
Clinical Trial Process | A Thread🧵
Like and Retweet for better reach! 💊🩺💉
We have discussed the drug discovery process in a previous 🧵. In this 🧵 we will attempt to shed some light on the clinical trials process to enhance our understanding of the drug discovery process
Like and Retweet for better reach! 💊🩺💉
We have discussed the drug discovery process in a previous 🧵. In this 🧵 we will attempt to shed some light on the clinical trials process to enhance our understanding of the drug discovery process
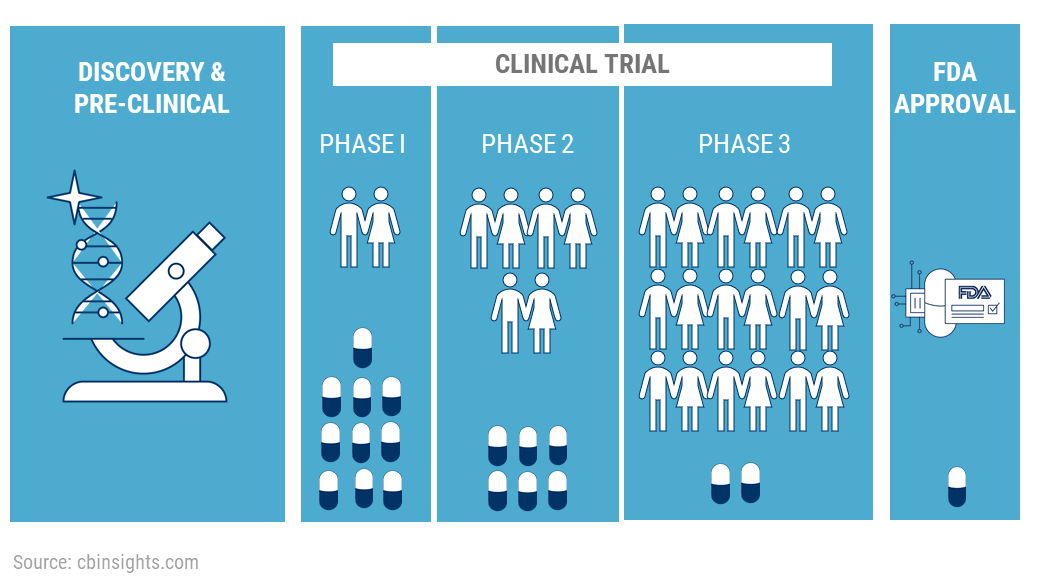
Topics Covered :
1. What are clinical trials
2. Why are they conducted
3. Phase 0 Trials
4. Phase 1 Trials
5. Types of studies in Phase 1
6. Phase 2 Trials
7. Phase 3 Trials
8. Filing of NDA
9. Phase 4 Trials
10. Success rates
1. What are clinical trials
2. Why are they conducted
3. Phase 0 Trials
4. Phase 1 Trials
5. Types of studies in Phase 1
6. Phase 2 Trials
7. Phase 3 Trials
8. Filing of NDA
9. Phase 4 Trials
10. Success rates
1. What are clinical trials ?
A type of research study that tests how well new medical approaches work in people. These studies test new methods of screening, prevention, diagnosis, or treatment of a disease. Before doing a clinical trial, investigators conduct preclinical
A type of research study that tests how well new medical approaches work in people. These studies test new methods of screening, prevention, diagnosis, or treatment of a disease. Before doing a clinical trial, investigators conduct preclinical
research using human cell cultures or animal models. For example, they might test whether a new medication is toxic to a small sample of human cells in a laboratory.
2. Why are they conducted ?
Clinical trials are conducted to evaluate if a drug is safe for consumption by
2. Why are they conducted ?
Clinical trials are conducted to evaluate if a drug is safe for consumption by
human beings and if it is actually effective in curing or preventing a medical condition or disease. Keep in mind, this will be the first time that the drug will be tested on human beings.
3. Phase 0 trials
Phase 0 trials are also known as human micro-dosing study.
3. Phase 0 trials
Phase 0 trials are also known as human micro-dosing study.

The researchers give a single sub-therapeutic dose to a very small group of people - about 10-15. A sub-therapeutic dose is a very small dose that will not have any therapeutic effect on the body. It is done to make sure that the compound, which has never been exposed to humans,
is not toxic and is safe for ingestion.
4. Phase 1 trials - In this phase, researchers try to figure out what is the highest dose a human can take without any serious side effects. Researchers will also try to figure out what is the best way to deliver the drug to the human body.
4. Phase 1 trials - In this phase, researchers try to figure out what is the highest dose a human can take without any serious side effects. Researchers will also try to figure out what is the best way to deliver the drug to the human body.

For example, orally- which is in the form of a tablet or capsule, through an injection, a nasal spray, etc. The study is usually conducted on a small group of healthy volunteers, usually 20-100. These volunteers have to be disease free - they cannot be suffering from any kind
of condition as the researchers do not yet know how the drug will react in the body of a person suffering from certain conditions.
5. Types of studies in Phase 1:
There are 3 main types of studies conducted in Phase 1 trials - Single Ascending Dose(SAD),
5. Types of studies in Phase 1:
There are 3 main types of studies conducted in Phase 1 trials - Single Ascending Dose(SAD),

Multiple Ascending Dose(MAD) and food effect.
Single Ascending Dose(SAD): In SAD, volunteers are given a single dose of the drug and are observed for a period of time. If the drug performs as intended, the next group of volunteers are given a higher dose of the same drug.
Single Ascending Dose(SAD): In SAD, volunteers are given a single dose of the drug and are observed for a period of time. If the drug performs as intended, the next group of volunteers are given a higher dose of the same drug.
The dosage keeps increasing until the side effects of the drug become apparent. This is called the maximum tolerated dose. This study is performed to understand what dosage is ideal and what dosage will cause serious side effects.
Multiple Ascending Dose(MAD):
In MAD, different groups of volunteers are given multiple increasing doses of the drug. This study is performed to understand how taking multiple doses of the drug over a period of time affects the body. The difference between SAD and MAD is that
In MAD, different groups of volunteers are given multiple increasing doses of the drug. This study is performed to understand how taking multiple doses of the drug over a period of time affects the body. The difference between SAD and MAD is that

in SAD, each group receives only one dose of the drug whereas in MAD, each group receives multiple doses that increase with time.
Food Effect: These studies are conducted to study how food intake affects the absorption of the drug in the body. To study this, participants are
Food Effect: These studies are conducted to study how food intake affects the absorption of the drug in the body. To study this, participants are
given two identical doses - one while fasting and one after a meal. This is done to understand when the drug should be administered.
6. Phase 2 Trials -
In Phase 2, the drug is going to be tested on people actually suffering from the disease or the condition.
6. Phase 2 Trials -
In Phase 2, the drug is going to be tested on people actually suffering from the disease or the condition.

The researchers have determined that the drug is safe for consumption and are now looking to test its efficacy - which means that they are going to see if it is actually helpful in treating the disease. This study is conducted on about 50-300 patients. They are given the same
dose that was determined to be safe in phase 1. Some participants also receive a placebo - which is a fake version of the drug that will not have any effect on the body. This is done to understand if the drug is actually helping the person suffering from the condition or not.
Investigators monitor participants for several months or years to see how effective the medication is and to gather more information about any side effects it might cause.
7. Phase 3 Trials:
Phase 3 trials are the most important and provide the researchers with long
7. Phase 3 Trials:
Phase 3 trials are the most important and provide the researchers with long

term safety data. The Phase 3 trials are randomized and double-blind. Randomized means that patients are divided into 2 groups at random. One group will receive the new drug whereas one group will receive an already existing drug. Double blind means that even the researchers do
not know which participants are receiving the new medication and which are receiving the existing medication. This is done to eliminate bias on the researcher's side. The study is conducted on upto 3000 participants and are often multi-center trials, which means that the drug
is now tested in multiple locations simultaneously. It lasts for several years. The purpose of this study is to study the efficacy of the drug and monitor any side effects that may show up in the long term.
8. Filing of NDA: Once all these trials have been completed, the
8. Filing of NDA: Once all these trials have been completed, the
company compiles all the data from the years of preclinical and clinical studies into a document which is filed with the US FDA. This document is called an NDA which stands for new drug application. This is the final authorization that is needed for the company to be able to
market and sell this drug. What the FDA is specifically looking for is if the drug is more effective in curing the condition than the drugs that are already on the market. They have to weigh the benefits that the drug provides against the side effects and only approve
those drugs in which the benefit outweighs the cost.
9. Phase 4 Trials: Phase 4 testing is called pharmacovigilance. In phase 4, the long term effects of the drug are studied after it is released to the public. When the drug is marketed globally, it is taken by a diverse group
9. Phase 4 Trials: Phase 4 testing is called pharmacovigilance. In phase 4, the long term effects of the drug are studied after it is released to the public. When the drug is marketed globally, it is taken by a diverse group
of people from different regions who also suffer from various other diseases. The effects of the drug are monitored and if the drug has any adverse effects, it is recalled.
10. Success rates: Only 5 in 5,000 drugs that enter preclinical testing progress to human testing.
10. Success rates: Only 5 in 5,000 drugs that enter preclinical testing progress to human testing.

One of these 5 drugs that are tested in people is approved.
i) Phase 1 is called pharmacology phase. About 70% of the drugs in phase 1 move on to the next phase
ii) Phase 2 is called the exploratory phase. About 33% of the drugs in phase 2 move on to phase 3.
i) Phase 1 is called pharmacology phase. About 70% of the drugs in phase 1 move on to the next phase
ii) Phase 2 is called the exploratory phase. About 33% of the drugs in phase 2 move on to phase 3.
iii) Phase 3 is known as the confirmatory phase as it confirms the safety and efficacy of the drug on a wide range of people. Only 25-30% of the drugs make it past Phase 3.
iv) Phase 4 clinical trials are called post marketing study or surveillance as it happens after the drug has been released to the public. 70-90% of the drugs in this phase succeed in staying in the market.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









