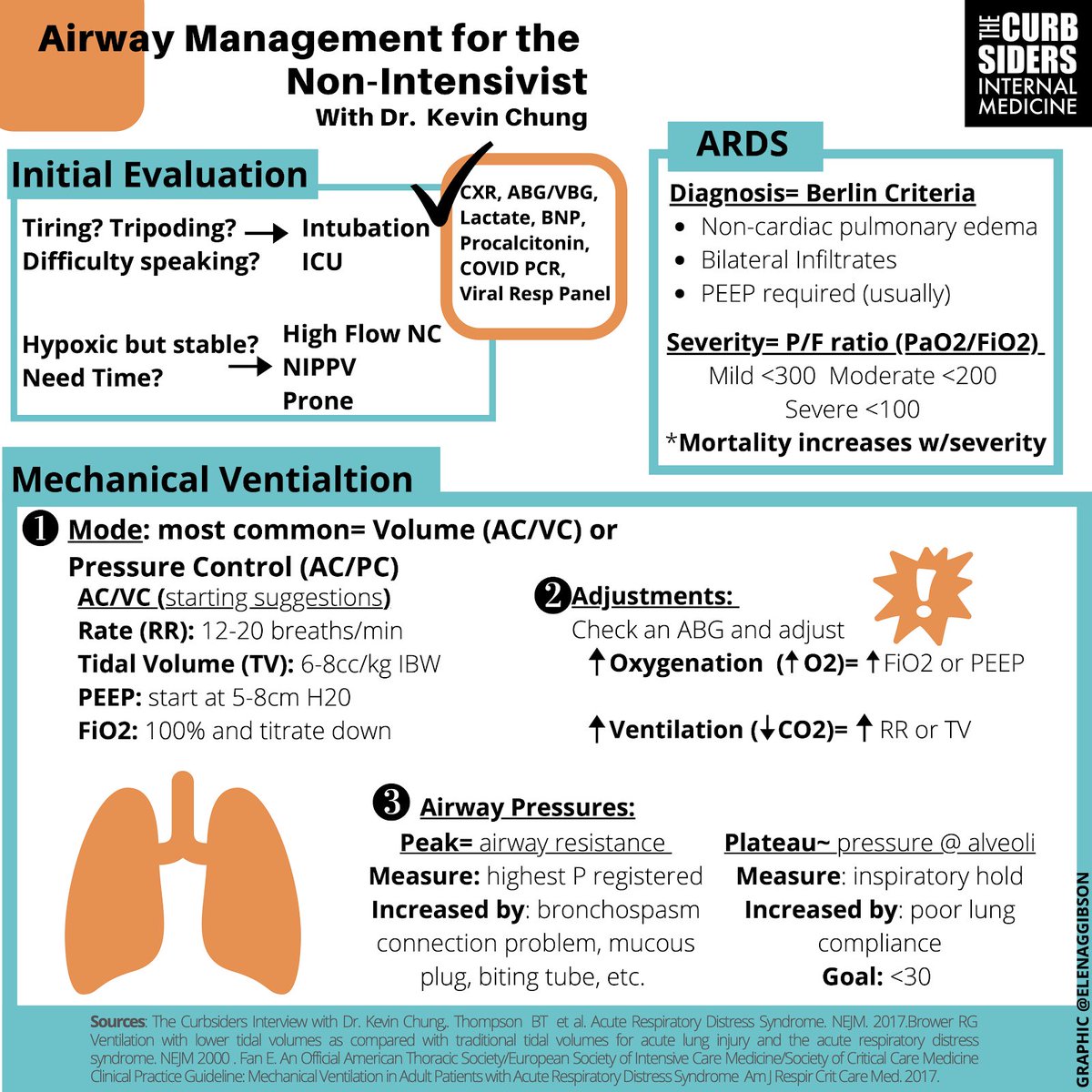
1. SGLT2 inhibitors have significant long-term protection of GFR. However, because they cause afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction, expect to see an acute drop in GFR after initiating.
3. Patients already on thiazide can experience significant volume loss with SGLT2i initiation. Consider reducing or stopping thiazides
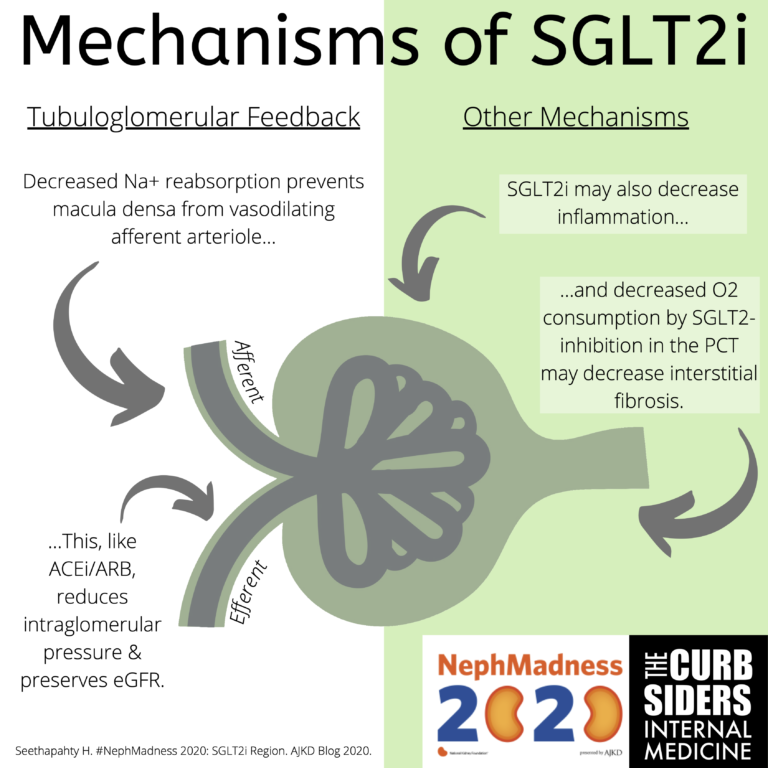
Traditionally, tubuloglomerular feedback has been considered a major mechanism of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) effect in diabetic kidney disease.
Sodium is reabsorbed at an increased rate along with that glucose, meaning that the macula densa ‘sees’ less sodium
The afferent arteriole vasodilates, increasing intraglomerular pressure, and over time this contributes to fibrosis and nephron loss. ajkdblog.org/2020/03/13/nep…
This reduces intraglomerular pressure and protects the nephron
ajkdblog.org/2020/03/13/nep…
SGLT2i can still provide improvement in renal outcomes for diabetic kidney disease in pts on maximum doses of ACE inhibitor (which increases efferent flow). pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30990260/
May also limit podocyte dysfunction and act on upregulated SGLT2 expression in proteinuria.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30089717/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30045814/
These two effects may decrease nephron fibrosis and cardiac inflammation.
SGLT2i may block Na-H exchange in the heart to decrease oxidative damage & thrombosis as well as promote natriuresis ajkdblog.org/2020/03/13/nep…
Genital fungal infections are common, and these are usually responsive to antifungal treatment and do not require stopping the medication
Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis is another rare though possible side effect as patients may have DKA with normal blood glucose levels given the induced glycosuria.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28605608
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30990260/