
With much talk about wearables & devices picking up unappreciated atrial fibrillation, I was intrigued by this randomized trial of effect of an implantable loop recorder to detect afib on outcomes. These slides are from #ESCCongress presentation. Kudos Jesper Svendsen and team. 

The team identified participants with a high risk of stroke and randomized them to an implantable loop recorder (Reveal LINQ by Medtronic), with a primary outcome of stroke or systemic embolism. Question: would better detection of afib improve outcomes? 

They randomized 1:3 - so most people were in the control group. 1501 randomized to the implantable recorder (and 1420 received it, that will be important later) and 4503 in the control group (and none crossed over and received the recorder). They followed them for median 65 mos. 

The randomization worked quite well (see below). And the group was high risk, with a mean age of 75; 18% with prior stroke; >90% with htn; 28% with diabetes. Mean SBP ~150. 
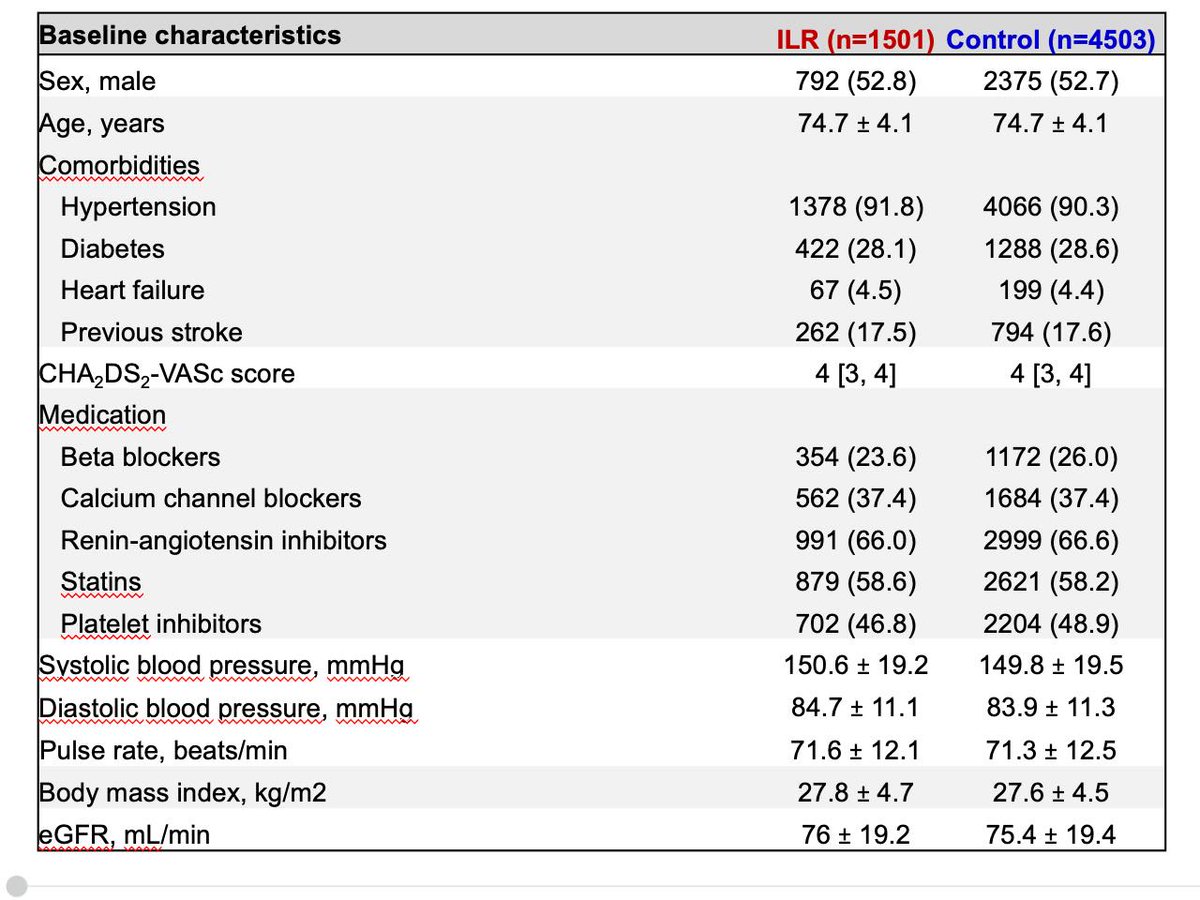
As expected, if you look for afib 24/7 you will find it more often than in a group that is getting usual care. About a third of the group w/the recorder registered afib; compared w/12% of the usual care group. HR 3.17; 95% CI 2.8-3.6. I expected more; but 3x more is notable. 
And then, as expected, if you find more afib, then more people will receive anticoagulation; that is the thesis, more diagnosis, more treatment = better outcome. That is what is being tested. Here… ~30% of the recorder group received anticoagulation; 13% of the usual care group. 

So loop recorder finds more afib; more people get anticoagulated… then what happened? No sig improvement in stroke or embolism. 4.5% v 5.6% in the control group. Close to significance with a p value of 0.11. But should trials be thumbs up or down…or more nuanced interpretation. 

The secondary outcome: Combined Outcome: Ischemic stroke, systemic arterial embolism, or transient ischemic attack (TIA) … was even closer… 6.4% v 7.0% in the control group. P=0.47. More afib diagnosis and anticoagulation prophylaxis didn’t help much with this combined outcome. 

Anther secondary outcome was Combined outcome: Stroke, systemic arterial embolism, or cardiovascular (CV) death … here a little more advantage… 6.9% v 8.3% in control… but p=0.10… and it is a secondary outcome. Where is the benefit? Not looking great. 

And then another secondary outcome was all-cause death. Could more afib diagnosis and anticoagulation prophylaxis defer death? Here is there just about nothing to see. 11.2% v 11.3% in control group. P=1.00. Yikes, not even a hint of mortality benefit. 

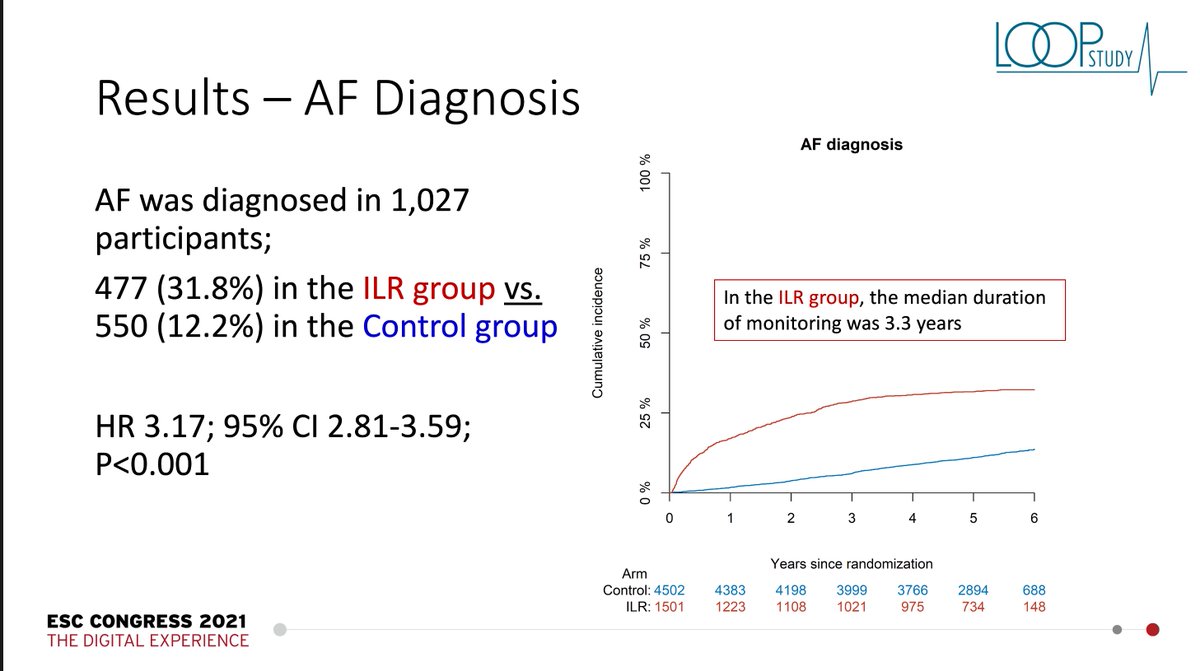
So what about adverse events. What happened with bleeding? As expected, if you give more anticoagulation, you get more bleeding. But the difference was small and, actually, not significant. 4.3% v 3.5% in the controls. But it is in the expected direction. 
So was there anything advocates of extreme monitoring (I am actually one of those) can take away? Subgroup analysis indicated that those with the highest BP had more benefit and the interaction across BP was significant. But still this has to be considered an exploratory finding. 

But here is a kicker… prespecified analysis of people who received the intervention for >=3 years had a sig benefit with the recorder, with benefit appearing after year 2. 3.9% v 5.6%. P=0.02. OK, hard to know what to do with that. Make the finding a bit more ambiguous. 

I respect authors for their circumspect conclusions… report that the recorder had no sig reduction in stroke/embolism. The question is still open though, and in need of more RCTs. Who benefits? Who should be anticoagulated? Should burden of afib matter? Other factors? 

And then, why implantable? How would wearables have compared? And then this is also a cautionary tale for the assumption that picking up afib with any device will inevitably improve outcomes. Esp in the low risk groups that most commonly are the ones with wearables.
And this important study indicates the need we have to test the impact of much of the new information we have in medicine… the ability to monitor is telling us much. We need evidence and wisdom to determine what we should do with it. Assumptions are not enough.
And the assumption here… high-risk population most likely to benefit… more screening would lead to more treatment and a definitive benefit… was just not borne out. So burden of proof is on those who want to believe in more monitoring leads to better outcomes.
Meanwhile, what is going to happen to sales of these devices… will they keep going in for screening?
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh












