
"MacArthur's Pearl Harbor" AKA the Dec 8, 1941 destruction of FEAF air power at Clarke Field is the subject of this thread.
(Photo: Destroyed P-35 fighters on Clark Field)
1/
(Photo: Destroyed P-35 fighters on Clark Field)
1/

One of the important things to know about General Douglas MacArthur was that almost nothing said or written about him can be trusted without extensive research to validate its truthfulness.
There were a lot of reasons for this. The biggest being that if the Clinton era
2/
There were a lot of reasons for this. The biggest being that if the Clinton era
2/

political concept of “The Politics of Personal Destruction” had been around in the 1930s through 1950s, Gen. MacArthur’s face would have been its poster boy.
Everything he did was personal & that made everything everyone else did in opposition to him “personal” to them. Thus
3/
Everything he did was personal & that made everything everyone else did in opposition to him “personal” to them. Thus
3/

...followed rounds of name calling, selective reporting & political partisanship that have utterly polluted the historical record and require lots of research to untangle.
A case in point is the Dec. 8th 1941 attack on Clark Field and the massacre of the FEAF B-17 force.
4/
A case in point is the Dec. 8th 1941 attack on Clark Field and the massacre of the FEAF B-17 force.
4/

This 2007 article by Michael Gough titled “Failure and Destruction, Clark Field, the Philippines, December 8, 1941″ is a good example of the accepted narrative of the Clark Field attack.
The problem with it is its underlying assumptions are wrong.
5/
militaryhistoryonline.com/wwii/articles/…
The problem with it is its underlying assumptions are wrong.
5/
militaryhistoryonline.com/wwii/articles/…

The biggest is the assumption 19 B-17D's (w/o tail guns or self-sealing fuel tanks) of the 19th Bombardment Group could have done anything useful before dying horribly.
Just...no.
Both the blame MacArthur for not making a decision on the loss of the FEAF at Clark field,
6/
Just...no.
Both the blame MacArthur for not making a decision on the loss of the FEAF at Clark field,
6/
and the USAAF’s “If only the B-17’s struck first” propaganda defending General Hap Arnold’s and General Marshall’s reputations post-war, just are not supported by the facts.
7/
7/
Let' suppose at 0330 8 Dec 1941, HQ USAFFE gave Gen. Brereton permission to launch his bomber force at Clark (19 B-17s) against the Japanese facilities on Formosa.
What damage would have been inflicted on the Japanese?
Absolutely Nothing...because Formosa was fogged in.
8/


What damage would have been inflicted on the Japanese?
Absolutely Nothing...because Formosa was fogged in.
8/



The 19th Bombardment Group B-17's would have returned to Clark field at 8:00am on 8 Dec 1941 to get refueled and been on the ground when the delayed by fog IJNAS air strike arrived to destroy them.
9/

9/


More modern evaluations — AKA less colored by immediate post-war reputation protection and organizational agendas — of the FEAF performance are more telling.
The best look at that I have seen on that debacle is in Chpt 10 of Why Air Forces Fail: The Anatomy of Defeat
10/
The best look at that I have seen on that debacle is in Chpt 10 of Why Air Forces Fail: The Anatomy of Defeat
10/

edited by Robin Higham and Stephen J. Harris, which evaluated the real readiness of the Far Eastern Air Force on Dec 8, 1941.
11/
cybermodeler.com/hobby/ref/upk/…
11/
cybermodeler.com/hobby/ref/upk/…
That essay, titled “The United States in the Pacific” by Mark Parillo, addresses the FEAF Philippines performance starting at page 296.
The bottom line was that the B-17 force at Clark field did not have:
1) The photo intelligence to effectively strike Formosa with
12/
The bottom line was that the B-17 force at Clark field did not have:
1) The photo intelligence to effectively strike Formosa with
12/

...the limited number of bombs available at Clark Field. There were no pre-war overflights of Formosa, no human intelligence and thus no intelligence photos for inexperience photo interpreters to work from,
2) The B-17 did not have the accuracy to strike ships at sea.
13/
2) The B-17 did not have the accuracy to strike ships at sea.
13/

3) Nor did the B-17 force have the logistical chops in its supporting P-40 fighters. Which lacked both coolant & O2 for high altitude operations & had no drop tanks to conduct escorted strikes w/B-17s.
14/

14/


5) The B-17 force at Clark Air field were pre B-17E models lacking tail guns and powered turret guns. Thus they were dead meat for Japanese A6M Zero/Zeke fighters with 20mm cannon on Formosa.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B-17_Flyi…
15/
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B-17_Flyi…
15/

6) There was no effective ground early warning system at Clark Field, as Captain Chennault’s exercise-tested-as-effective telephone, radio & binocular equipped ground observer system was drummed out of the Army Air Service as a threat to the Bomber Mafia clique’s B-17 budget.
16/
16/
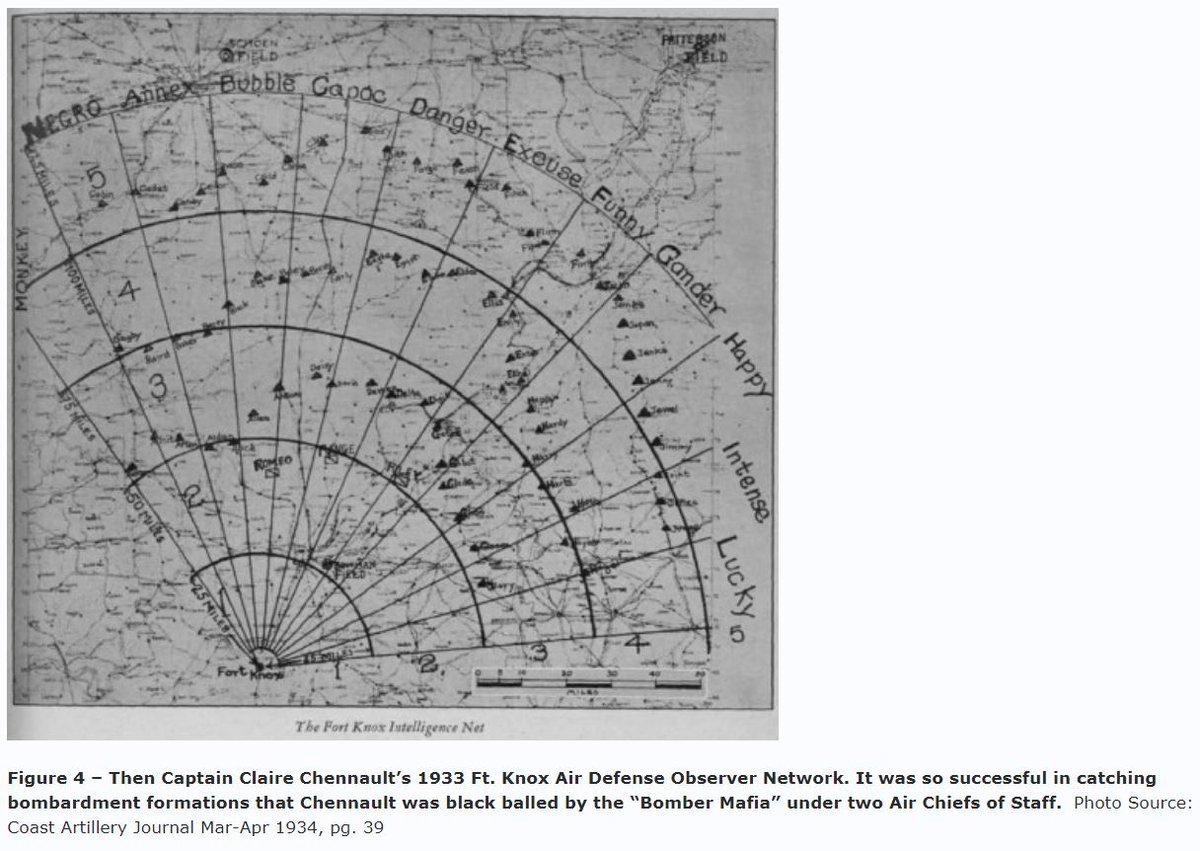
The B-17 force was sold as a high value “force in being” to the War Dept. & Gen Marshall in particular, such that it made the force’s commitment without a clear high-value target — like a Japanese invasion convoy — a non-starter, given a lack of clear targets on Formosa.
17/
17/

The B-17s were billed a strategic force in being not to be committed lightly. MacArthur didn’t commit them & got his head handed to him.
In 20-20 hindsight, the best option after skipping on the dawn launch of Dec 8th would have been to send B-17s and many P-40s to Mindanao
18/
In 20-20 hindsight, the best option after skipping on the dawn launch of Dec 8th would have been to send B-17s and many P-40s to Mindanao
18/
for a try on Dec 9th.
But had MacArthur dropped his B-17s on Formosa Dec 9th, swarms of vengeful A6M Zeros would have clawed them out of the sky on their return trip to Clark field.
Which they could have done, as they were both faster than B-17s and had the range to trail
19/
But had MacArthur dropped his B-17s on Formosa Dec 9th, swarms of vengeful A6M Zeros would have clawed them out of the sky on their return trip to Clark field.
Which they could have done, as they were both faster than B-17s and had the range to trail
19/

them all the way to Clark Field. And MacArthur would have been dinged for committing them before he knew what he was up against.
Sometimes everything you do is wrong, including nothing.
Such was the case for MacArthur on Dec 8th 1941.
20/
Sometimes everything you do is wrong, including nothing.
Such was the case for MacArthur on Dec 8th 1941.
20/

The pattern of Axis versus Allied air power in WW2 was that the two major Axis powers had made the transition to 1st-generation piston-engined monoplane fighters & bombers. It took a year of these advanced aircraft being in service before they could be used to best advantage
21/

21/


Germany & Japan had that time, in combat, to make that transition. The FEAF at Clark Field didn't.
Clark field was too close to a modern, combat tested Japanese airpower to survive & nothing Gen MacArthur did or didn’t do would have changed that.
The enemy gets a vote.
/End.
Clark field was too close to a modern, combat tested Japanese airpower to survive & nothing Gen MacArthur did or didn’t do would have changed that.
The enemy gets a vote.
/End.
@threadreaderapp please unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh
















