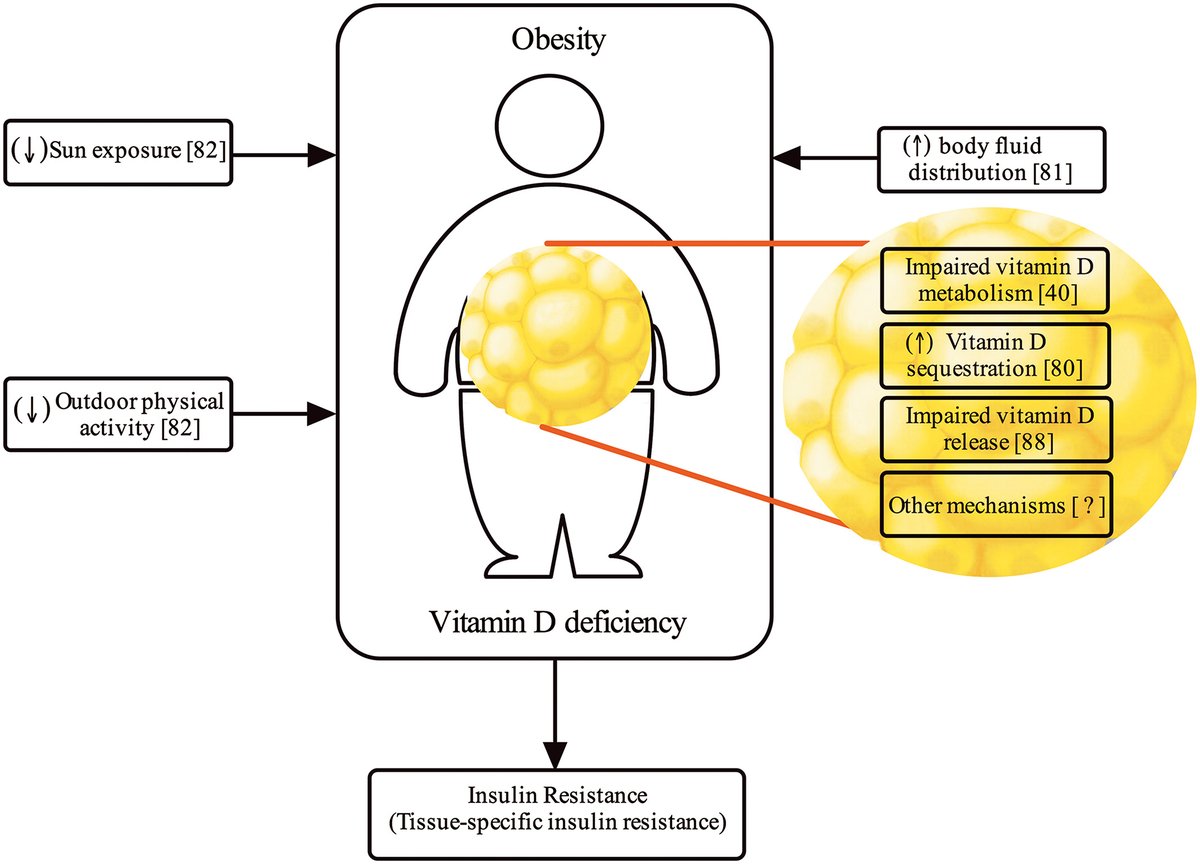
a. In 154 obese subs serum 1,25-Vit D was significantly lower
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15001609/
b. Authors conclude % body fat is inversely related to serum 25-OHD levels in healthy women
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12519845/
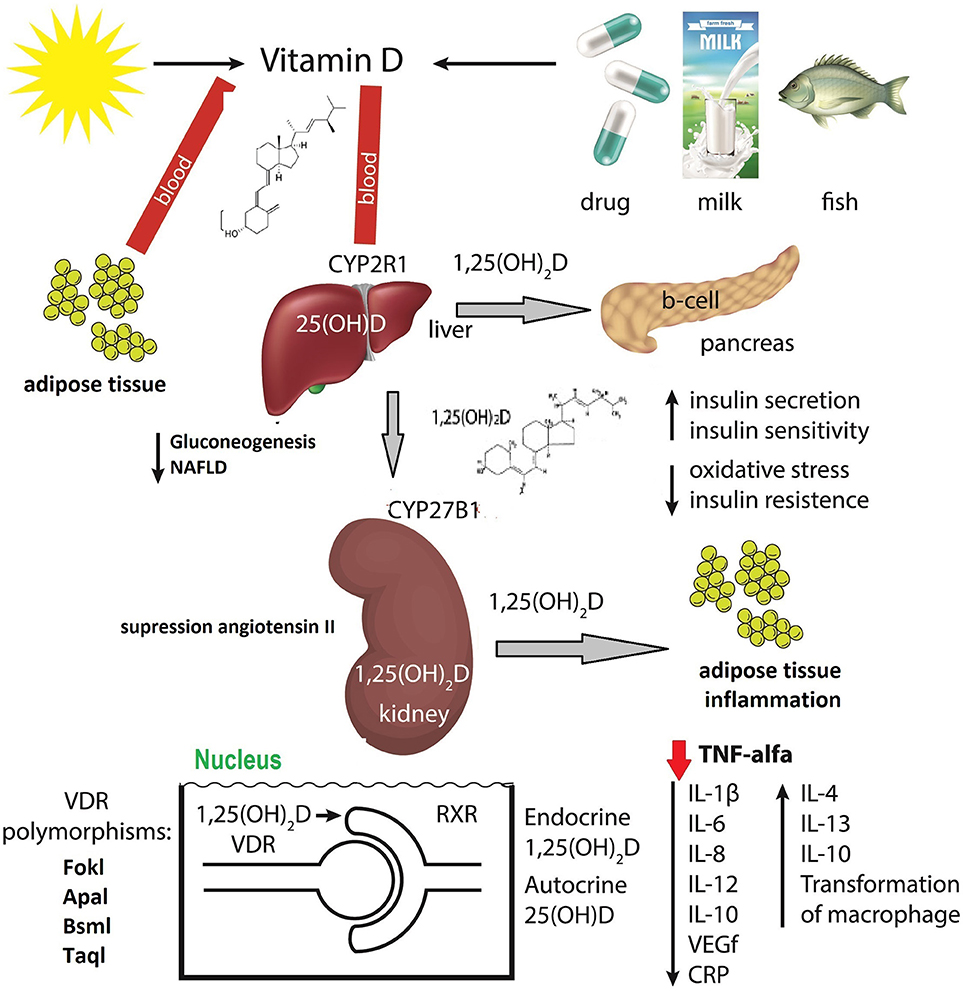
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
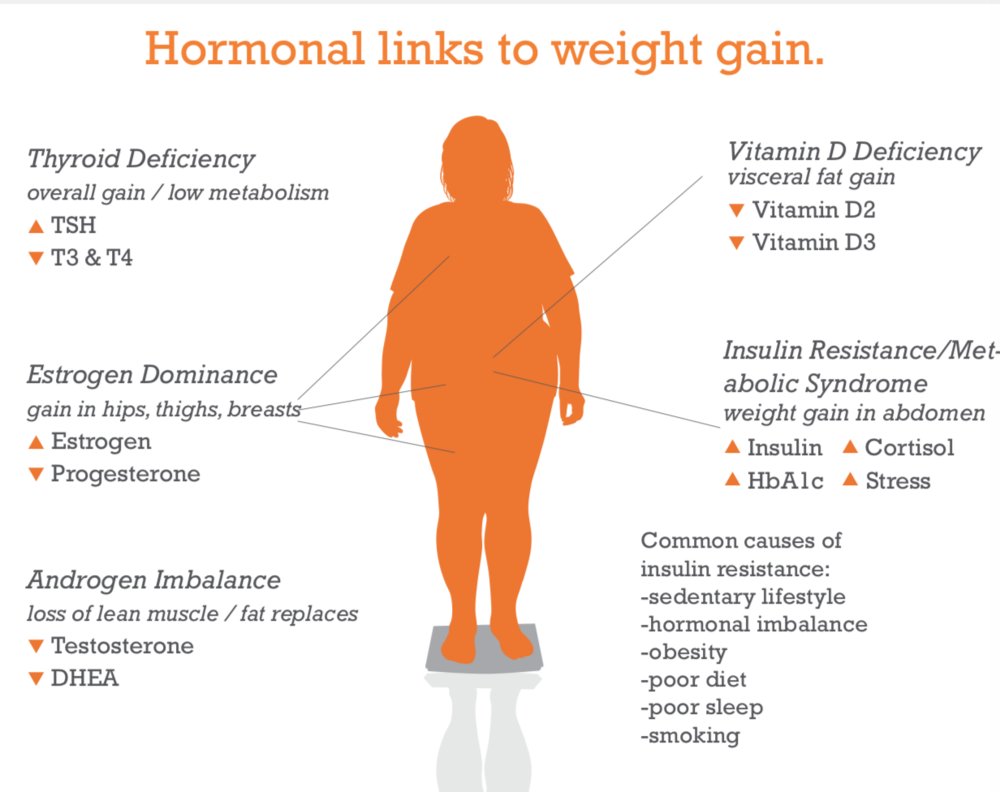
a. RCT (2012) reported weight loss, presumably associated with a reduction in body fat, is associated with increased serum 25(OH)D concentration in overweight or obese women (n=383).
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22402737/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
a. RCT w/ 218 overweight & obese women, found that women who fulfilled their vitamin D requirements experienced more weight loss (3.2 kg) than the women who did not have adequate blood levels.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24622804/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
a. Vitamin D could suppress the storage of fat cells, effectively reducing fat accumulation
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18254883/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22249823/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21154195/
- There’s an intricate relationship between vitamin D status and body weight. Getting enough vitamin D may help enhance weight loss and decrease body fat.
- In turn, losing weight can increase vitamin D levels and help you maximize its other benefits.