Quantifying proteinuria has confused me for the longest time so I wanted to revisit some definitions. A thread.
1. Proteinuria =/= albuminuria
- Glomerular prot: mostly albumin
- Tubular prot: LMW proteins (e.g., B2M)
- Overflow prot: light chains, myoglobin, hb
- Postrenal prot: inflammation, bleed, malignancy
- Glomerular prot: mostly albumin
- Tubular prot: LMW proteins (e.g., B2M)
- Overflow prot: light chains, myoglobin, hb
- Postrenal prot: inflammation, bleed, malignancy
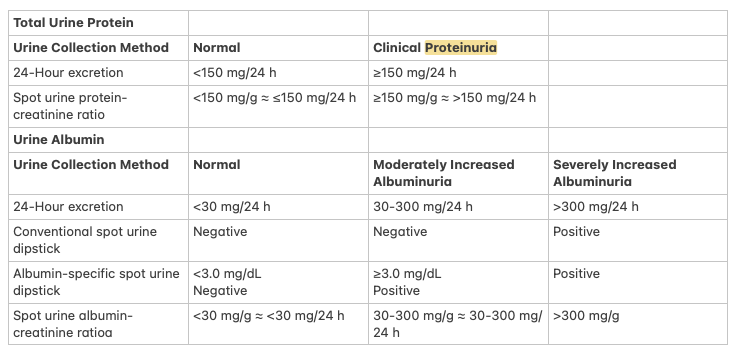
2. What is proteinuria?
- Normal protein excretion: < 150 mg/24h or spot PCR < 50 mg/g; < 300 mg/24h (pregnancy)
- Moderate prot: 150-500
- Severe prot: 500-3500
- Nephrotic-range: > 3500 mg/24h
- Proteinuria without albuminuria suggests nonglomerular causes
- Normal protein excretion: < 150 mg/24h or spot PCR < 50 mg/g; < 300 mg/24h (pregnancy)
- Moderate prot: 150-500
- Severe prot: 500-3500
- Nephrotic-range: > 3500 mg/24h
- Proteinuria without albuminuria suggests nonglomerular causes
3. What is albuminuria?
- Normal albumin excretion (A1): < 30 mg/24h or spot ACR: < 30 mg/g or albumin-specific spot dipstick < 3 mg/dL
- Moderate albuminuria (A2): 30–300 mg/24h or mg/g (spot ACR)
- Severe or "high-grade" (A3): > 300 mg/24h or mg/g (spot ACR)
- Normal albumin excretion (A1): < 30 mg/24h or spot ACR: < 30 mg/g or albumin-specific spot dipstick < 3 mg/dL
- Moderate albuminuria (A2): 30–300 mg/24h or mg/g (spot ACR)
- Severe or "high-grade" (A3): > 300 mg/24h or mg/g (spot ACR)
One other pearl: spot proteinuria/albuminuria must be interpreted with caution in
1. Extremities of muscle mass as high muscle mass urine Cr increases and spot readings may underestimate
2. AKI: Cr excretion decreases and spot readings may overestimate
1. Extremities of muscle mass as high muscle mass urine Cr increases and spot readings may underestimate
2. AKI: Cr excretion decreases and spot readings may overestimate
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh