
1/ Russia recently began throttling access to Twitter, their first acknowledged use of throttling for censorship.
My lab investigated, and what we found is an alarming consolidation of Russia's Internet controls.
#russia #throttling
Read our full report:throttletwitter.com
My lab investigated, and what we found is an alarming consolidation of Russia's Internet controls.
#russia #throttling
Read our full report:throttletwitter.com
2/ Throttling (slowing a site down) is easy for censors to do but hard for users to attribute or circumvent. Detecting it is tricky—lots of innocent things can make a site slow—and censorship detection platforms aren’t yet well equipped to spot it.
3/ This is the first known case where Russia has used throttling (vs outright blocking) to pressure sites into imposing its desired content restrictions.
vk.com/wall-76229642_…
Events started March 10, and we teamed with in-county activists on a rapid-focus investigation.
vk.com/wall-76229642_…
Events started March 10, and we teamed with in-county activists on a rapid-focus investigation.
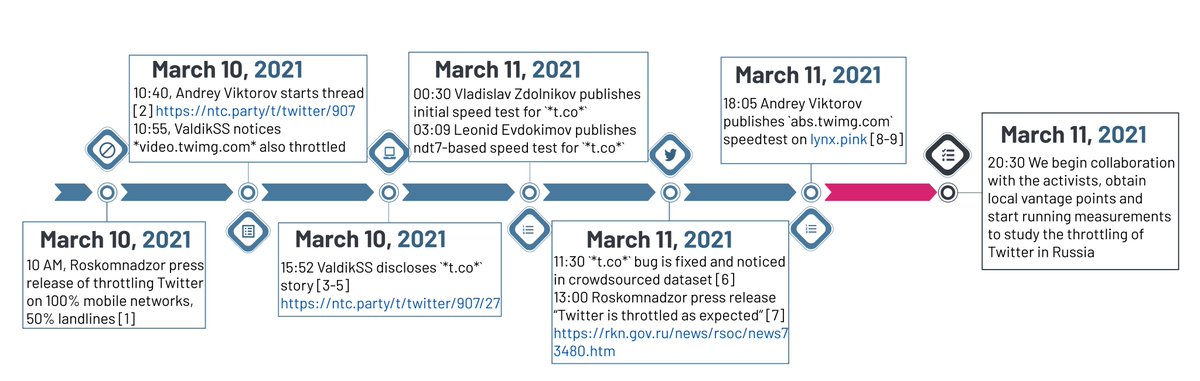
4/ You can tell it's new because it was buggy. At first throttling was triggered by TLS SNI names matching *․twimg․com, *twitter․com, and *t․co*, inadvertently slowing sites like reddi𝘁.𝗰𝗼m and microsof𝘁.𝗰𝗼m. That's fixed now, but Twitter remains throttled.
5/ Russia used to block sites in a decentralized way, with ISP staff carrying out gov't orders. The throttling is different. It's done close to end users but *not* co-located with the blocking devices. The behavior is coordinated across ISPs, indicating it's centrally managed.
6/ We determined that the throttling devices inspect the first packet from both downstream and upstream, and in certain cases the inspection can be extended to packets sent later in a flow as well.
7/ Technically, there are several ways to circumvent the throttling: e.g., prepending random packets, fragmentation (GoodbyeDPI or Zapret), TLS packet stuffing, or tunneling via an encrypted proxy.
But for now, only power-users are likely aware and capable enough to do these.
But for now, only power-users are likely aware and capable enough to do these.
8/ This incident should be a wake-up call. Twitter won't be the last site that Russia (and other gov'ts) attempt to throttle. Browsers and sites should implement TLS Encrypted Client Hello (ECH) to make it more difficult for censors to block or throttle based on the SNI header.
9/ Finally, we hope Twitter will be transparent about its back-and-forth with the Russian censors. The public deserves to know about their government's demands, and the technical community needs to band together in response to this new threat to Internet freedom.
10/ This report was done in collaboration with: Diwen Xue, @reethika_, @ValdikSS, @mathemonkey, @libneko, Arham Jain, @ewust, @bassosimone.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


