Theoretical prediction of the effect omicron mutations on monoclonal antibodies by @jbloom_lab
Authors believe that this combination of mutations located on the RBD could potentially reduce the effect of monoclonal antibodies targeting that area of the virus.
See thread👇
1/5
Authors believe that this combination of mutations located on the RBD could potentially reduce the effect of monoclonal antibodies targeting that area of the virus.
See thread👇
1/5
https://twitter.com/jbloom_lab/status/1468001874989121542
This study is based on the apparent individual & additive effect of mutations based on a computer model of the RBD.
They did a computational method called “deep mutational scanning” which is used to study multiple mutations at once.
It is however not a biophysical model.
2/
They did a computational method called “deep mutational scanning” which is used to study multiple mutations at once.
It is however not a biophysical model.
2/
Authors conclude
“Sites 484, 446 & 417 are the biggest drivers of this antigenic change, although other mutations also contribute. Mutations at sites 346, 378, 444 & 504 could make it worse”
3/
“Sites 484, 446 & 417 are the biggest drivers of this antigenic change, although other mutations also contribute. Mutations at sites 346, 378, 444 & 504 could make it worse”
3/
While such computational studies are important in adding information, they do not necessarily predict the real biology of:
1) the whole immune process in the human body especially in vaccinated people/prior infection
2) the remote effect of mutations that occur outside RBD
4/
1) the whole immune process in the human body especially in vaccinated people/prior infection
2) the remote effect of mutations that occur outside RBD
4/
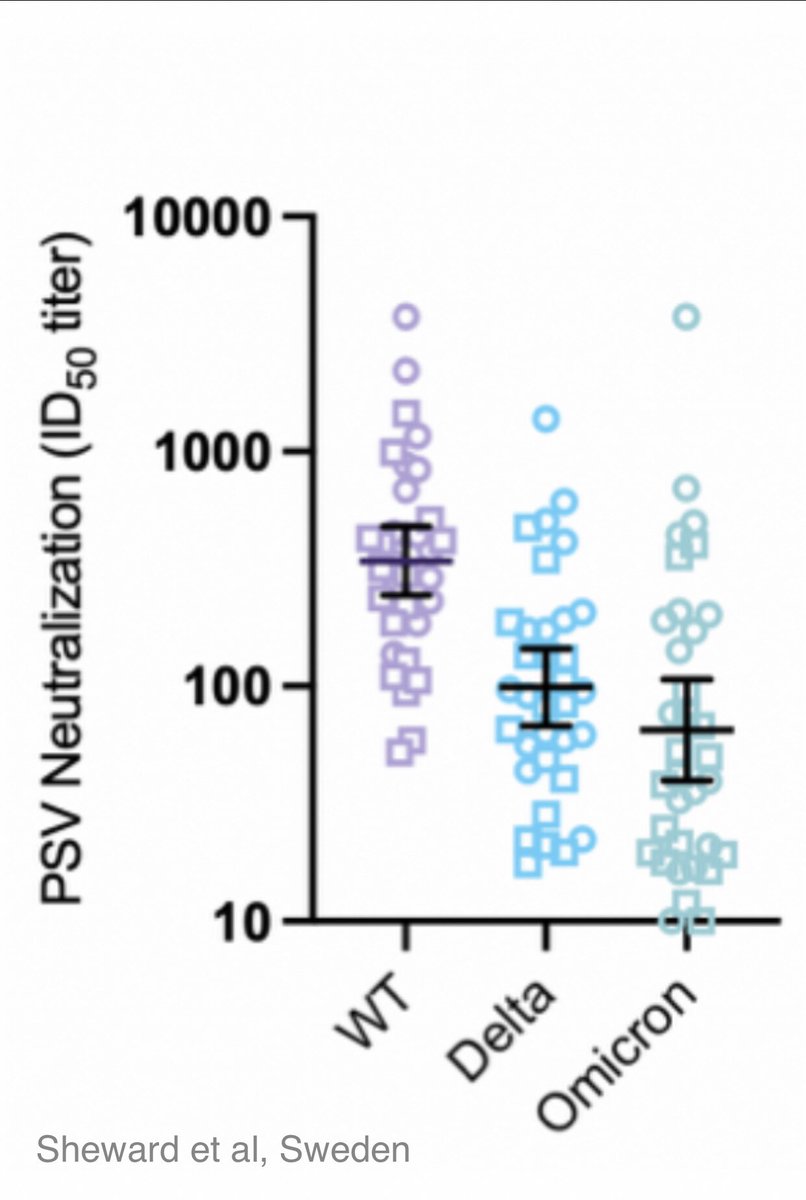
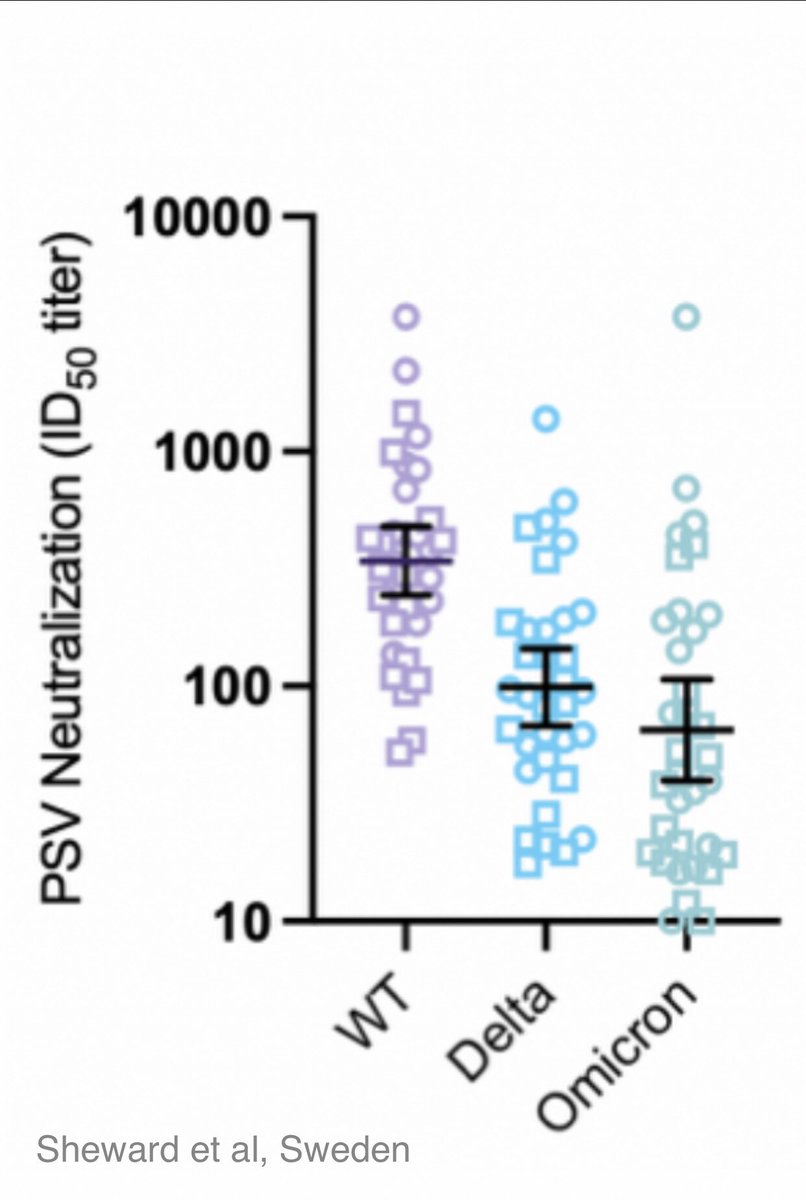
Authors however find that the Omicron variant’s calculated score is about the same as a polymutant spike (PMS20) that was artificially engineered in a pseudovirus to maximize escape antibodies.
This was previously substantiated through neutralising studies using PMS20 spike.
5/
This was previously substantiated through neutralising studies using PMS20 spike.
5/
At this time we need to understand that regardless of the Greek name, the virus is the same one that started the pandemic in 2019, ~like the same car with a few custom alterations.
As it adapts to its new found human host, let’s wait for peer-reviewed clinical studies.
6/6
As it adapts to its new found human host, let’s wait for peer-reviewed clinical studies.
6/6
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh