary 💪🏽 + chordae tendinae + RA/RV ❤️
⬛️ Anterior 🍃 (largest)
◾️Posterior
▪️Septal (smallest)
(note: throughout #tweetorial, see image descriptions for more content)
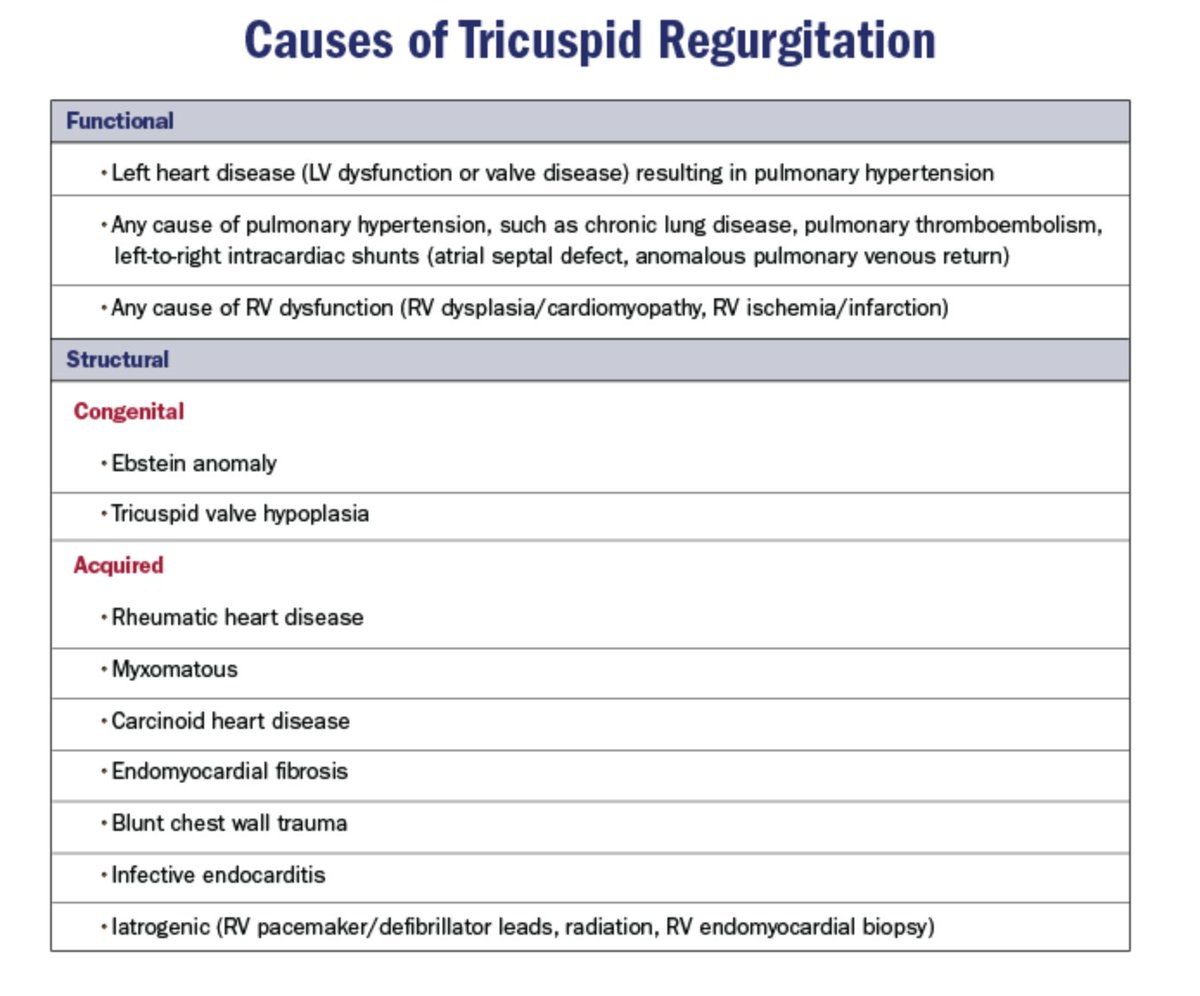
Keep chart ⬇️ DDx in mind when reading #EchoFirst
~80% of significant TR = FTR/2º to TA dilatation + leaflet tethering ⬅️ RV remodeling ⬅️ volume and/or pressure overload
Structural (1º) cause = less common
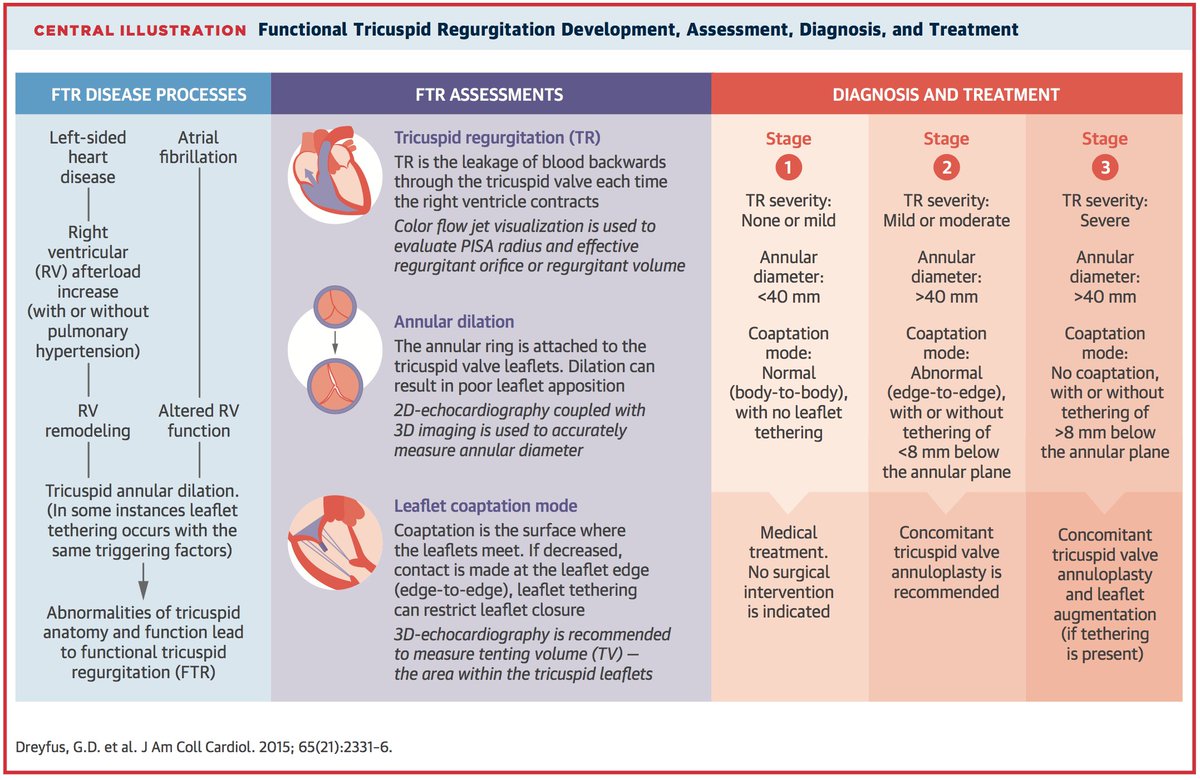
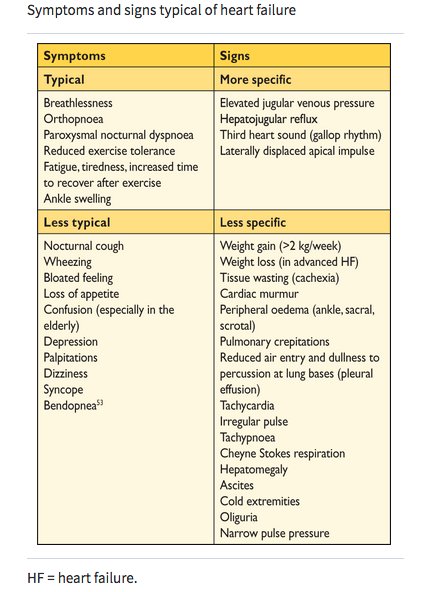
Exam 🧐:
✅ Elevated “c-V” waves in JVP
✅ Systolic murmur at LSB that ⬆️ w/inspiration
✅ Pulsatile liver edge, hepatomegaly, ascites
🚨 Murmur can be absent even in advanced TR!
Sx 😷: fatigue, abd fullness, edema, palps (if +AF)
⬇️ from @NEJM
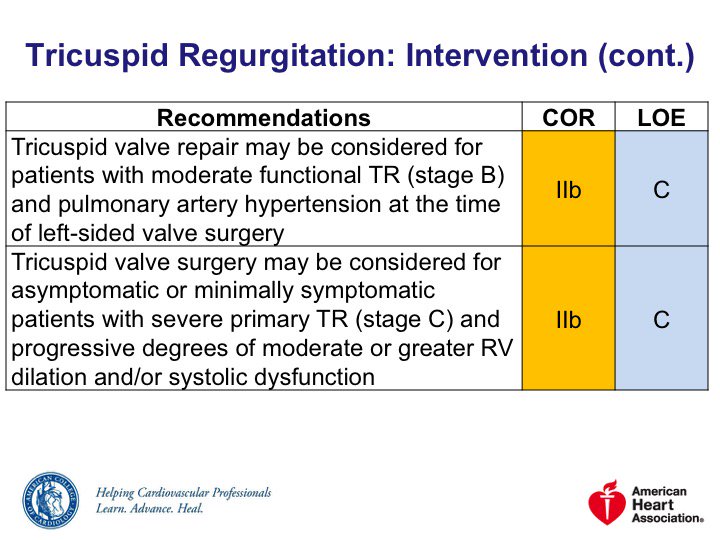
2014 @ACCinTouch @AHAScience Valve Guidelines: bit.ly/2uQkv7P
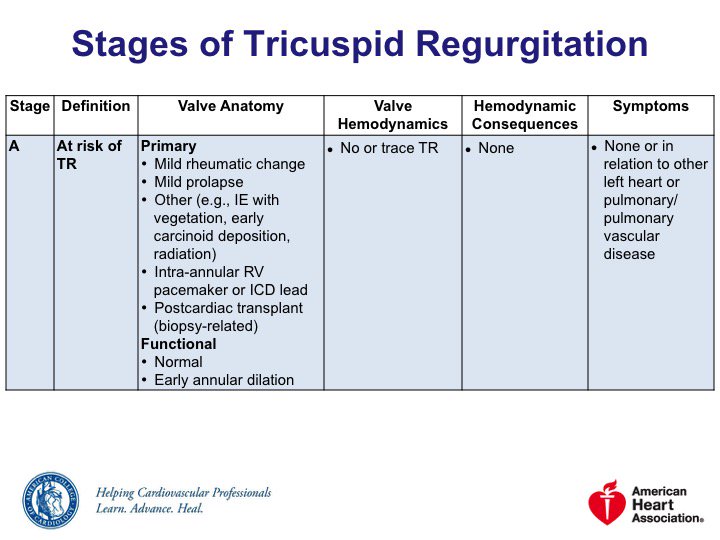
🔹Stage A = risk of TR
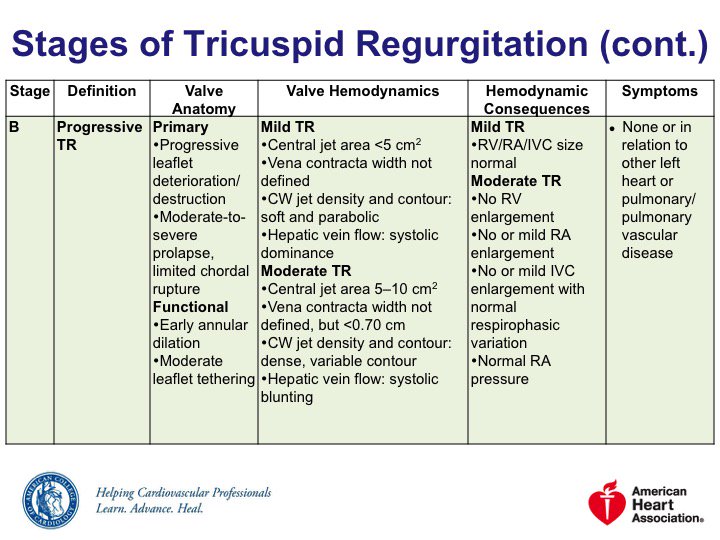
🔹Stage B = progressive TR
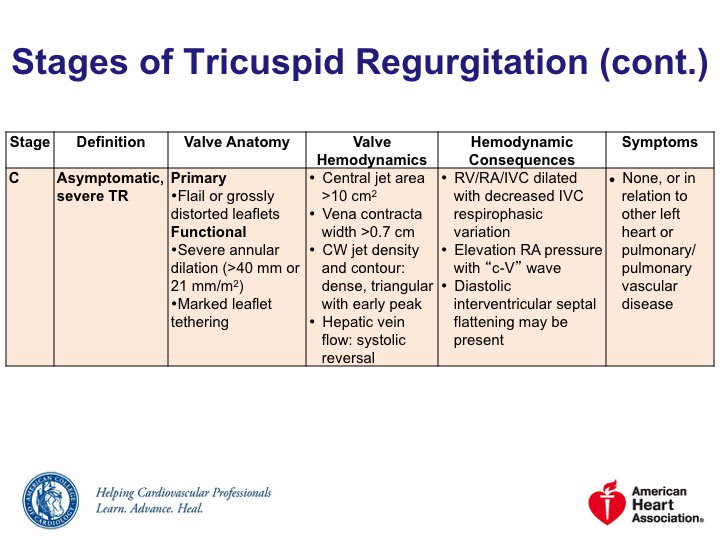
🔹Stage C = asymptomatic severe TR
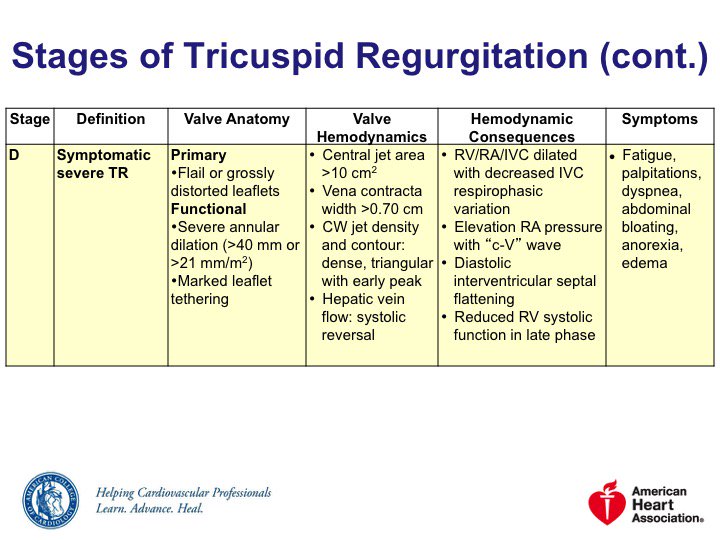
🔹Stage D = symptomatic severe TR
Severe isolated TR a/w excess mortality & morbidity
CXR & ECG ➡️ RV/RV dilation
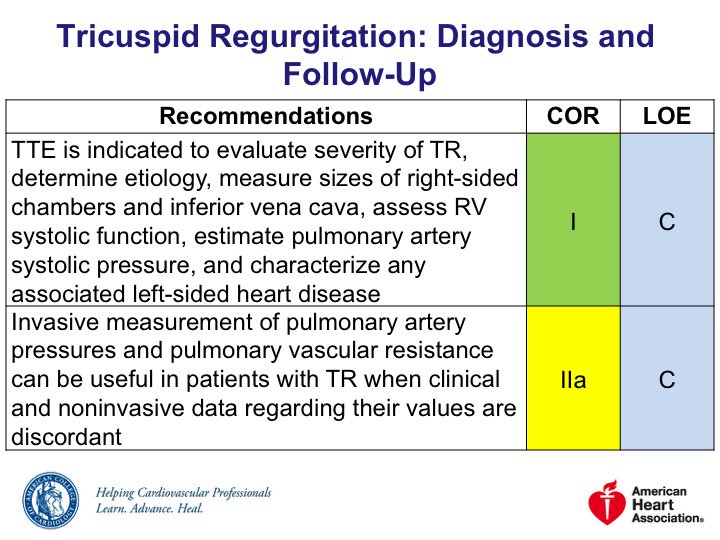
Dx standard = #EchoFirst for
🔸TR severity/etiology
🔸Chamber size & fxn (#whyCMR can help here, too)
🔸IVC
🔸RVSP/PASP
🔸Hepatic venous flow
🔸Left ❤️ disease
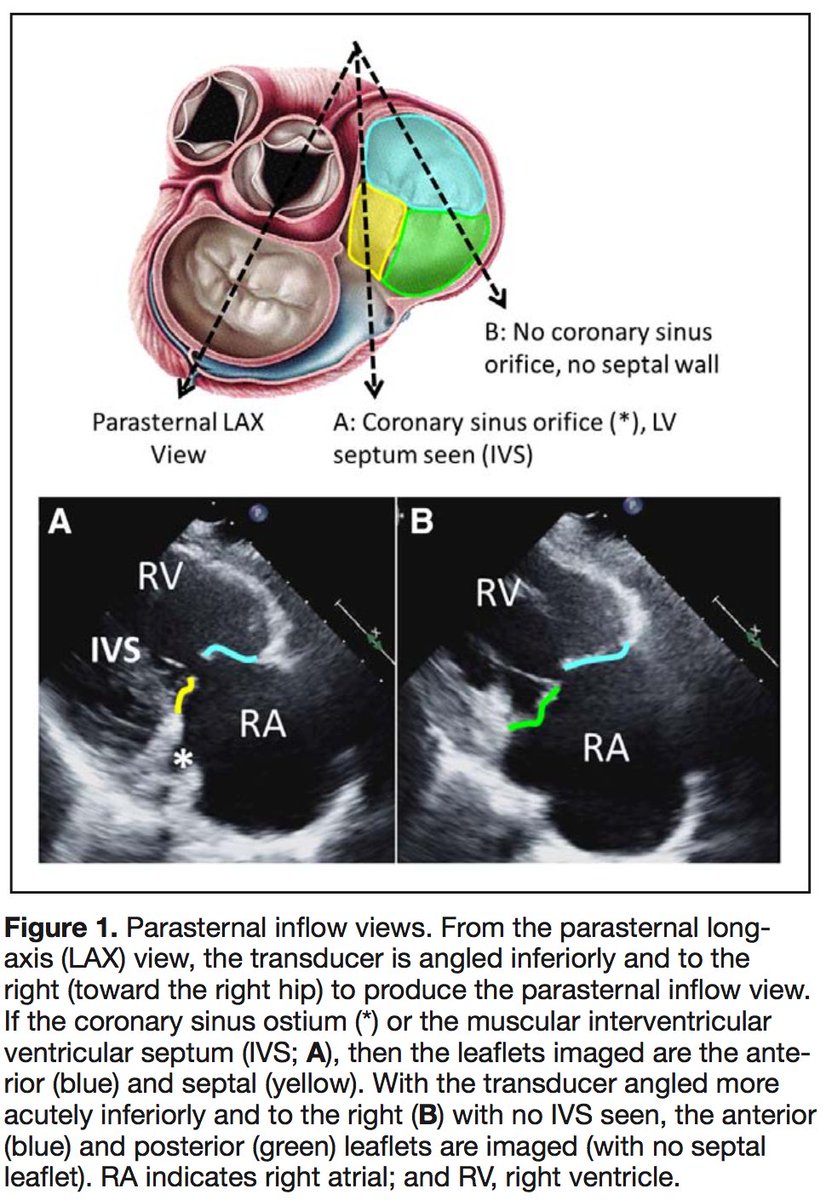
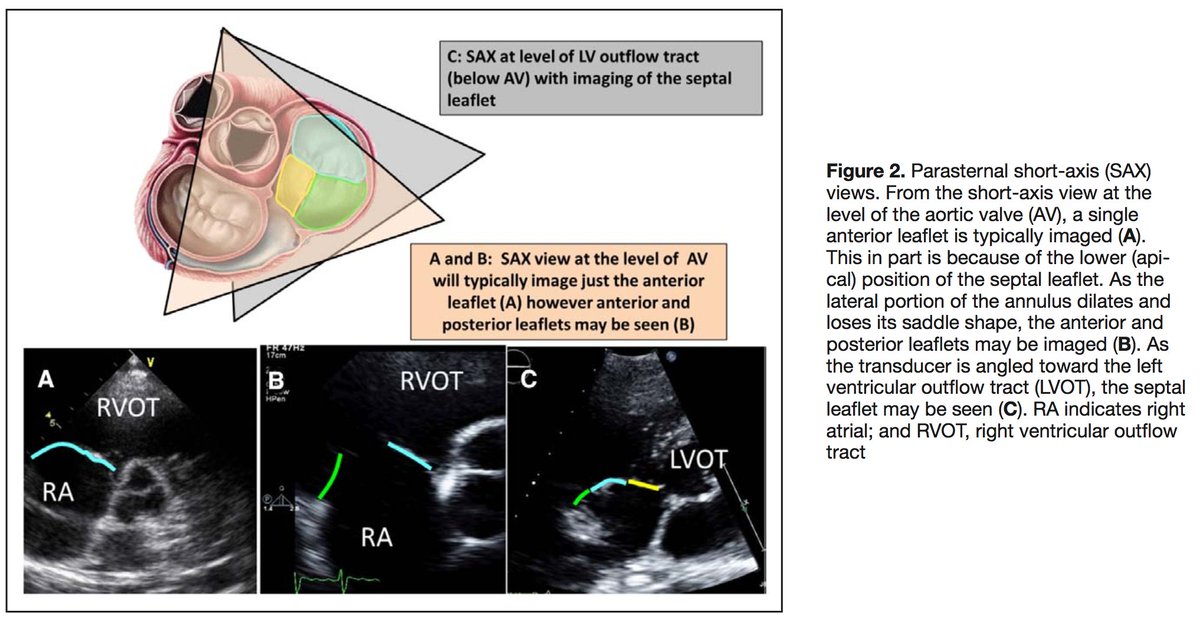
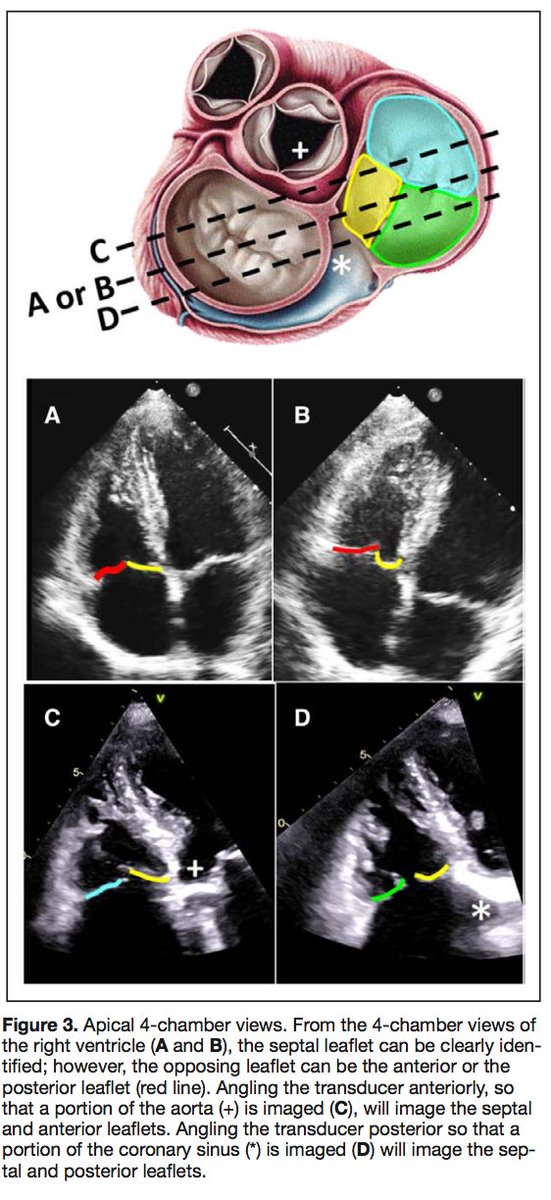
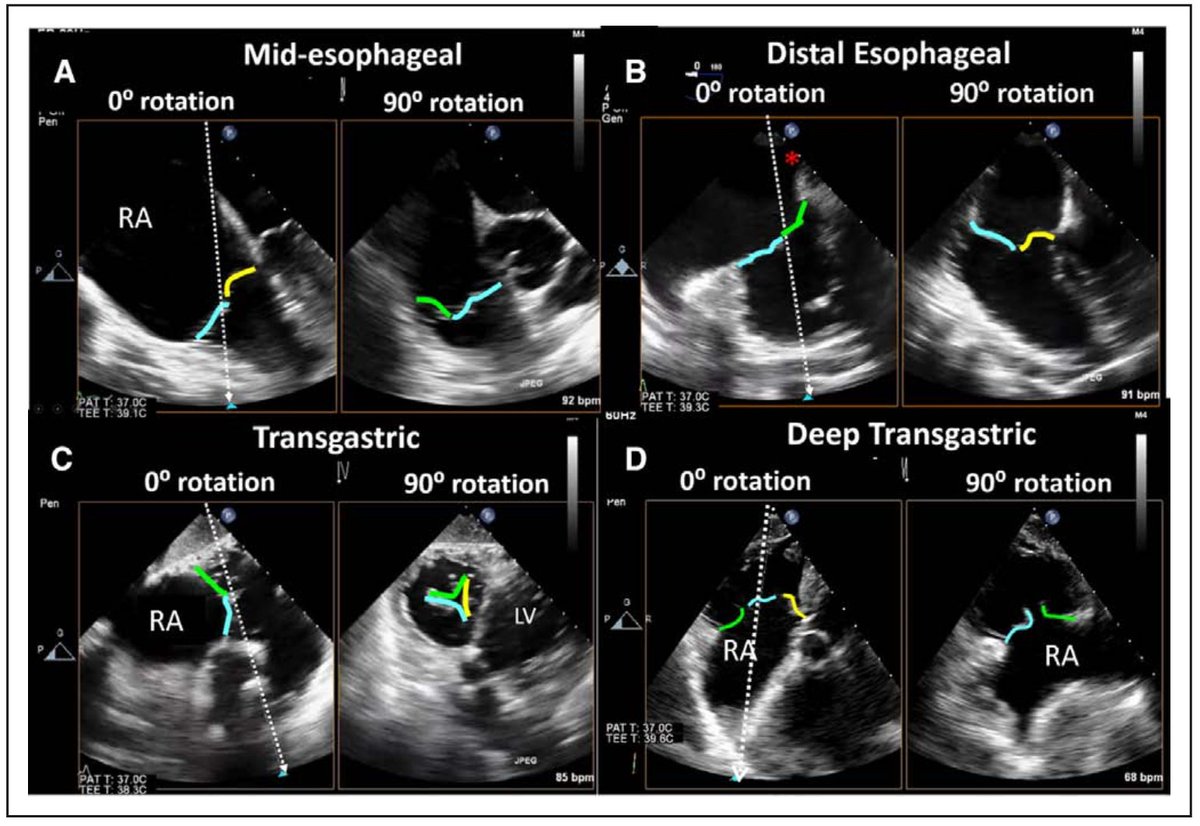
Be mindful 🤔 of your imaging view/modality limitations!
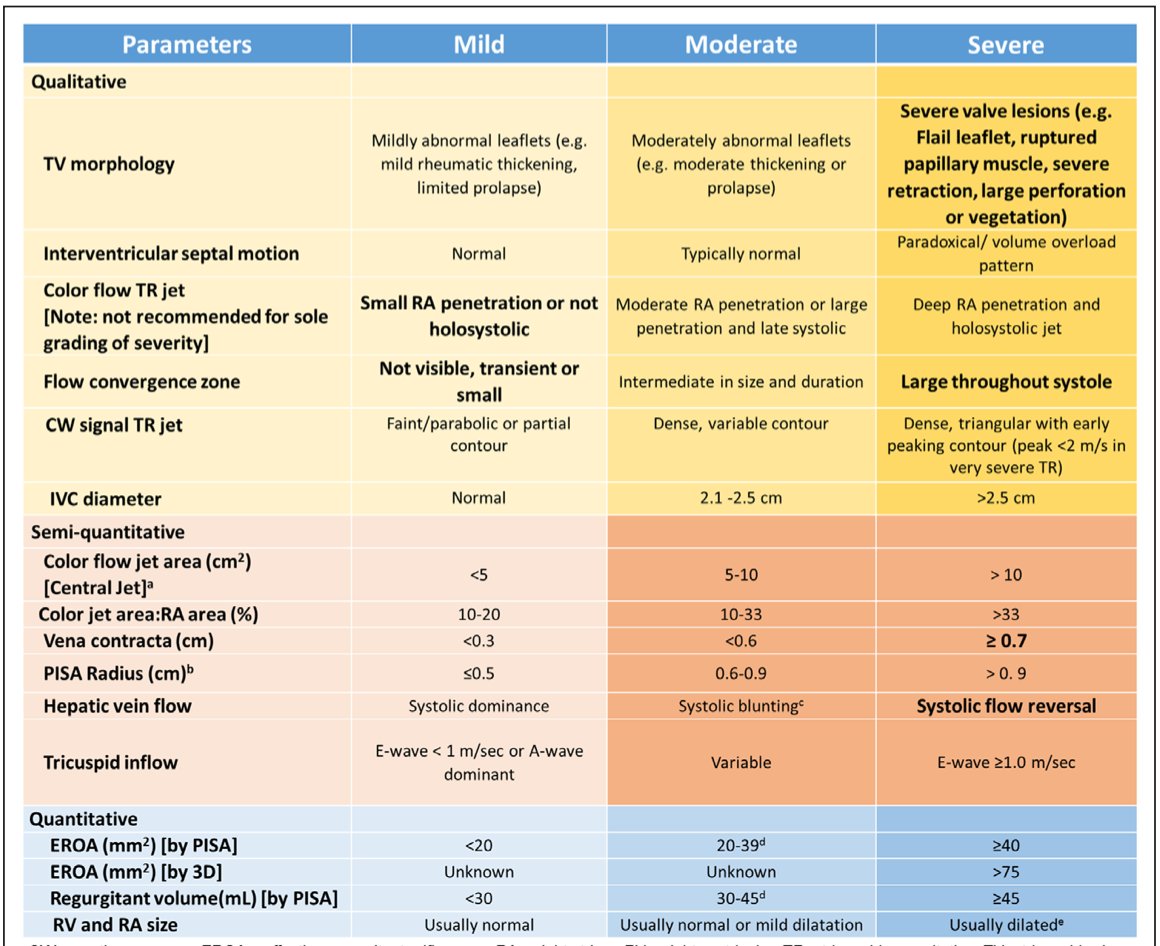
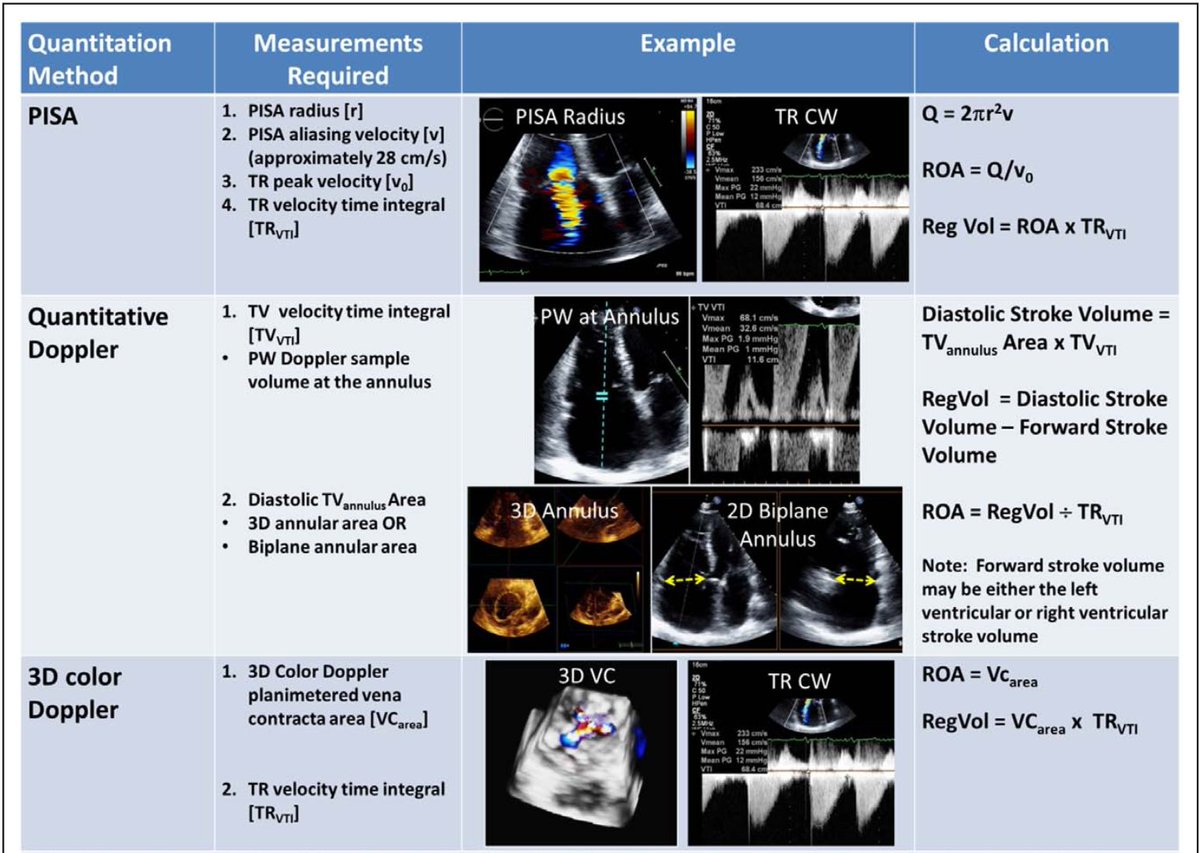
Characterizing TR severity needs *integrative* assessment of multiple qualitative+quantitative parameters
Great read: @ASE360 Guidelines for Right Heart Echo Assessment: bit.ly/2O4u7Vb
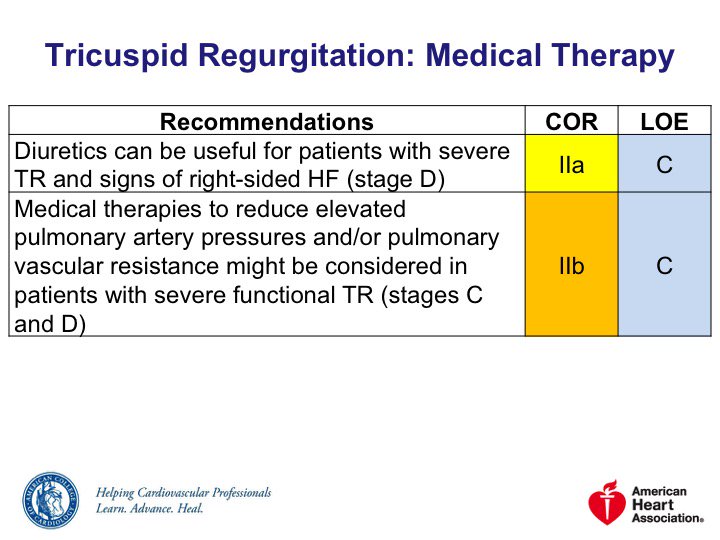
Stage D:
◽️Diuretics can be useful
◽️Loop diuretics typical
🚨 Aggressive diuresis can ⬇️ LVSV and CO
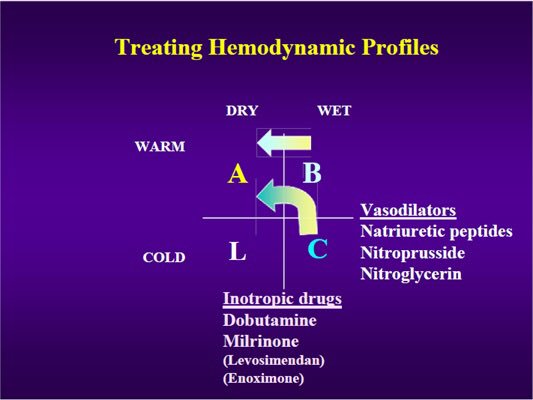
Stages C/D, severe FTR:
◾️Consider other medical therapies to down arrow PASP and/or PVR
◾️Specific pulmonary vasodilators may help in #cvPH
Tons of great reads out there-in addition to those in tweets:
@JACC 2015 bit.ly/2Ls4K1k
@Circ 2016 bit.ly/2A0l6cX
@Lancet 2016 bit.ly/2Lwca3m
@ESC 2017 bit.ly/2uU4PR0