2021 has been a rich year in science, with a bounty of discoveries about biology and medicine, human prehistory, and the physical world.
Now, we want to know which one you consider this year’s top breakthrough. (THREAD) 🧵
Now, we want to know which one you consider this year’s top breakthrough. (THREAD) 🧵
Starting today, you can cast your vote in this thread for your favorite #BOTY in the three categories below. The winners will enter a final contest that runs 6–13 December. On 17 December, the People's Choice winner will be revealed. 🏆
If you would like to learn more about this year’s People’s Choice candidates, follow this thread after the polls for a short description of each, or read more here: fcld.ly/mwibvax
Happy reading—and voting!
Happy reading—and voting!
Ancient Origins: Choose your favorite. ⬇
Health and Medicine: Choose your favorite. ⬇
From Molecules to Space: Choose your favorite. ⬇
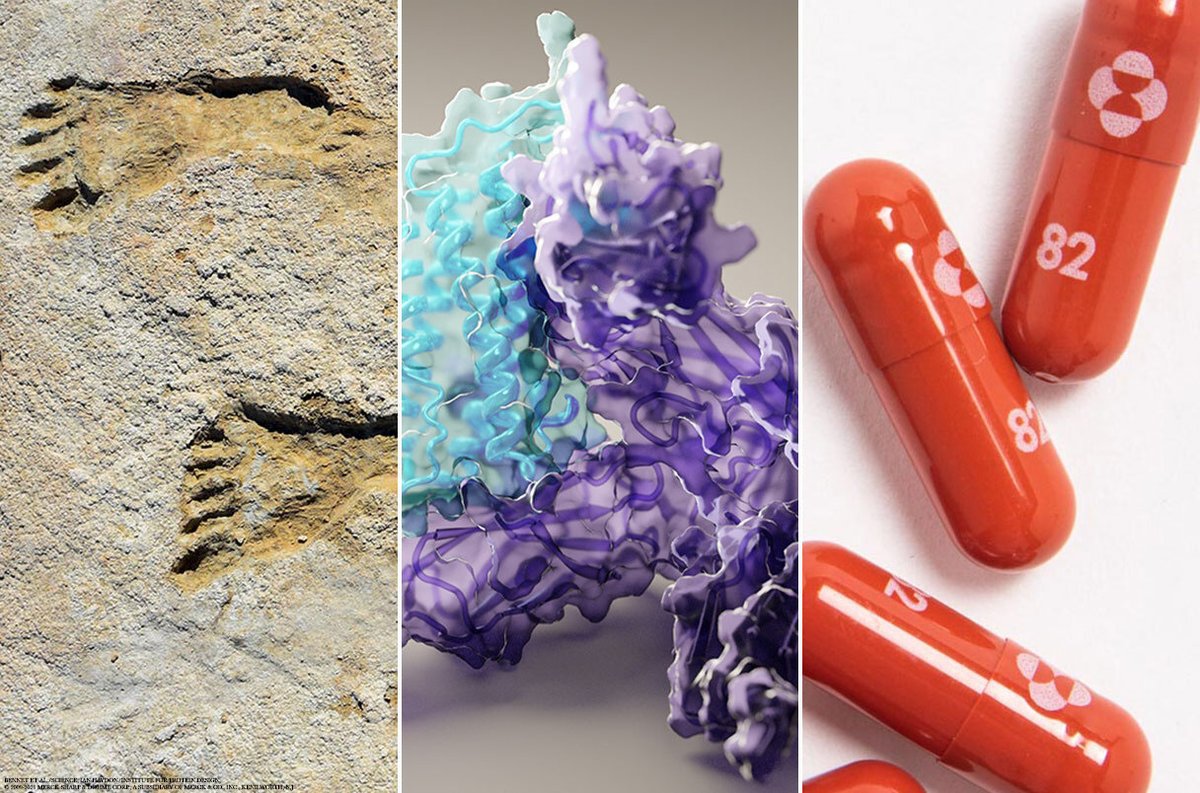
First 👣 in the Americas? Between 23,000 and 21,000 years ago, people squished through the mud along a lakeshore in New Mexico. If the preserved footprints dates are right, the discovery would be the strongest evidence yet that people reached the Americas earlier than thought. 

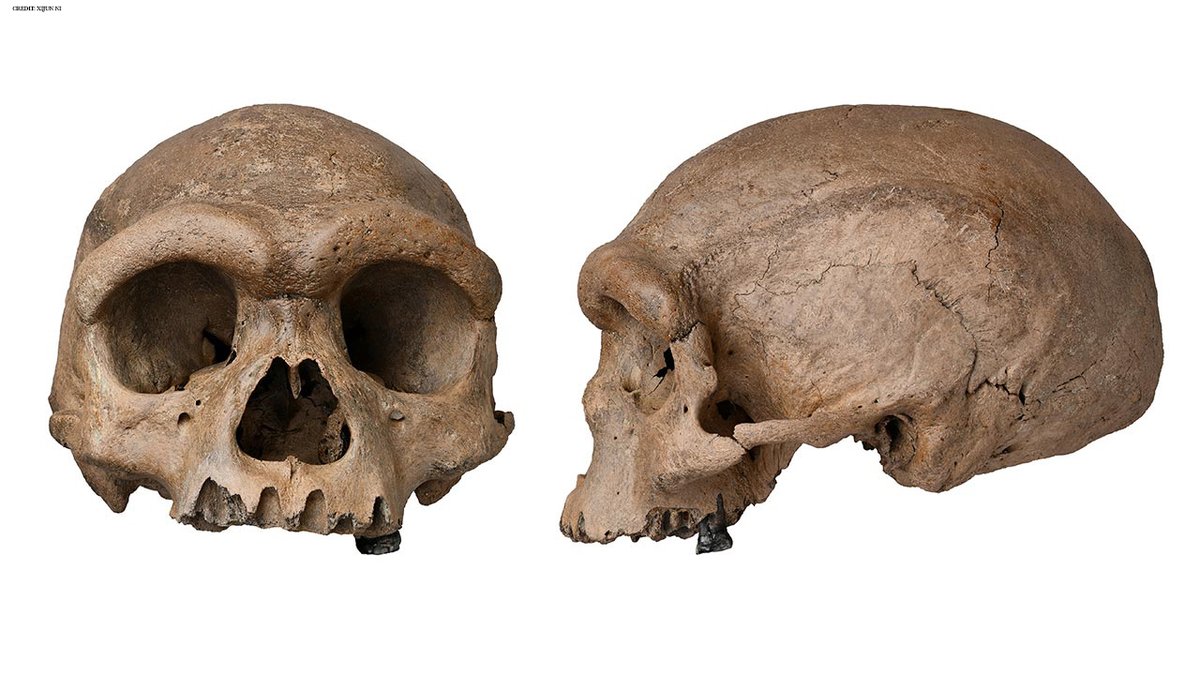
Who was Dragon Man? The stunningly preserved skull, unveiled in a new Chinese journal this year, could be the most complete fossil of our long-lost sister lineage, the Denisovans. Or, some scientists say, a new human species. Either way, this 146,000-year-old has a story to tell. 

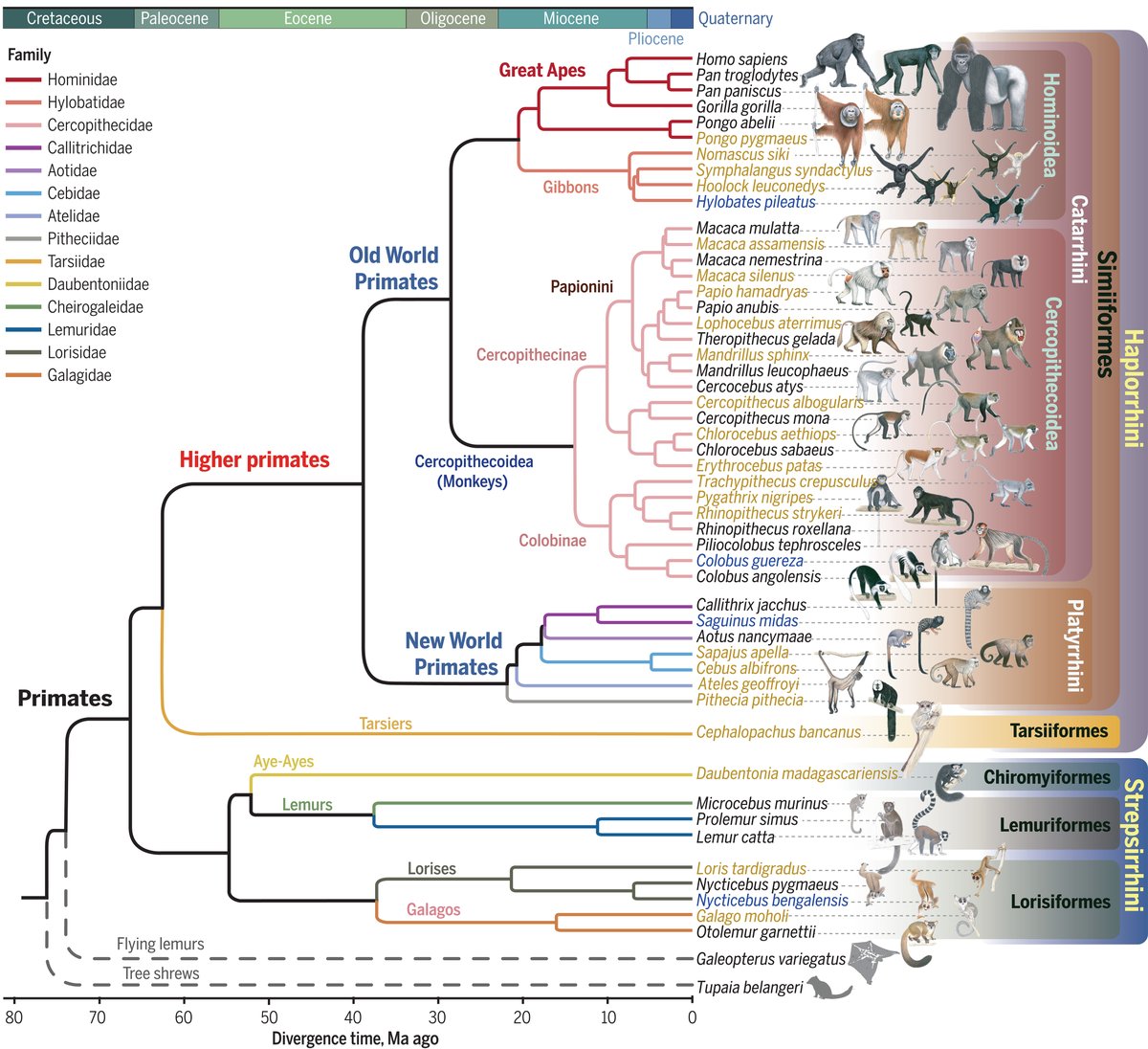
For years, scientists have known that ancient sediments harbor DNA samples from our earliest human relatives. But this year, multiple teams made strides in finding—and untangling—those threads, rewriting the histories of humans and animals living in caves from Spain to Siberia. 

The origins of horses—which transformed the lives of Bronze Age peoples—have long been shrouded in mystery. But a study of 300 ancient horse genomes found that the ancestors of all modern horses made their first appearance 4200 years ago on the western Eurasian steppe. 

This year brought early success at using the CRISPR editing tool to modify genes inside the human body. An injection of genetic code for CRISPR reduced production of a toxic liver protein in several patients and modestly improved vision in two people with inherited blindness. 
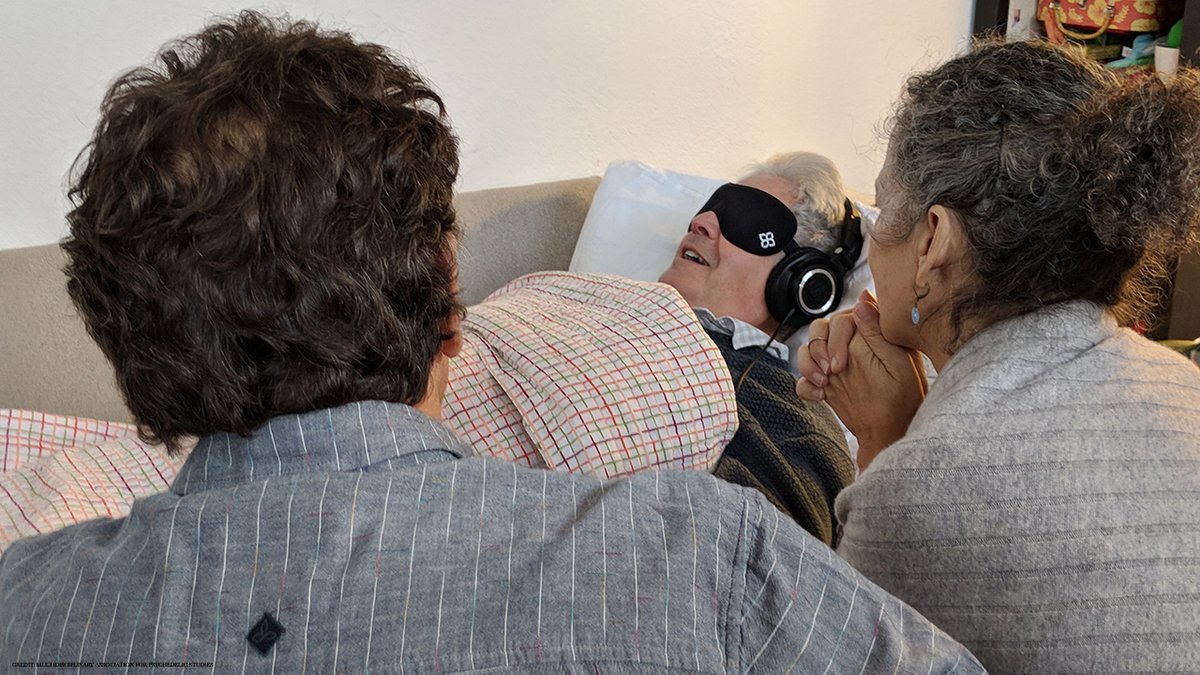
For decades, scientists trying to edge psychedelic drugs into mainstream medicine have faced an uphill battle. In May, they achieved results: They found that talk therapy plus the drug ecstasy effectively treated post-traumatic stress disorder in two-thirds of trial participants. 
Understanding early embryonic development can provide insight into miscarriages and birth defects and help scientists hone in vitro fertilization protocols. New ways to cultivate embryos from mice and stem cells could obviate the need to use real human embryos in some studies. 

Vaccines have dominated the fight against COVID-19, but a new weapon may soon be added to the arsenal: antiviral pills that suppress symptoms and prevent death if taken early enough in infection. Results from drug companies suggest they may prevent 50% to 89% of hospitalizations. 

In April, new measurements confirmed that a fleeting subatomic particle called the muon may be ever so slightly more magnetic than theory predicts. That small anomaly—just 2.5 parts in 1 billion—is a welcome threat to particle physicists’ prevailing theory, the standard model. 

NASA’s InSight lander has faced no end of challenges on Mars. But this year, its marsquake readings yielded the first full view of the Red Planet’s crust, mantle, and core. The crust and mantle are thinner than Earth’s—but the core is vast, taking up over half the planet’s width. 

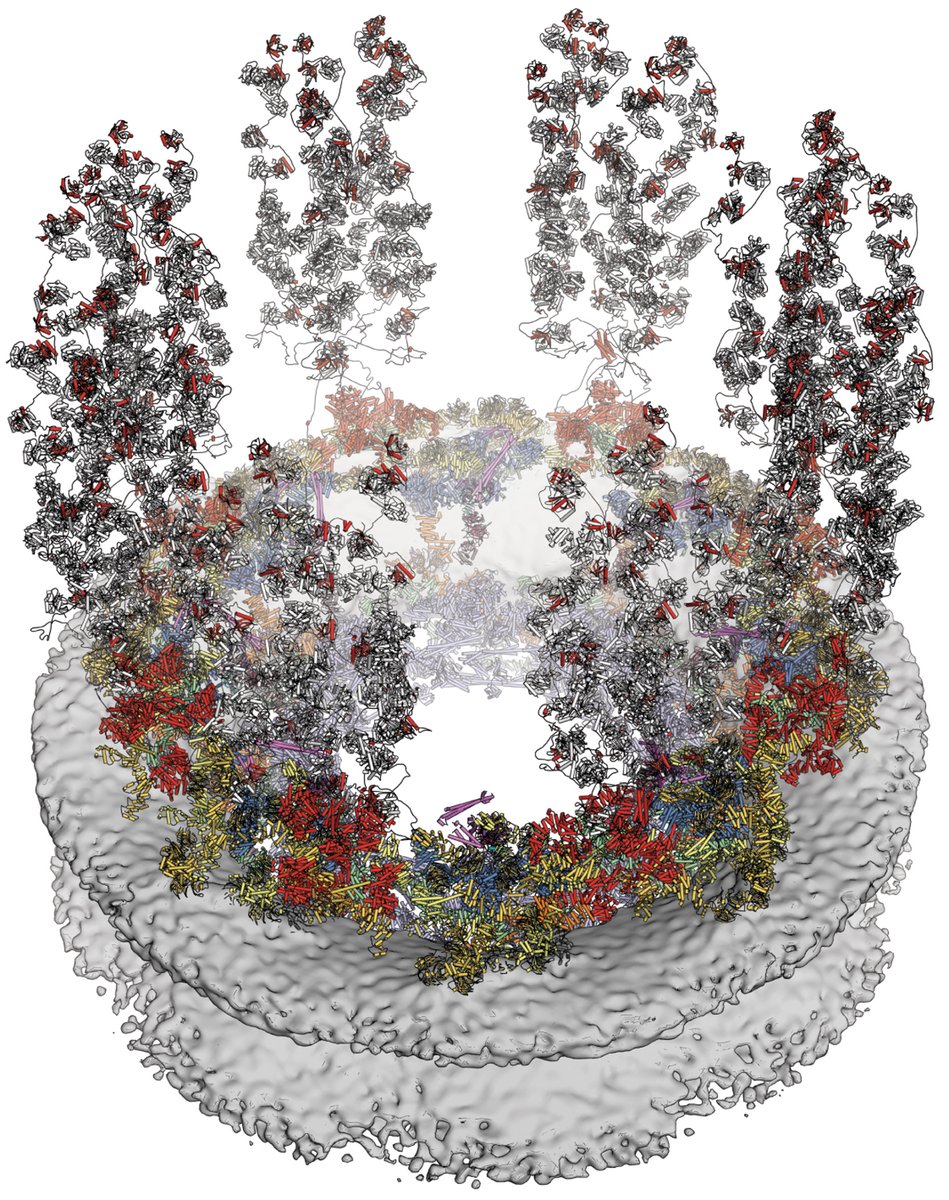
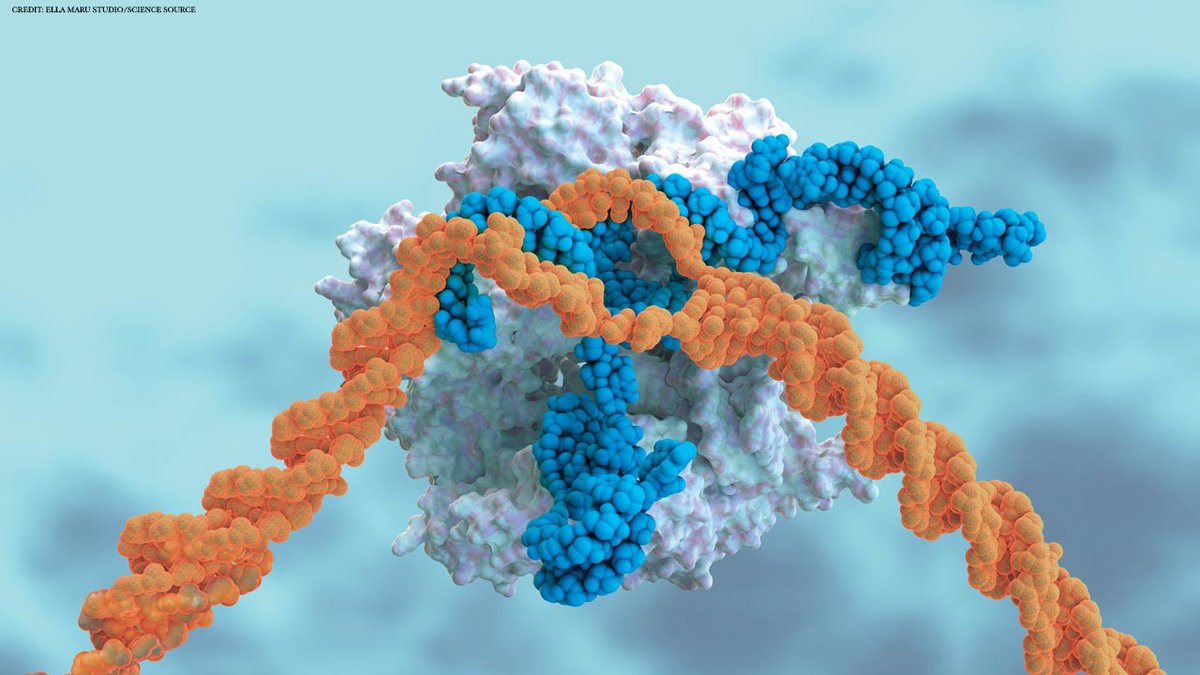
Scientists have long struggled to solve one of nature’s biggest challenges: predicting the 3D shape a string of amino acids will fold into as it becomes a working protein. AI delivered big results this year, predicting the structures of thousands of proteins and complexes. 

In an August result that surprised many, including researchers, the U.S. National Ignition Facility’s giant laser sparked a fusion reaction that came tantalizingly close to reaching the so-called “breakeven” point, when more energy is produced by the reaction than went into it. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh