Here's innervation of the leg/foot & approach to FOOT DROP
#MedEd #MedStudentTwitter
@CPSolvers @Tracey1milligan @MadSattinJ
@MedTweetorials @DxRxEdu @AANMember @StaceyLClardy @ContinuumAAN
1
Just 5 nerves for each extremity- no neurophobia needed!
2
Femoral
Obturator
Sciatic
Peroneal
Tibial
And the sciatic is really just the peroneal and tibial bound together!
And the leg/foot are much easier than the hand because the foot does much less intricate movements than the hand!
3/
- Iliopsoas (flexes leg at hip)
- Quadriceps (extends knee--so it supports the patella reflex)
4/
5/
Hip flexion weakness and knee extension weakness including diminished/lost knee reflex
(rarely isolated knee extension weakness if affected in inguinal canal distal to innervation of psoas)
6/
*Pearl–unilateral leg weakness in anticoagulated patient? Look for psoas hematoma with CT ab/pelvis* I've seen pts get lumbar MRI and this dx missed!
7
8/
Femoral AND obturator are both served by L2-3-4. So if either nerve affected test actions of other!
If BOTH femoral AND obturator appear affected, consider lumbosacral plexus issue or polyradiculopathy
9/
Sciatic runs down posterior leg, and innervates hamstrings before dividing into peroneal and tibial posterior to the knee.
Let's first talk about peroneal and tibial and then come back to sciatic
10/
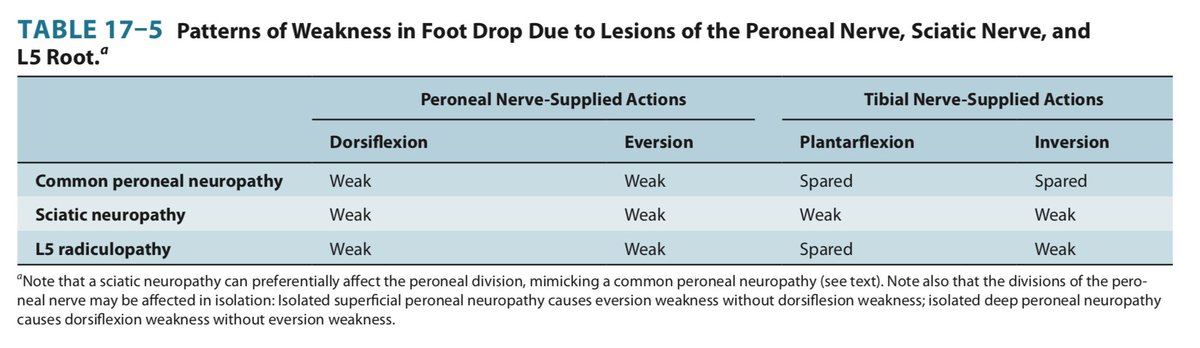
PERONEAL: toP of foot–Dorsiflexion and Eversion (and toe extensors)
TIBIAL: Bottom of foot–Plantarflexion and Inversion (and toe flexors
11/
toP of foot: Peroneal
Bottom of foot: tiBial
PED: peroneal eversion/dorisflexion
TIP: tibial inversion/plantarflexion
PerOneal: uP and Out
tIbial: down and In
Or memorize one: other does the opposite movements!
12/
When examining patients, I say:
Eversion = rotate ankle outward as if looking for gum on the outer sole of your shoe
Inversion = rotate ankle in as if looking for gum on your instep
13/
This causes foot drop (weak dorsiflexion) with weak EVERSION.
14/
- Sciatic (which can cause loss of all peroneal/tibial function = weak dorsi/plantarflexion and e/inversion, BUT often preferentially affects JUST peroneal!)
15/
(L5 radic can also cause hip abduction weakness)
16/
17/
18/
19/
It's peroneal +tibial.
It can be injured in pelvic/hip trauma, prolonged compression of buttock (toilet seat neuropathy, chronic bed-bound state), misplaced gluteal injection.
"Sciatica" is usually from S1 compression, not sciatic compression
20/
Tibial part of sciatic does all hamstring muscles (knee flexion) except one: short head of biceps femoris done by peroneal
Remember sciatic neuropathy can preferentially affect peroneal component, mimicking peroneal neuropathy....
21/
If not affected, peroneal neuropathy at usual place: fibular head.
If affected, sciatic neuropathy!
(common RITE/ Neuro boards question!)
22/
Lateral femoral cutaneous, which does lateral thigh sensation. Compression/injury of this nerve leads to meralgia paresthetica (outer thigh numbness)
23/
24/


