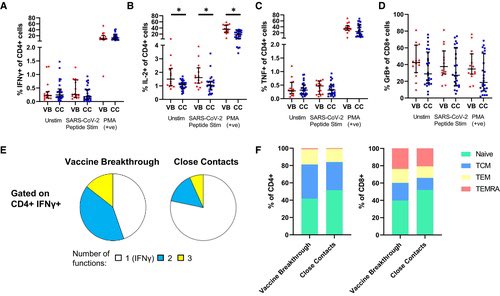
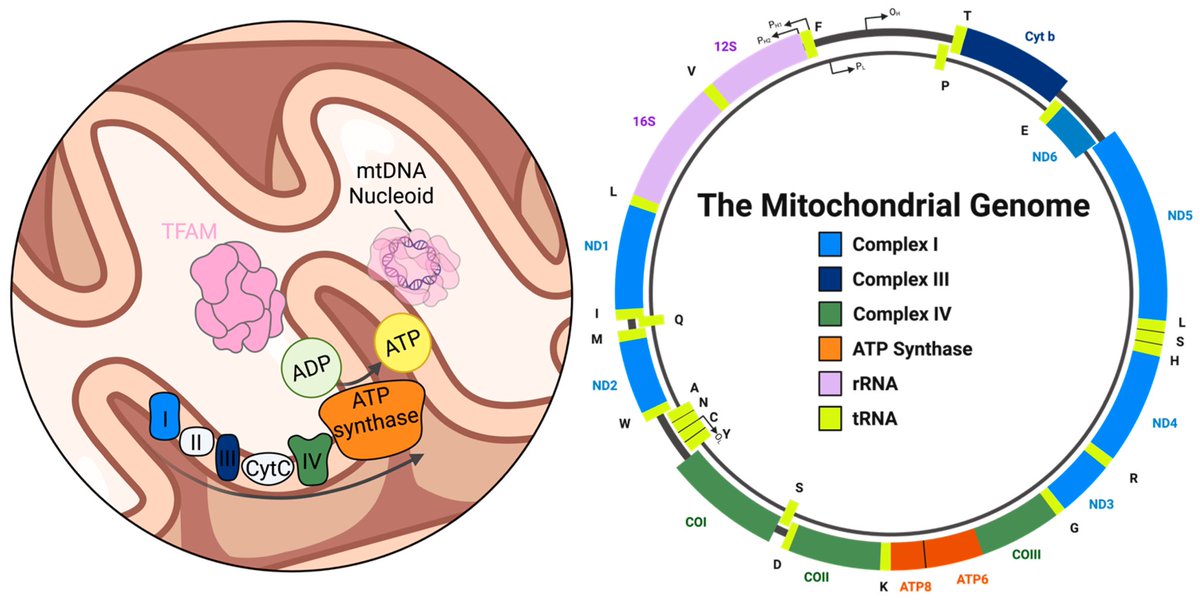
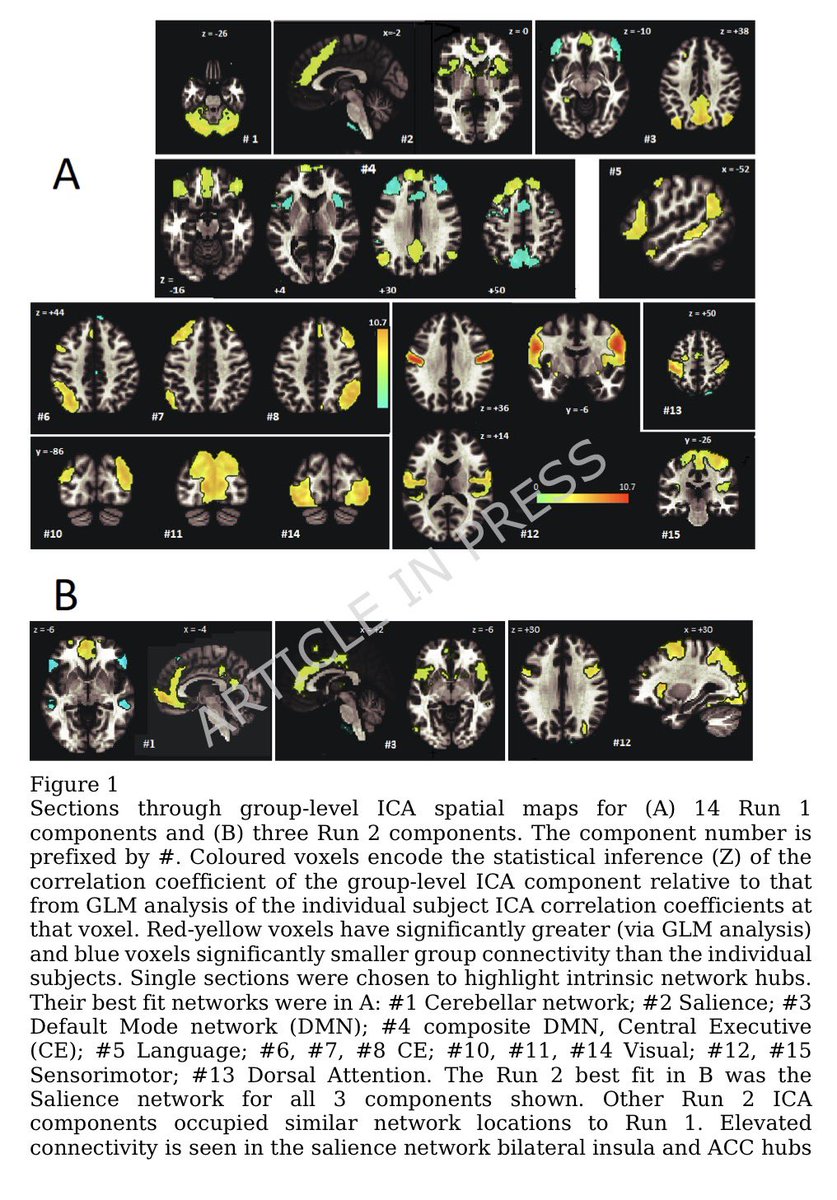
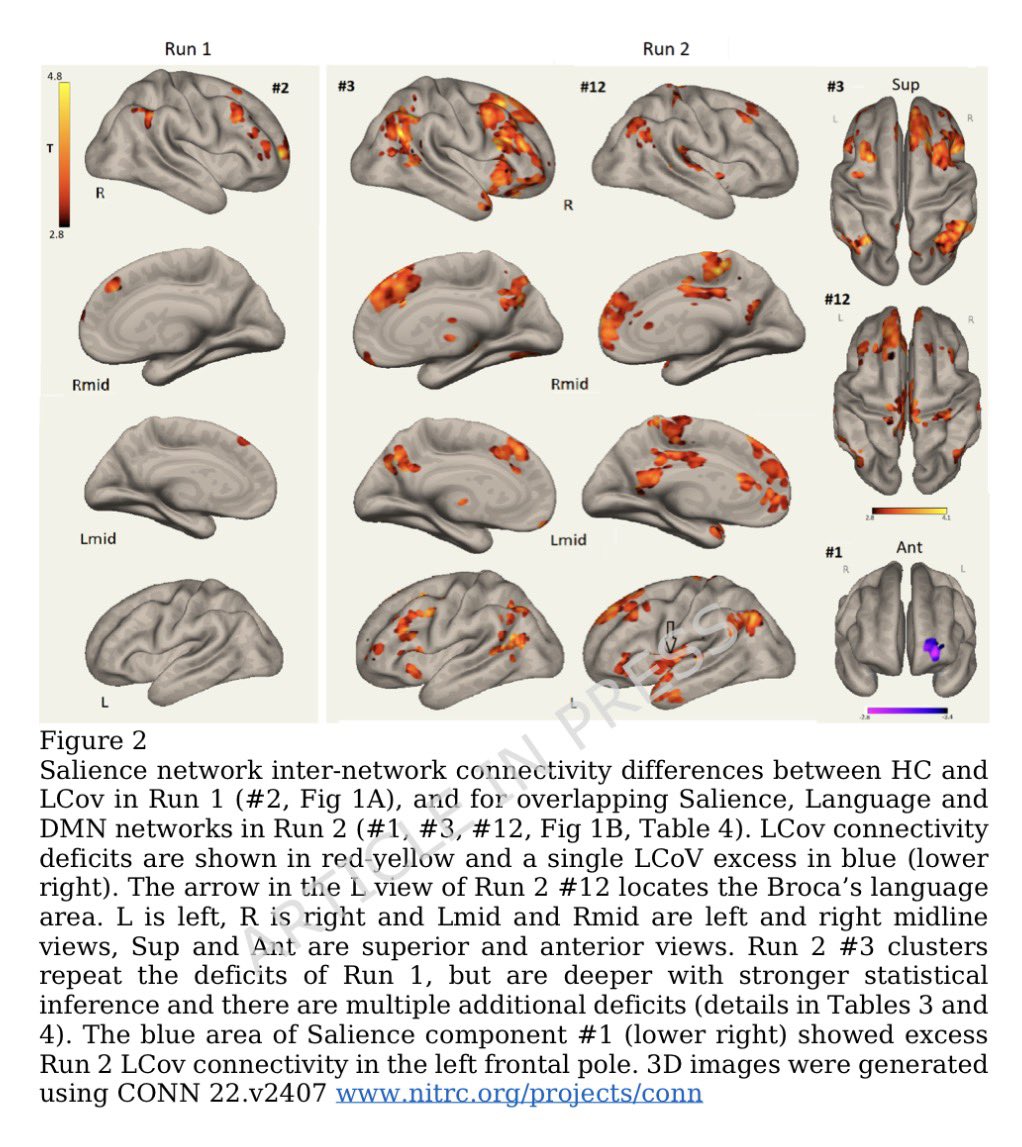
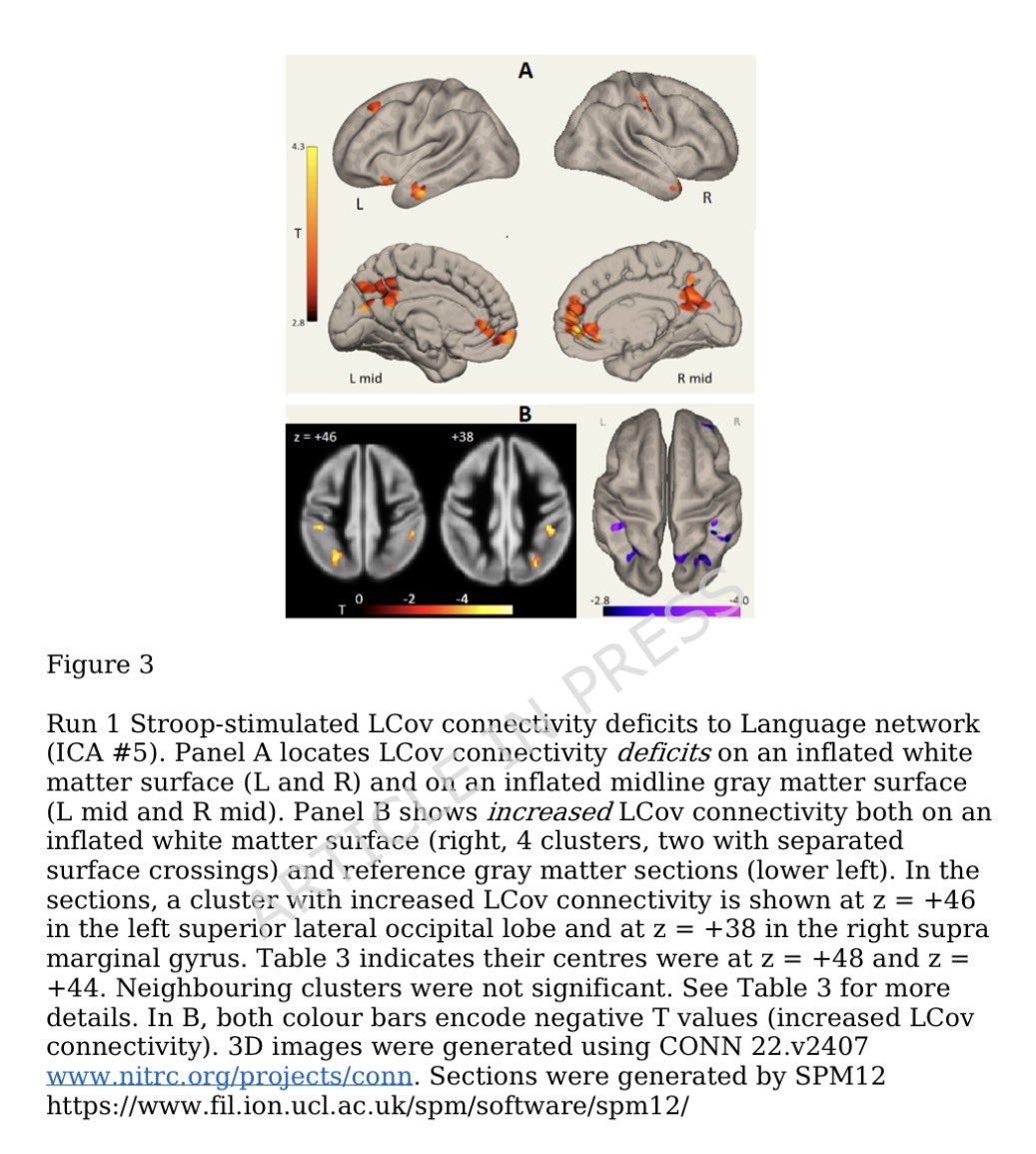
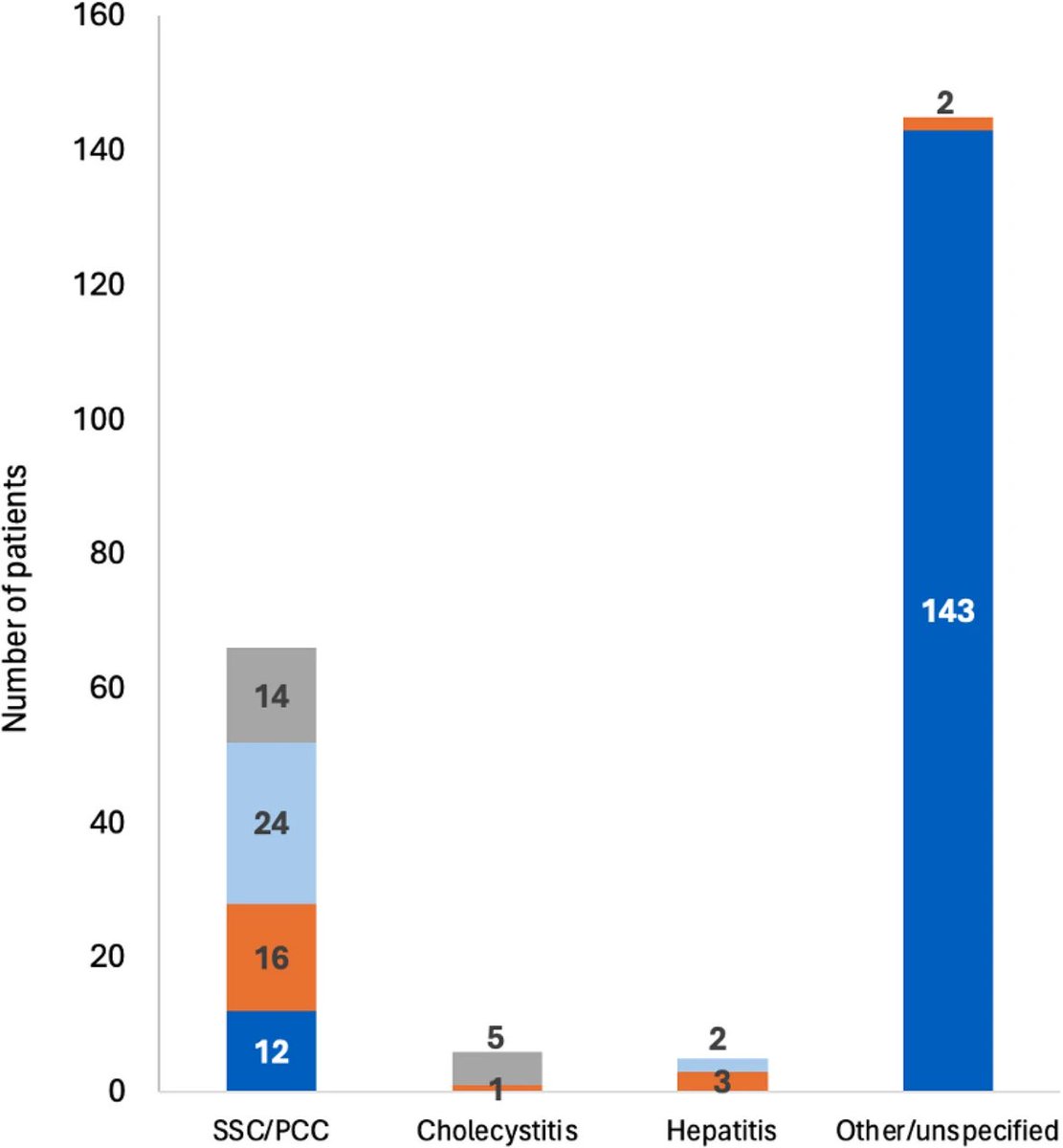
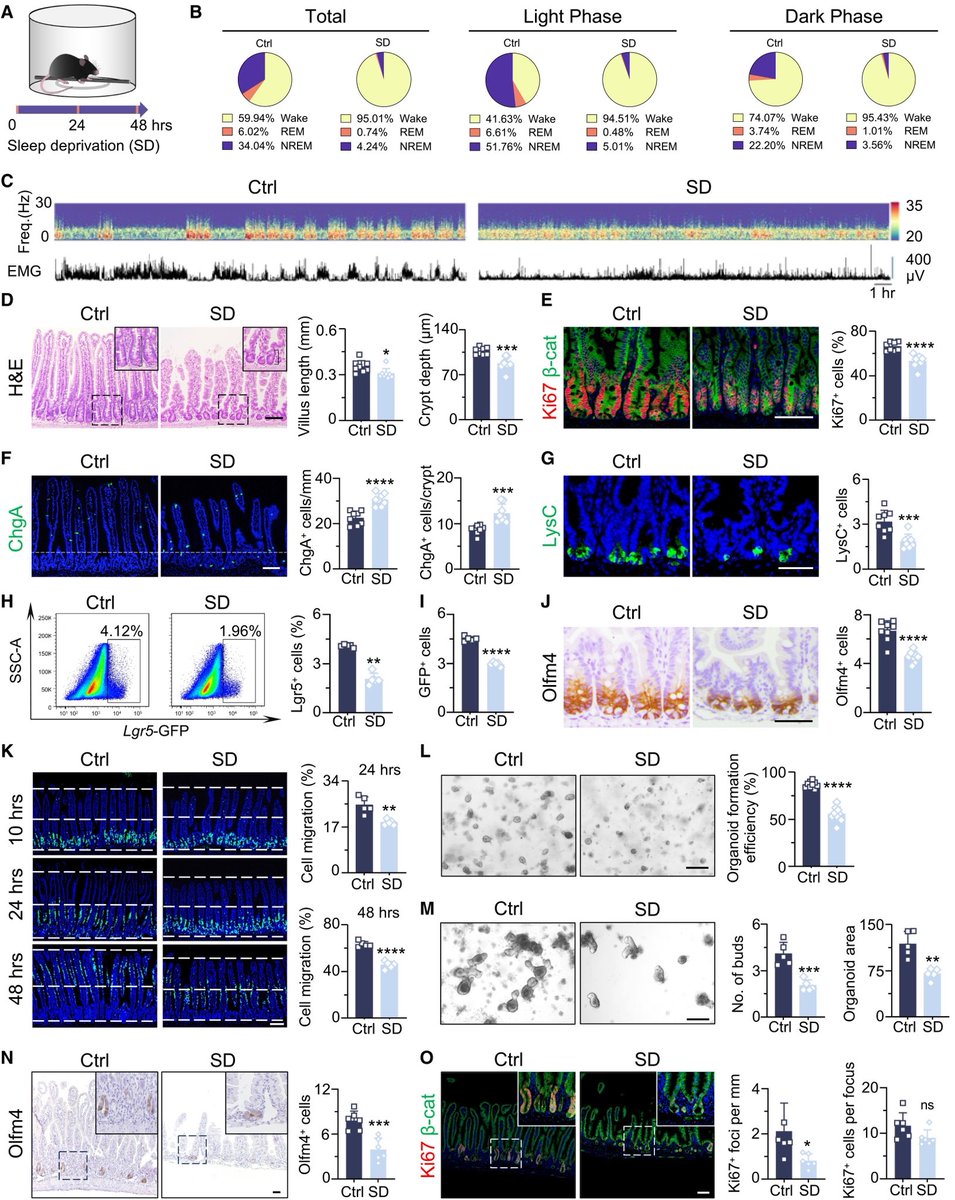
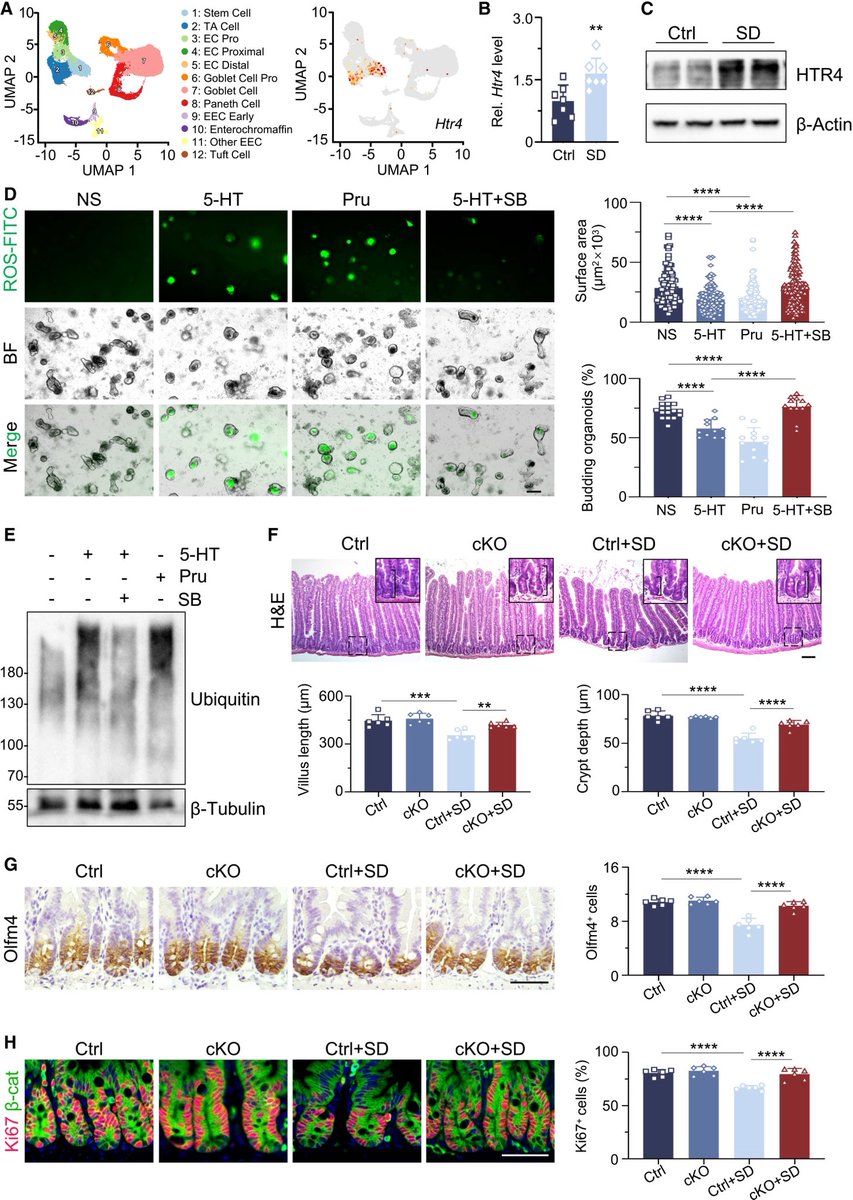
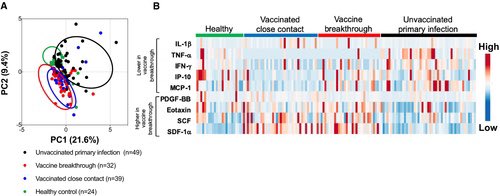
This study from #Singapore compares the immune characteristics of 55 patients with vaccine breakthrough #SARSCoV2 infection and 86 uninfected vaccinated close contacts. 1/
Antibody levels, including neutralizing antibodies, were similar in vaccine breakthrough patients and close contacts. 2/ 

Memory B cell levels, as assessed by B cell ELISpot, were lower in vaccine breakthrough patients than close contacts. 3/ 

The cytokine profile of vaccine breakthrough patients was similar to uninfected vaccinated individuals, with lower inflammatory profile compared to unvaccinated individuals with primary infection. 5/ 
Conclusions:
1-These results highlight the potential role of memory B cells in protection from Delta vaccine breakthrough infection.
2-The results suggest that memory B cell levels may be a correlate of protection against Delta variant infection in vaccinated populations 6/
1-These results highlight the potential role of memory B cells in protection from Delta vaccine breakthrough infection.
2-The results suggest that memory B cell levels may be a correlate of protection against Delta variant infection in vaccinated populations 6/

3-If so, this will be useful for determining the level of susceptibility in a population. It will also be useful in the design of future vaccines or vaccine boosters. 7/
embopress.org/doi/full/10.15…
embopress.org/doi/full/10.15…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh