#THREAD
53 years ago today, May 3rd 1968, following conflict between students & University of Paris authorities, students protested the closure of the Sorbonne, setting off a wave of civil unrest by MILLIONS of students & workers.
"Be realistic, demand the impossible".
#May68
53 years ago today, May 3rd 1968, following conflict between students & University of Paris authorities, students protested the closure of the Sorbonne, setting off a wave of civil unrest by MILLIONS of students & workers.
"Be realistic, demand the impossible".
#May68

In the late 60s, French youth assumed they were living under a quasi-benign dictatorship.
The main opposition parties, Radicals & Socialists, had essentially collapsed, which meant that progressive political change via conventional parliamentary channels was all but ruled out.



The main opposition parties, Radicals & Socialists, had essentially collapsed, which meant that progressive political change via conventional parliamentary channels was all but ruled out.




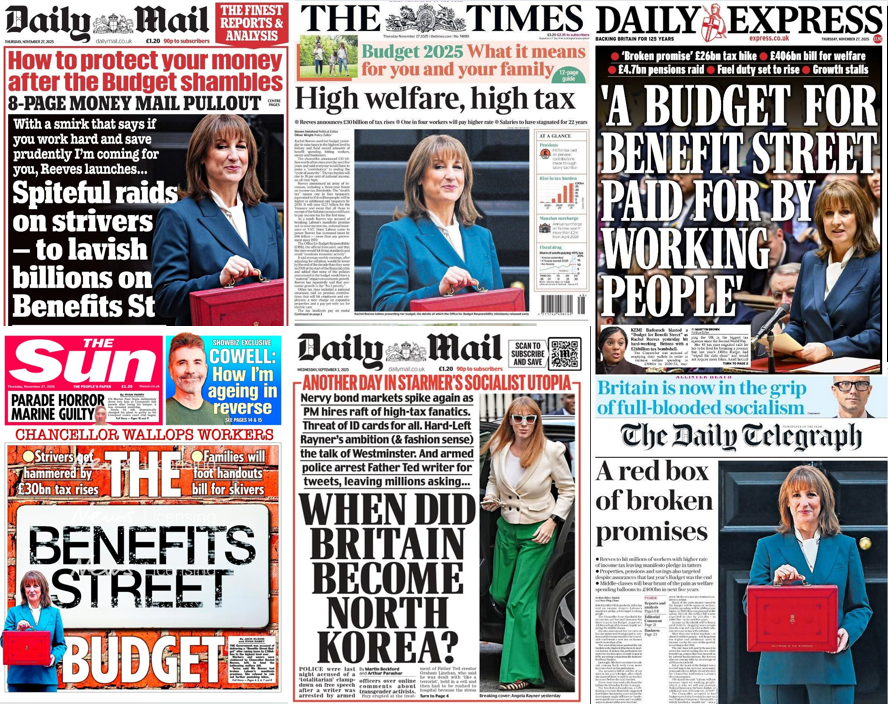
In 1967, students at the University of Paris had staged protests against restrictions on dormitory visits that prevented male & female students from sleeping with each other. In January 1968, student leader Daniel Cohn-Bendit verbally attacked France’s Minister of Youth & Sports. 

Cohn-Bendit complained the Minister had failed to address the students’ sexual frustrations. The Minister suggested he cool off his ardour by jumping into the pool, whereupon Cohn-Bendit replied that the Ministers remark was just what one would expect from a fascist regime. 

The exchange earned Cohn-Bendit a reputation as an antiauthoritarian provocateur, and he soon acquired an almost cultlike following among French youth.
In March an attack on the American Express office in central Paris resulted in the arrest of several students.
In March an attack on the American Express office in central Paris resulted in the arrest of several students.

At a protest a few days later in support of the students, more students were arrested, including Cohn-Bendit himself, who, it was rumoured, was threatened with deportation.
The March 22 Movement, which lobbied for the arrested students’ release, emerged in response.
The March 22 Movement, which lobbied for the arrested students’ release, emerged in response.

Fearing an escalation of the protests, the dean of Nanterre shut down the campus, & since the students were barred from protesting at Nanterre, they decided to take their grievances to the Sorbonne, in the heart of Paris’s Latin Quarter. 

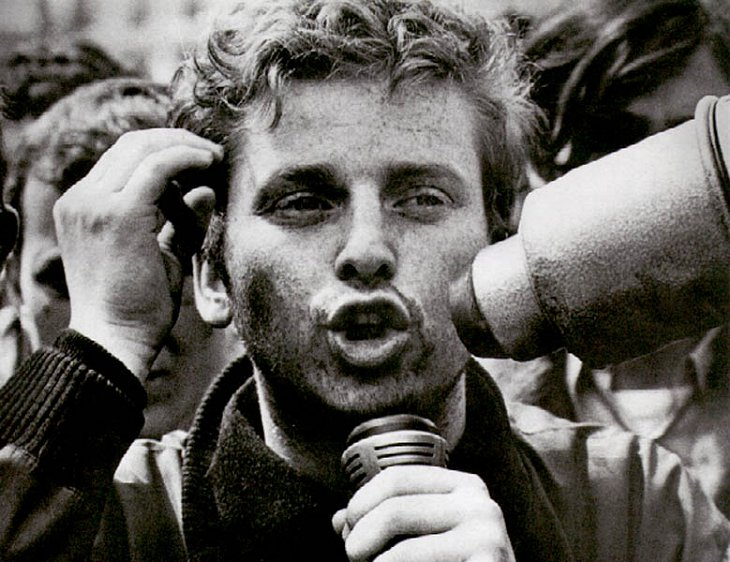
On May 3, the police clear the university’s courtyard, where 300 students had assembled. The mass arrests that followed, with help from the national riot police, sparked violent resistance from bystanders, who began pelting the police with cobblestones & erecting barricades. 



The police responded with tear gas, clubbings, & more arrests. The University was closed & student leaders proposed a rally for May 10 to demand its reopening, the release of students who were still being held by the police, & an end to the intimidating police presence on campus. 

On May 10th, 40,000 student protesters gathered. Police blocked the marchers’ path, so some students began removing cobblestones & erecting barricades for protection.
At around 2 a.m. May 11, the police attacked, firing tear gas & beating students & bystanders with truncheons.



At around 2 a.m. May 11, the police attacked, firing tear gas & beating students & bystanders with truncheons.
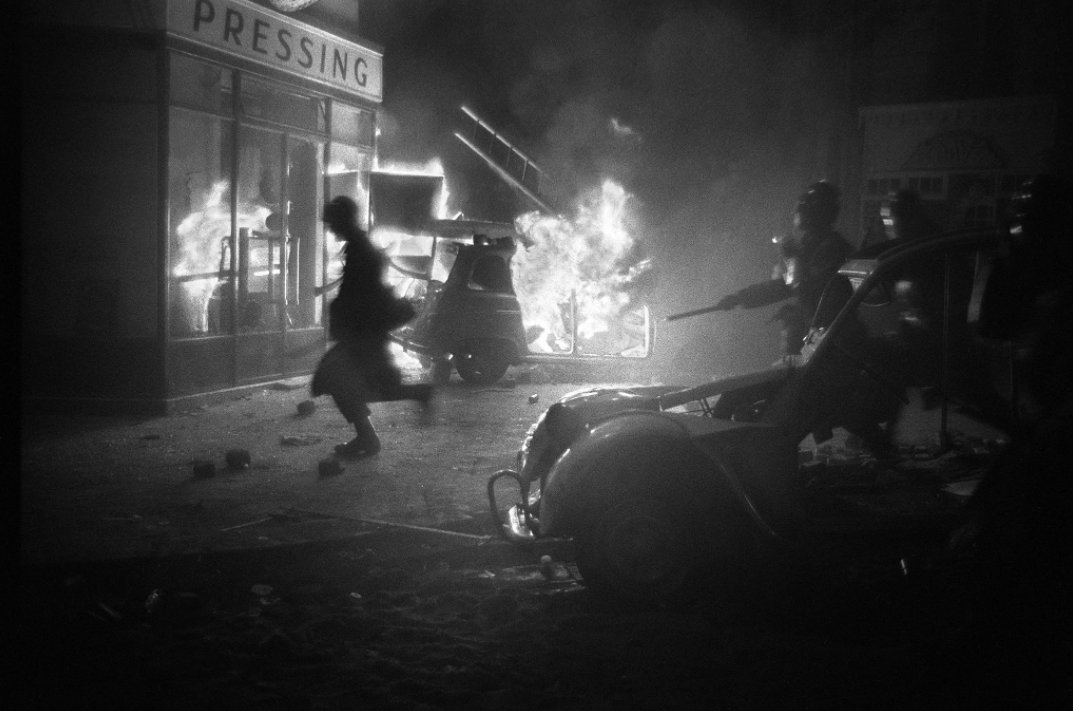




The confrontation continued until dawn. By the time the dust had cleared, nearly 500 students had been arrested & hundreds hospitalized, including more than 250 police officers. The Latin Quarter lay in ruins, & public sympathy for the students, already considerable, increased. 





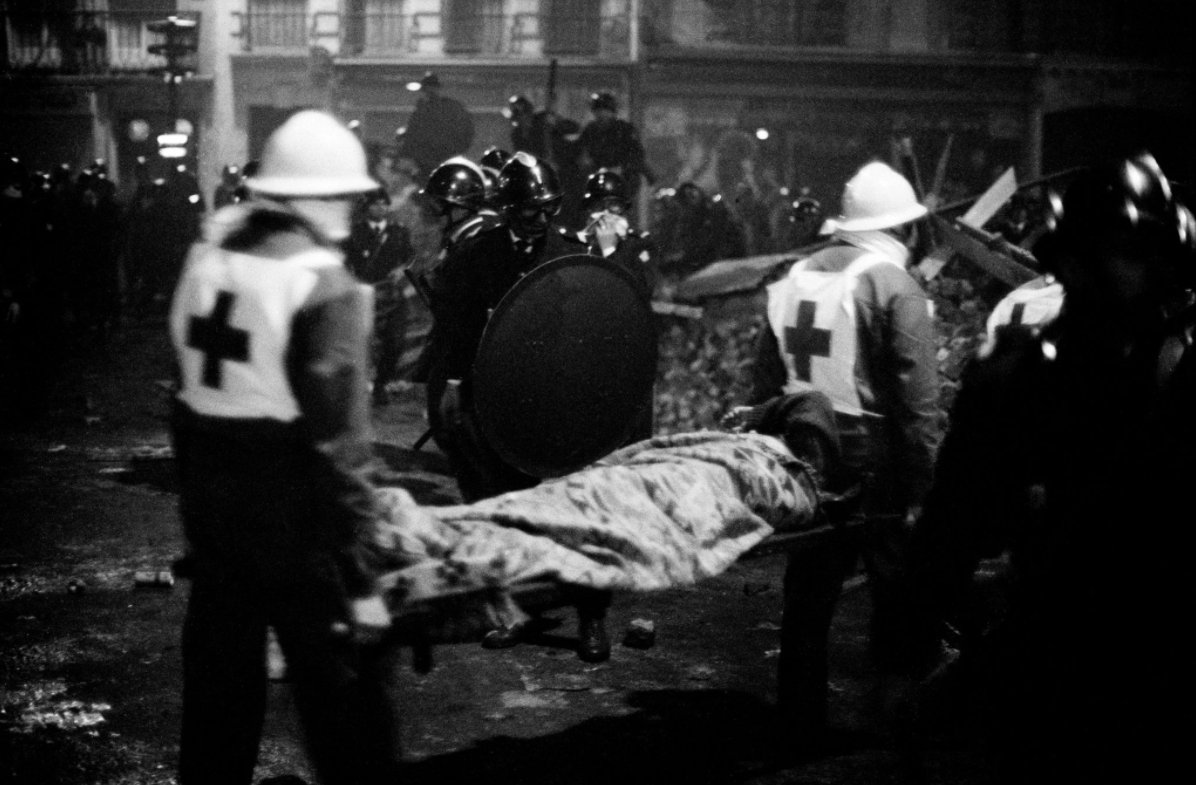

The protest movement came to engulf the whole of France, opening up new possibilities for radical change: the dismantling of authoritarian political structures; the democratization of social & cultural institutions ranging from education to the news media & beyond. 

The next several days witnessed the largest wildcat general strike in French history: MILLIONS of workers poured into the streets in support of the students as well as to set forth their own demands. Scores of factories - including those of Renault - were seized by workers. 



The French state was badly shaken, yet it weathered the crisis. Charles de Gaulle delivered a dramatic May 30 radio address in which he raised the spectre of a communist takeover, but the French Communist Party had long ago abandoned the dream of a revolutionary seizure of power. 

The strikes continued but de Gaulle also announced an election for June 23, assuming that the French people were ready for a return to stability.
He also implicitly threatened to use the army to impose order if the forces of “intimidation” & “tyranny” did not back down.
He also implicitly threatened to use the army to impose order if the forces of “intimidation” & “tyranny” did not back down.

Hundreds of thousands of people throughout the country marched in counterdemonstrations in support of de Gaulle.
Although strikes & student demonstrations continued into June, the student movement gradually lost momentum, & de Gaulle’s party won a resounding victory.
Although strikes & student demonstrations continued into June, the student movement gradually lost momentum, & de Gaulle’s party won a resounding victory.

French society did undergo profound changes in the aftermath, but were more measured & incremental than many wanted.
The May revolt initiated a transformation of “everyday life”, a phrase crucial to understanding the cultural-political implications of #May68, in France & beyond.
The May revolt initiated a transformation of “everyday life”, a phrase crucial to understanding the cultural-political implications of #May68, in France & beyond.

The critique of everyday life encouraged activists to focus attention on a variety of qualitative issues & concerns that transcended the narrowly economic orientation of orthodox Marxism: the “sixty-eighters” sought to unmask new forms of ideological coercion & social control. 
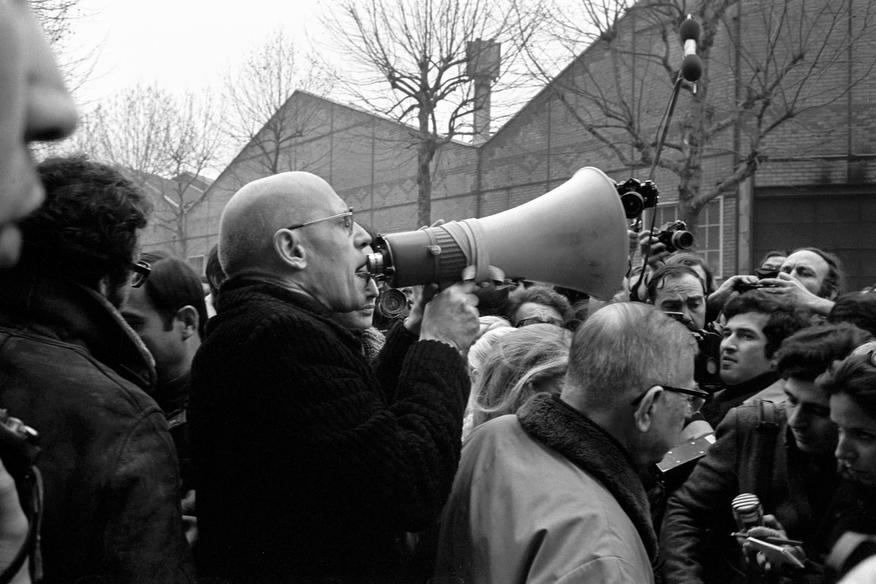

They realized that with the advent of consumer society, the scope of commodification had transcended the workplace & encompassed almost every aspect of social life, opening up critique of new areas of social emancipation, including feminism, environmentalism, racism & gay rights. 



50 years later & we STILL need to confront the underlying problems: political authoritarianism & corruption; media control; structural & institutional disadvantage; consumerism; insecure work; nationalism & levels of wealth inequality not seen since the 1930s; & climate change. 

#May68 has its critics, who see it as a childish chaotic outburst, achieving little & substituting economic justice for 'identity politics'. Others see it as the Left at its best: critiquing an authoritarian elite while fighting for both economic equality AND social emancipation. 



One of the most significant problems the Left must confront is ubiquitous corporate #propaganda.
The Left is mistaken in thinking that simply 'speaking truth to power', or countering propaganda with truth, is an effective strategy. On it's own, it isn't:
The Left is mistaken in thinking that simply 'speaking truth to power', or countering propaganda with truth, is an effective strategy. On it's own, it isn't:
https://twitter.com/docrussjackson/status/1376451860622630912
A #THREAD about how forty years of uninterrupted neoliberal ideology has facilitated an elite who have hoarded at least $30 TRILLION offshore, & who fund political parties & free-market #propaganda which legitimate environmental & human exploitation:
https://twitter.com/docrussjackson/status/1359445197113950208
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh