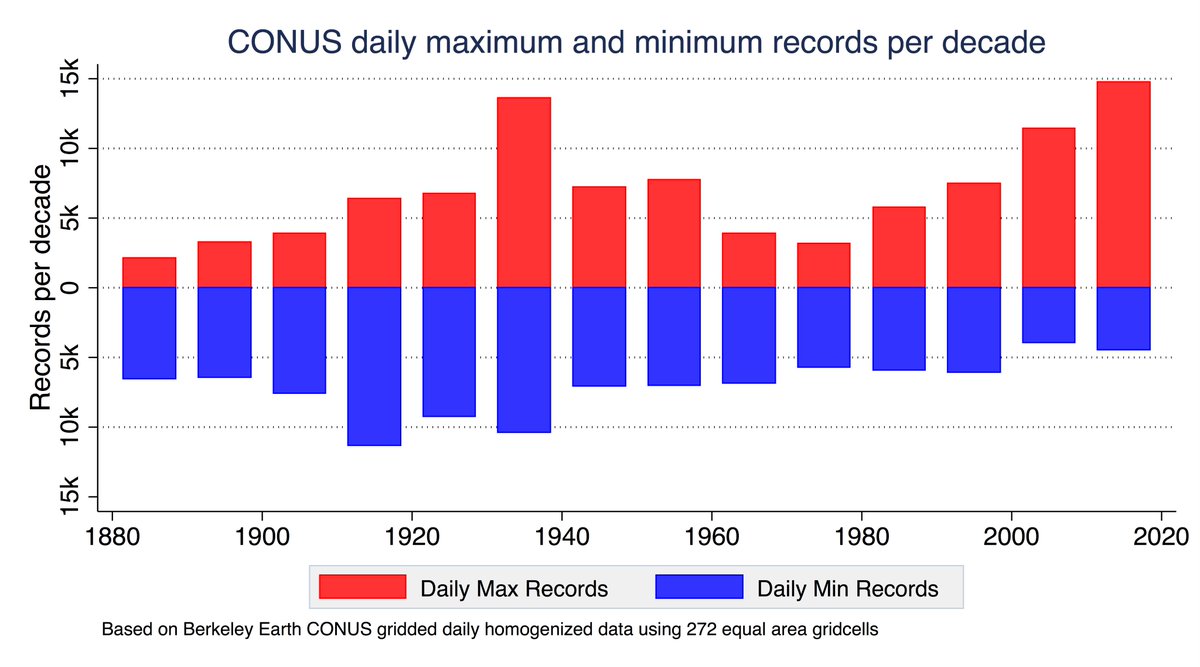
The last 12 months have been the driest period in the Western US since records began in 1895.
In a typical year the the western US gets around 17 inches of rain on average. Over the last 12 months we have only gotten 8.7 inches.
In a typical year the the western US gets around 17 inches of rain on average. Over the last 12 months we have only gotten 8.7 inches.

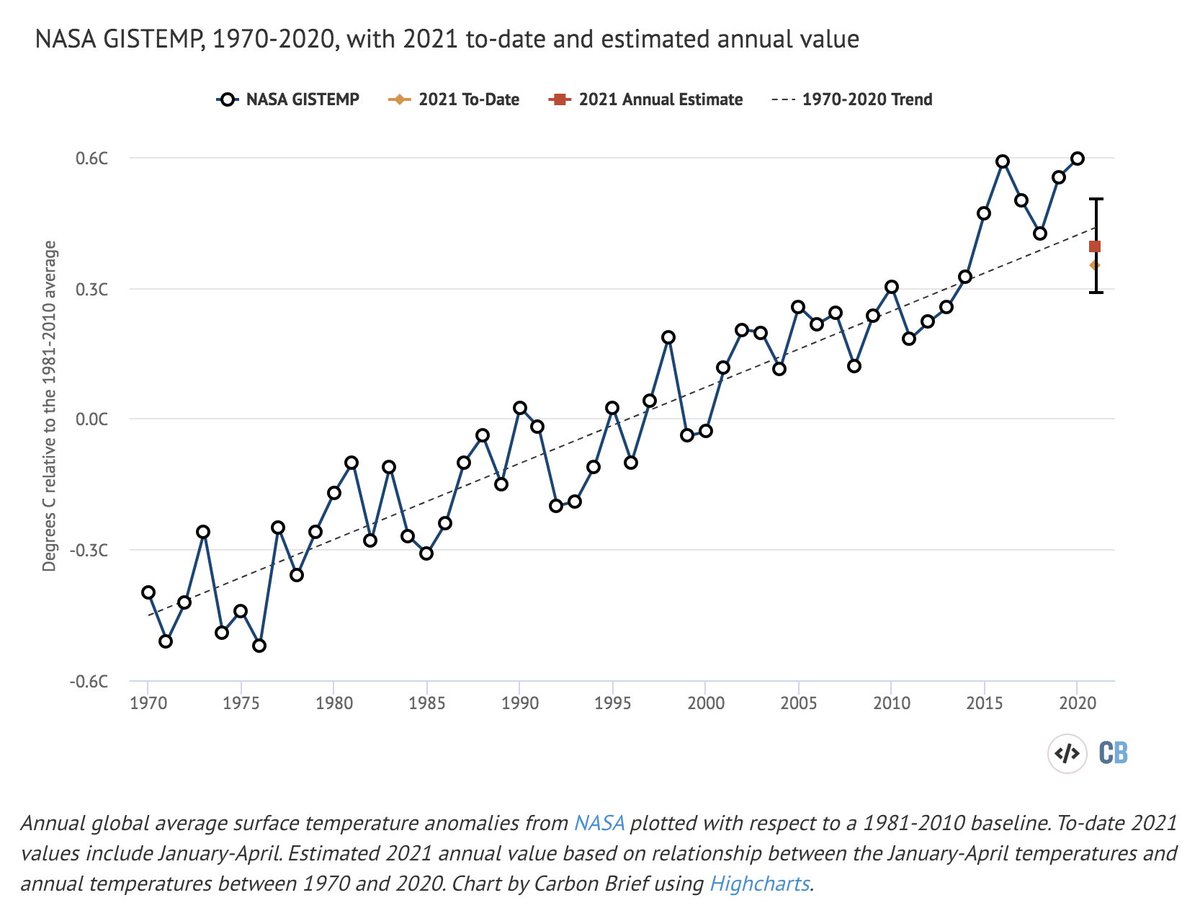
During the same period, the region has warmed nearly 2C, with nearly all of that warming occurring in the years since 1970. Warmer temperatures dry out soils and vegetation, and helps drive the catastrophic wildfires we have experienced in the past few years. 

While there is a clear link between climate change and heavier (if at times less frequent) rainfall, the links between average precipitation and climate are more complex. For details, see my @CarbonBrief explainer: carbonbrief.org/explainer-what… 

Also note that the initial graph is for NOAA's "West" climate region, which includes CA and NV. The picture is largely the same when including the Southwest (UT, CO, AZ, NM). If you look at everything west of the Rockies, the last 12 months were the second driest after 1977: 



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh