There are 5 values that you can pass in position property
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
In this thread we will be look at all of them
{ 2 / 19 }
- static
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
In this thread we will be look at all of them
{ 2 / 19 }
Let's start with understanding what document flow is?
📌 Elements are displayed on the screen as they written in the HTML document
Consider the following piece of code:
H1, P, H3 and div are displayed on the screen in exact order as they written in the HTML file
{ 3 / 19 }

📌 Elements are displayed on the screen as they written in the HTML document
Consider the following piece of code:
H1, P, H3 and div are displayed on the screen in exact order as they written in the HTML file
{ 3 / 19 }


Alright let's start with position concept. The first value we have is "static"
HTML elements are positioned static by default. An element with position: static; is not positioned in any special way; it is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page:
{ 4 / 19 }
HTML elements are positioned static by default. An element with position: static; is not positioned in any special way; it is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page:
{ 4 / 19 }
Moving forward, next we have is
📌 Relative Position
- Relative positioning do not take an element out of document flow
- Relative positioning is relative to element's original position which can be changed using offset
{ 5 / 19 }
📌 Relative Position
- Relative positioning do not take an element out of document flow
- Relative positioning is relative to element's original position which can be changed using offset
{ 5 / 19 }
🔹 Relative position is relative to itself.
For example: Consider the code and output in the attached image below
As you can see red box is shifted 100px from left because I applied left offset after giving it relative positioning
{ 6 / 19 }

For example: Consider the code and output in the attached image below
As you can see red box is shifted 100px from left because I applied left offset after giving it relative positioning
{ 6 / 19 }


In the attached image below, the black dotted area would be the original position of red box if I don't apply position relative in it.
As you can see it proved that relative position is relative to itself
{ 7 / 19 }
As you can see it proved that relative position is relative to itself
{ 7 / 19 }

So now let me shift the blue box 100px towards left. So how can I do that? it's simple
.blue {
position: relative;
right: 100px;
}
Notice here that document flow is as it is. So the relative position does not affect the document flow
{ 8 / 19 }
.blue {
position: relative;
right: 100px;
}
Notice here that document flow is as it is. So the relative position does not affect the document flow
{ 8 / 19 }

📌 Absolute Position
- The element is removed from the normal document flow
- You can consider it as, after applying absolute position the element will no longer in the flow and no space is created for the element in the page layout
{ 9 / 19 }
- The element is removed from the normal document flow
- You can consider it as, after applying absolute position the element will no longer in the flow and no space is created for the element in the page layout
{ 9 / 19 }
For example:
If I apply absolute position in the red box, then the red box will be out of the flow and hence no space will be allocated to it.
See the image below, red box is out of flow and hence yellow box is at top and followed by green and blue
* Yellow box is below red
If I apply absolute position in the red box, then the red box will be out of the flow and hence no space will be allocated to it.
See the image below, red box is out of flow and hence yellow box is at top and followed by green and blue
* Yellow box is below red

- The absolute position of an element is relative to its closest ancestor, which has some position property.
Consider the code below, Red is the parent div and black is the child div. In this particular case, body is the parent of red div
{ 11 / 19 }
Consider the code below, Red is the parent div and black is the child div. In this particular case, body is the parent of red div
{ 11 / 19 }

Now let me apply relative position to red(parent) div and absolute position to black(child) div.
As I mentioned absolute position is relative to closest ancestor having some position property
{ 12 / 19 }


As I mentioned absolute position is relative to closest ancestor having some position property
{ 12 / 19 }



Let's understand it in little more details👇
Consider this piece of code.
Here green div is a parent of red and red div is a parent of black
{ 13 / 19 }


Consider this piece of code.
Here green div is a parent of red and red div is a parent of black
{ 13 / 19 }



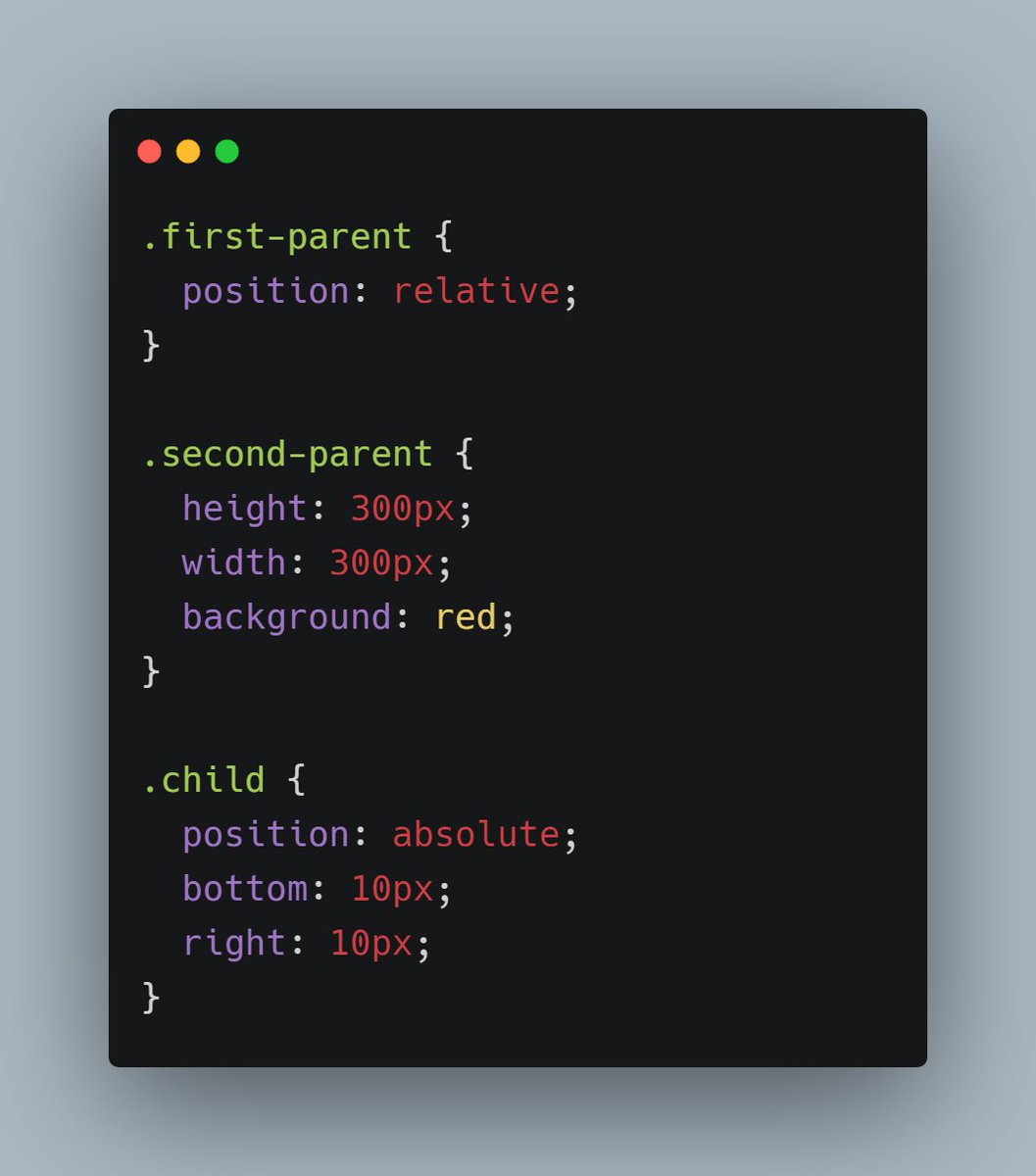
So let me apply position property in green and black. In black div we have absolute position so in that case black div will be relative to green not red
Because here black's closest ancestor is green which has some position property
{ 14 / 19 }

Because here black's closest ancestor is green which has some position property
{ 14 / 19 }

Next we have is position: fixed;
Fixed position elements is always relative to the viewport. Which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled
{ 15 / 19 }
Fixed position elements is always relative to the viewport. Which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled
{ 15 / 19 }
For example, consider this red element. It will always fixed at same place even if the page is scrolled.
Fixed element also break the document flow.
codepen.io/prathamkumar/p…
{ 16 / 19 }
Fixed element also break the document flow.
codepen.io/prathamkumar/p…
{ 16 / 19 }
Great! Moving even further, Next we have is
📌 Position: sticky
Sticky position is the mixture of relative and fixed position. It is positioned relative until a given offset position is met in the viewport - then it "sticks" in place (like position:fixed)
{ 17 / 19 }
📌 Position: sticky
Sticky position is the mixture of relative and fixed position. It is positioned relative until a given offset position is met in the viewport - then it "sticks" in place (like position:fixed)
{ 17 / 19 }
The sticky state does not break the document flow.
Play around with the output here for better understanding
codepen.io/prathamkumar/p…
{ 18 / 19 }
Play around with the output here for better understanding
codepen.io/prathamkumar/p…
{ 18 / 19 }
I think that's pretty much it. Did I forget to add something? Feel free to add below.
Thanks for reading ❤️
Thanks for reading ❤️
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh