💥Tweetorial on C3 Glomerulopathy (C3G)
⚡️what is C3 Glomerulopathy?
⚡️how to establish the diagnosis?
⚡️what is the role of Complements?
⚡️what is C3 Glomerulopathy?
⚡️how to establish the diagnosis?
⚡️what is the role of Complements?
💥C3 Glomerulopathy (C3G) represents rare kidney diseases affecting both children & adults
⚡️It encompasses 2 distinct conditions:
1- DDD (dense deposition disease)
2- C3GN (C3 Glomerulonephritis)
⚡️It encompasses 2 distinct conditions:
1- DDD (dense deposition disease)
2- C3GN (C3 Glomerulonephritis)
💥C3G is...
⚡️driven by dysregulation of alternate complement pathway
⚡️mediated by genetic mutations or acquired defects of complement cascade
⚡️characterized by deposition of (sole or dominant) C3 in kidney tissue
⚡️presented with clinical features of glomerulonephritis
⚡️driven by dysregulation of alternate complement pathway
⚡️mediated by genetic mutations or acquired defects of complement cascade
⚡️characterized by deposition of (sole or dominant) C3 in kidney tissue
⚡️presented with clinical features of glomerulonephritis
💥C3G is not a newly recognized entity
⚡️DDD was known as MPGN type 2
⚡️C3GN was classified as atypical MPGN type I & type 3
*Improved understanding of role of complements in pathogenesis has led to its reclassification into a distinct group -->C3 Glomerulopathies
⚡️DDD was known as MPGN type 2
⚡️C3GN was classified as atypical MPGN type I & type 3
*Improved understanding of role of complements in pathogenesis has led to its reclassification into a distinct group -->C3 Glomerulopathies

💥Natural history isn't well known due to its rarity &changes in nomenclature
⚡️most important clinical outcome-->progression to ESRD
⚡️occurs within 10yrs in 70% of children & 30-50% of affected adults
⚡️rapid recurrence in transplant with allograft loss in 50% of pts in 10 yrs
⚡️most important clinical outcome-->progression to ESRD
⚡️occurs within 10yrs in 70% of children & 30-50% of affected adults
⚡️rapid recurrence in transplant with allograft loss in 50% of pts in 10 yrs
💥Pathogenesis:
⚡️Alternate pathway is normally autoactive at low level but kept in check by regulatory proteins
⚡️abnormal amplification occurs due to its genetic deficiency or autoantibodies
⚡️unchecked complement activity then incites glomerular injury and scarring
⚡️Alternate pathway is normally autoactive at low level but kept in check by regulatory proteins
⚡️abnormal amplification occurs due to its genetic deficiency or autoantibodies
⚡️unchecked complement activity then incites glomerular injury and scarring
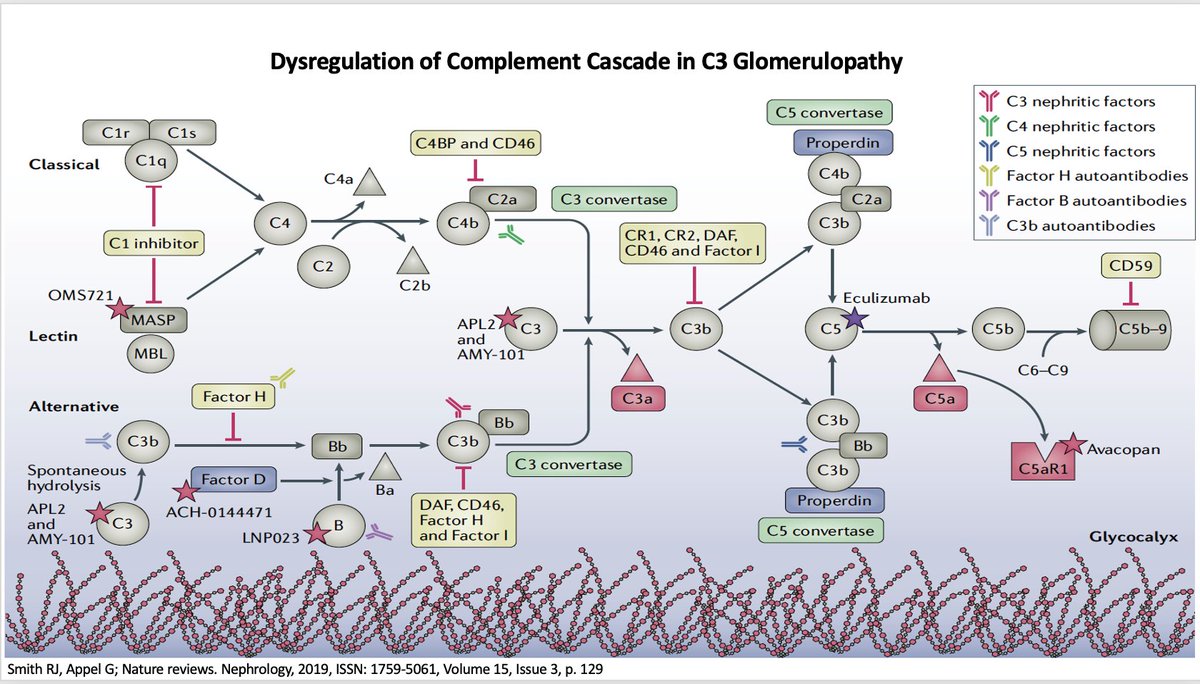
🌟Which of the following proteins is NOT the inhibitor of complement pathways?
💥Over-activation of Alternate Complement Cascade
⚡️Deficiency (or inactivation) of regulators leads to continued complement activation
⚡️Acquired factors stabilize C3/C5 convertases and prevent its decay leading to its uninhibited amplification
⚡️Deficiency (or inactivation) of regulators leads to continued complement activation
⚡️Acquired factors stabilize C3/C5 convertases and prevent its decay leading to its uninhibited amplification

💥Animal models provide important insights into pathogenesis
⚡️deletion of FactorH in mice (cfh-/-) --> C3G
⚡️deletion of Properdin in Cfh- mice--> (Cfh-, Cfp-) favors C3 convertase over C5--> DDD
⚡️deletion of FactorB in the mice (Cfh-, Cfb-)-->no C3 convertase -->prevents C3G
⚡️deletion of FactorH in mice (cfh-/-) --> C3G
⚡️deletion of Properdin in Cfh- mice--> (Cfh-, Cfp-) favors C3 convertase over C5--> DDD
⚡️deletion of FactorB in the mice (Cfh-, Cfb-)-->no C3 convertase -->prevents C3G
💥Clinical Presentation
⚡️wide variation: from isolated proteinuria, hematuria, to acute GN, AKI, nephrotic syndrome
⚡️all age groups are affected; mean age for DDD lower than C3GN
⚡️often preceded by upper resp infections
⚡️wide variation: from isolated proteinuria, hematuria, to acute GN, AKI, nephrotic syndrome
⚡️all age groups are affected; mean age for DDD lower than C3GN
⚡️often preceded by upper resp infections
💥About 25% of C3G-->from Genetic variants & deficiencies:
⚡️Convertase genes: C3 & CFB (Factor B)
⚡️Regulatory proteins genes: CFH (Factor H) & CFI (factor I)
⚡️Complement H related genes (CFHR5)
⚡️most common genomic rearrangement in CFH is usually in CFHR locus
⚡️Convertase genes: C3 & CFB (Factor B)
⚡️Regulatory proteins genes: CFH (Factor H) & CFI (factor I)
⚡️Complement H related genes (CFHR5)
⚡️most common genomic rearrangement in CFH is usually in CFHR locus
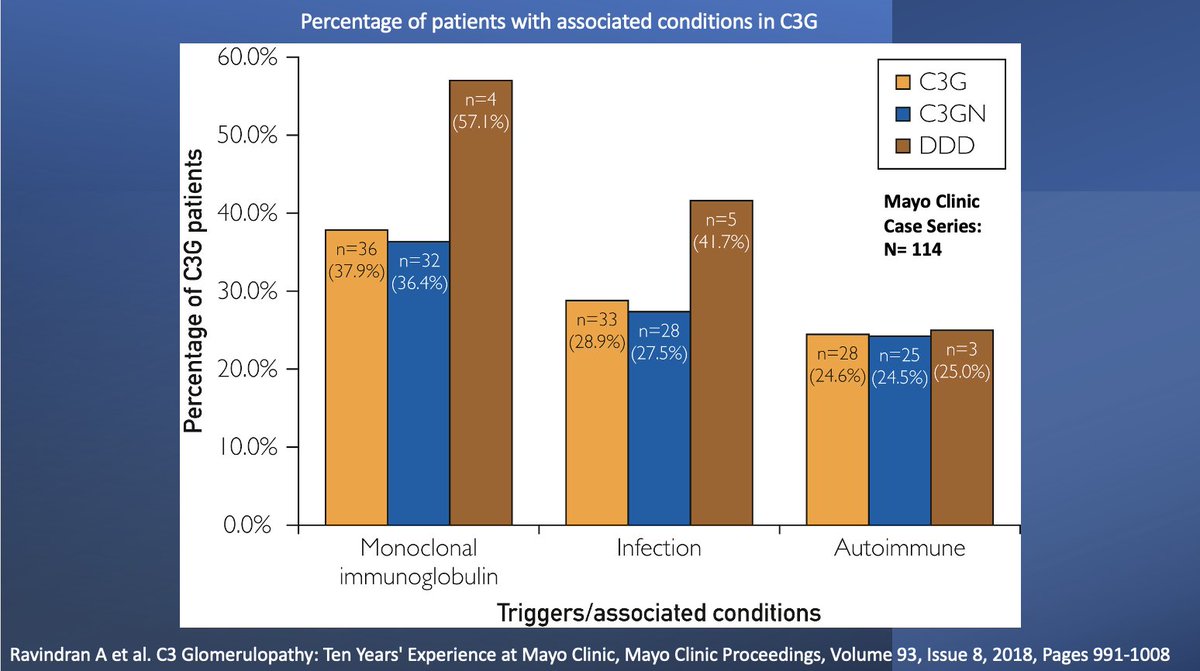
💥About 75% of C3G -->from Acquired factors
⚡️Autoantibodies to variety of complement proteins leads to dysregulation of cascade
⚡️C3 Nephritic factor: present in up to 80% of DDD & 50% of C3GN
⚡️C5 and C4 Nephritic factors
⚡️less common are autoantibodies to Factor H & B
⚡️Autoantibodies to variety of complement proteins leads to dysregulation of cascade
⚡️C3 Nephritic factor: present in up to 80% of DDD & 50% of C3GN
⚡️C5 and C4 Nephritic factors
⚡️less common are autoantibodies to Factor H & B
💥Evaluation:
-diagnosis is by kidney biopsy
-C3 is low in most but not all C3G
-routine work up of glomerulonephritis
-rule out infections, autoimmune diseases, monoclonal gammopathy, cryos
-needs comprehensive complement evaluation & genetics studies (specialized laboratories)
-diagnosis is by kidney biopsy
-C3 is low in most but not all C3G
-routine work up of glomerulonephritis
-rule out infections, autoimmune diseases, monoclonal gammopathy, cryos
-needs comprehensive complement evaluation & genetics studies (specialized laboratories)
💥Complement Evaluation
-overall complement activity (CH50, AH50)
-antigenic assays of complement proteins/split products
-autoantibodies: C3/C5 nephritic factors
💥Genetic Testing
-screening for C3, CFB, CFI, CFH, CFHR5
-copy number variation; rearrangement of CFH-CFHR cluster
-overall complement activity (CH50, AH50)
-antigenic assays of complement proteins/split products
-autoantibodies: C3/C5 nephritic factors
💥Genetic Testing
-screening for C3, CFB, CFI, CFH, CFHR5
-copy number variation; rearrangement of CFH-CFHR cluster
💥C3G is a histological diagnosis
-defined by presence of sole (or dominant) IF staining of C3 (at least two orders of magnitude more than other immune deposit)
-LM findings are diverse: from no hypercellularity to mesangial/membranous proliferative, exudative, or crescentic
-defined by presence of sole (or dominant) IF staining of C3 (at least two orders of magnitude more than other immune deposit)
-LM findings are diverse: from no hypercellularity to mesangial/membranous proliferative, exudative, or crescentic
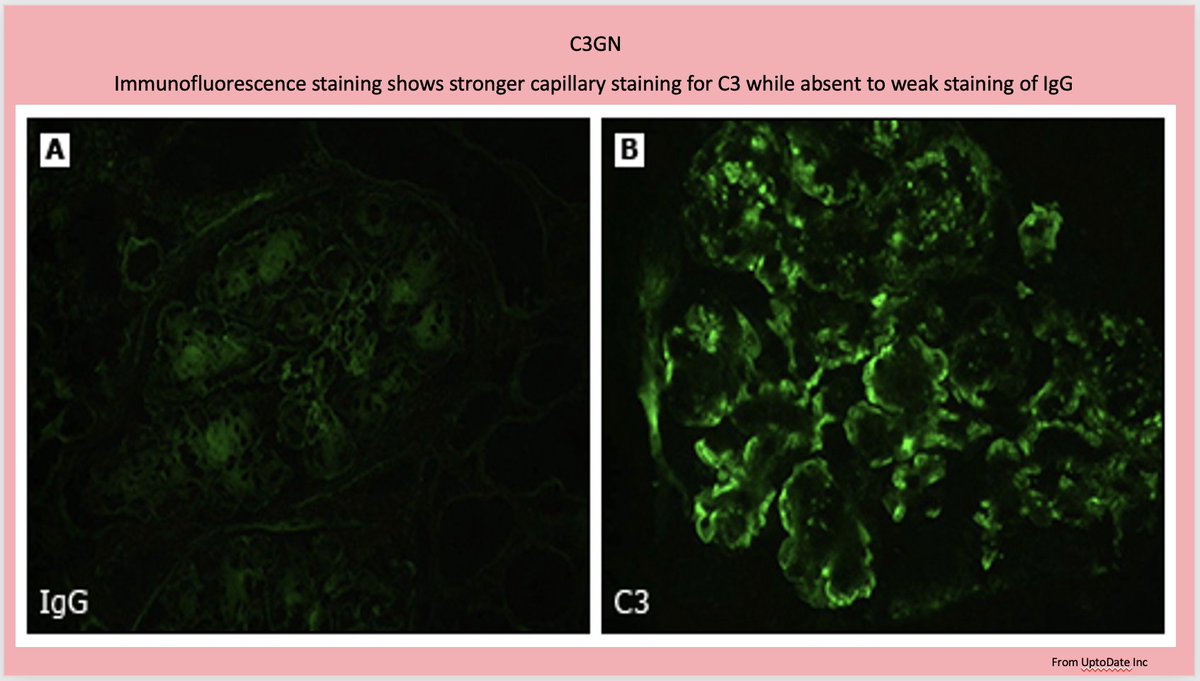
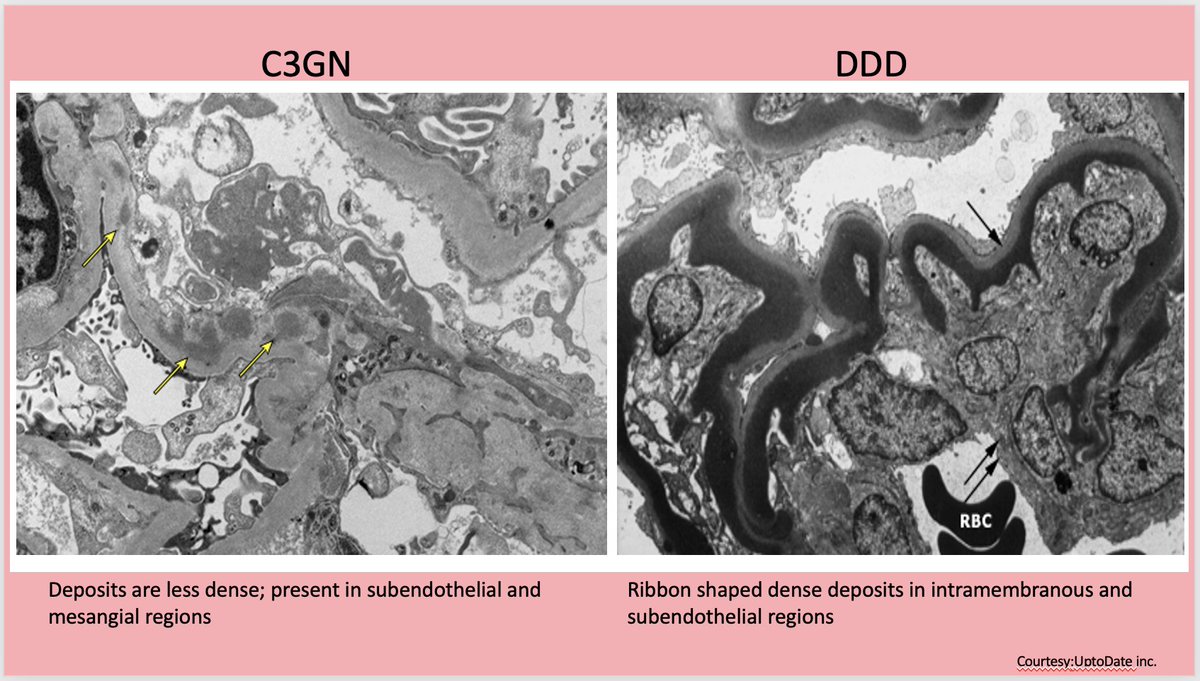
💥EM is necessary to differentiate between DDD & C3GN
⚡️DDD --> highly dense “sausage shaped” osmiophilic deposits in GBM
⚡️C3GN -->amorphous, cloudy deposits of much less density; within mesangial & sub-endothelial region
⚡️Sub-epithelial humps may also be present @renalpathdoc
⚡️DDD --> highly dense “sausage shaped” osmiophilic deposits in GBM
⚡️C3GN -->amorphous, cloudy deposits of much less density; within mesangial & sub-endothelial region
⚡️Sub-epithelial humps may also be present @renalpathdoc
⚡️Always rule out monoclonal gammopathy; especially, pts > 50 yrs age
⚡️Pronase to look for masked immunoglobulins in biopsy
⚡️Monoclonal protein interacts with complements similar to autoantibodies lead to its dysregulation and --> C3GN
⚡️Treat underlying monoclonal gammopathy
⚡️Pronase to look for masked immunoglobulins in biopsy
⚡️Monoclonal protein interacts with complements similar to autoantibodies lead to its dysregulation and --> C3GN
⚡️Treat underlying monoclonal gammopathy
💥Treatment(based on expert opinions)
⚡️Proteinuria <1.5 g/preserved renal fx
BP control/RAASi/statin
⚡️Proteinuria >1.5 g/worsening creat
MMF/pred; if no response, eculizumab
⚡️For RPGN: pulse steroids/Cytoxan or PLEX
⚡️Defect in Factor H: plasma infusion to replace deficiency
⚡️Proteinuria <1.5 g/preserved renal fx
BP control/RAASi/statin
⚡️Proteinuria >1.5 g/worsening creat
MMF/pred; if no response, eculizumab
⚡️For RPGN: pulse steroids/Cytoxan or PLEX
⚡️Defect in Factor H: plasma infusion to replace deficiency

⚡️Many drugs that interact with complements are either being investigated or under clinical trials for its use in various conditions
⚡️Further research focused on role of complement system in C3G has the potential to benefit other areas of kidney diseases and medicine in general
⚡️Further research focused on role of complement system in C3G has the potential to benefit other areas of kidney diseases and medicine in general
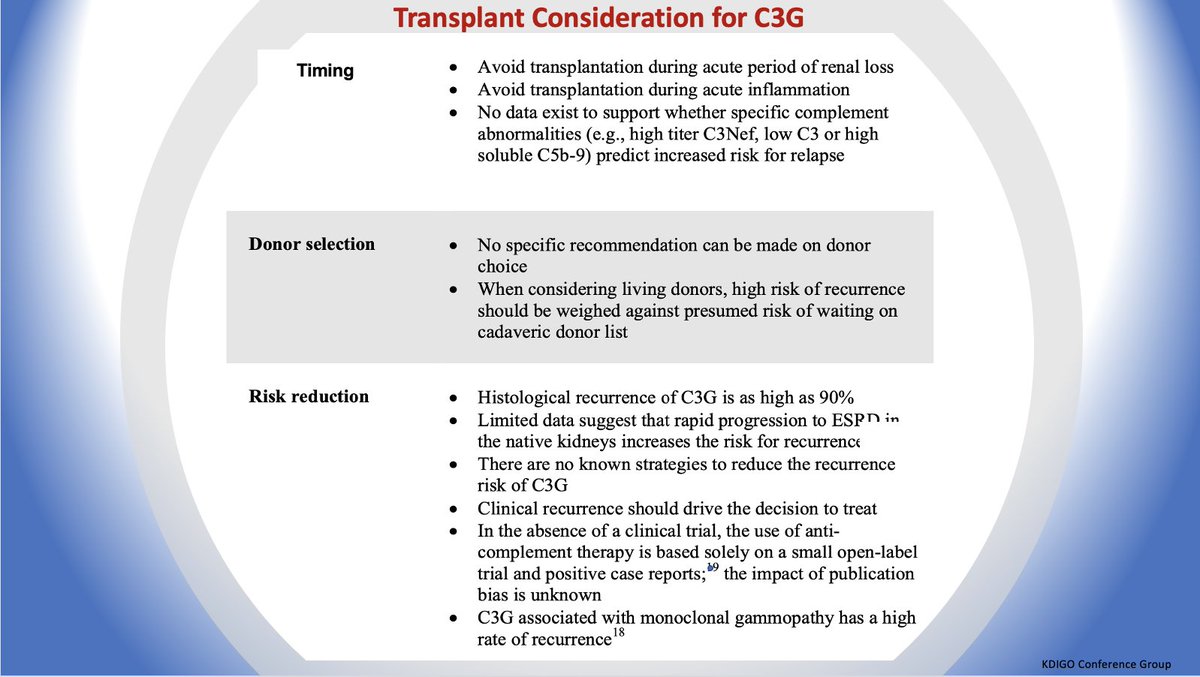
💥Transplant Considerations:
⚡️recurrence as high as 90% in transplant
⚡️no known strategies to reduce the recurrence
⚡️avoid transplant during active inflammation
⚡️rapid recurrence & allograft loss in 50% pts in 10 years
⚡️recurrence as high as 90% in transplant
⚡️no known strategies to reduce the recurrence
⚡️avoid transplant during active inflammation
⚡️rapid recurrence & allograft loss in 50% pts in 10 years
Thank you @NSMCInternship and its terrific 'bean pod' @brian_rifkin @nephromythri @lama_ghazi @hellokidneyMD @SaiAchi1 @dr_missyhanna @RenalFellowNtwk @AJKDonline @Nephro_Sparks @amyaimei @SwastiThinks #Nephtwitter #FOAMed
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh