Well, today let us see some more very basic yet important that we use daily and don't notice what happens in the background.
How does a WEB BROWSER work?
What is DNS, HTTP protocol?
You can start directly from 9/ tweet if you don't need basic introduction stuff.
🧵👇
1/
How does a WEB BROWSER work?
What is DNS, HTTP protocol?
You can start directly from 9/ tweet if you don't need basic introduction stuff.
🧵👇
1/

Companies typically make free web-browsers with some financial interest in how you use their product.
With this, they are able to track your computing habits and make revenue by selling your data to third-party vendors
2/
With this, they are able to track your computing habits and make revenue by selling your data to third-party vendors
2/
Okay, what exactly is a web browser?
In short, it is the place where you interact with the web.
Remember: The words internet and web are not interchangeable, They are related but two different things
In short, it is the place where you interact with the web.
Remember: The words internet and web are not interchangeable, They are related but two different things
Internet is a network connection that helps you to connect to the web.
The web is basically anything like a website, the app you listen to music, place to play online games, video calling your friend, streaming any movie or watching a youtube video, etc.
4/
The web is basically anything like a website, the app you listen to music, place to play online games, video calling your friend, streaming any movie or watching a youtube video, etc.
4/
Well again to mention all of those mentioned applications need an Internet connection to access them but are not mandatory to use on WEB BROWSER.
5/
5/
So web browsers are able to access sites that help you to see memes, watch youtube videos, post a comment on social media, etc. because they run on some standards and protocols
Go check out our last thread on Networking concepts to brush up about them
6/
Go check out our last thread on Networking concepts to brush up about them
https://twitter.com/0xViking/status/1497600068727099392
6/
So basically every website you visit will have the same standards to make sure that is accessible to people over the web.
Okay, let me explain each step on what happens when you visit a website by taking an example of you visiting youtube.
7/
Okay, let me explain each step on what happens when you visit a website by taking an example of you visiting youtube.
7/
I will also take a slight detour in between to explain a few other concepts when required.
As you know every web browser gives you a text box(address bar) on top of the application to enter the URL which you want to visit. So, in our case the URL is youtube.com
8/
As you know every web browser gives you a text box(address bar) on top of the application to enter the URL which you want to visit. So, in our case the URL is youtube.com
8/
When you type that site address and hit enter the website appears.
But when you hit enter there is a chain reaction of events that take place in a matter of seconds, nowadays not even a second.
Let's go step by step 👇
9/
But when you hit enter there is a chain reaction of events that take place in a matter of seconds, nowadays not even a second.
Let's go step by step 👇
9/

First of all, when you hit enter, the web browser has to find the location of the server where the site is stored/hosted.
so generally every domain we visit has a unique IP address assigned to it.
So what our browser does is, use a worldwide database service called DNS.
10/
so generally every domain we visit has a unique IP address assigned to it.
So what our browser does is, use a worldwide database service called DNS.
10/
BTW What is a DNS?
Domain Name System(DNS) is a service where it stores the domain name and corresponding IP address.
our browser will ask the DNS "Okay this is the domain name I wanted to load, can you give me the IP address for this?"
11/
Domain Name System(DNS) is a service where it stores the domain name and corresponding IP address.
our browser will ask the DNS "Okay this is the domain name I wanted to load, can you give me the IP address for this?"
11/
Before directly querying on DNS, the browser checks for the IP address in multiple other places like browser cache, call to 'gethostbyname' library function(Varies with the OS) to check locally, then requests to ISP cache, etc.,
This is to make the process faster
12/
This is to make the process faster
12/

So, once the browser gets the IP address of the site we want to visit, the computer(client) we are using will try to establish a connection with a computer where the site is stored/hosted(Server) using "Transmission Control Protocol(TCP)"
13/
13/
The client will send a request to the server asking is it open for connections
If the server has open ports that connect the sub connection, it will acknowledge the request.
Finally, the client will send one more message acknowledging that it received server acknowledgment
14/
If the server has open ports that connect the sub connection, it will acknowledge the request.
Finally, the client will send one more message acknowledging that it received server acknowledgment
14/
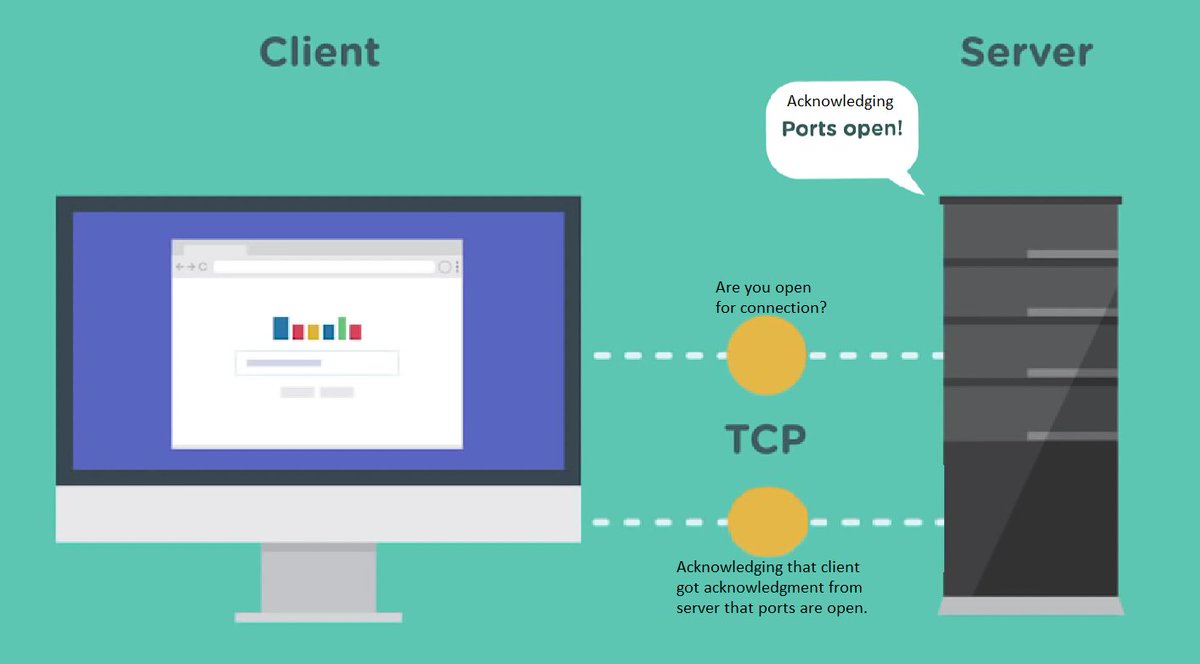
Connection is established
Now, the client can request the web pages over the HyperText Transfer Protocol(HTTP)
Let's take a moment to know more about HTTP
"HTTP is a protocol for fetching resources such as HTML documents, the foundation of any data exchange on the Web"
15/
Now, the client can request the web pages over the HyperText Transfer Protocol(HTTP)
Let's take a moment to know more about HTTP
"HTTP is a protocol for fetching resources such as HTML documents, the foundation of any data exchange on the Web"
15/
It is a client-server protocol, which means requests are initiated by the recipient, usually the Web browser.
A complete document is reconstructed from the different sub-documents fetched, for instance, text, layout description, images, videos, scripts, and more.
16/
A complete document is reconstructed from the different sub-documents fetched, for instance, text, layout description, images, videos, scripts, and more.
16/

Clients and servers communicate by exchanging individual messages (as opposed to a stream of data).
The messages sent by the client, usually a Web browser, are called requests, and the messages sent by the server as an answer are called responses.
17/
The messages sent by the client, usually a Web browser, are called requests, and the messages sent by the server as an answer are called responses.
17/
BTW, we are assuming that the website is stored on a single server, but essentially nowadays large sites which are massively used will have multiple servers stored in building in multiple cities worldwide called data centers.
18/
18/
Coming back, After the client request the server with an HTTP request the server will analyze the request and will build a response by collecting data from multiple sources like DBs, etc., usually in the form of HTML(HyperText Markup Language).
It can also be JSON, XML
19/
It can also be JSON, XML
19/
Now the server will send an HTTP response with the HTML page. back to the client who requested it.
Once the client gets a response from the server it will download the files server sent over the response.
Downloading alone will not be sufficient to see what we are seeing.
20/
Once the client gets a response from the server it will download the files server sent over the response.
Downloading alone will not be sufficient to see what we are seeing.
20/
So, Once the browser downloads multiple files like HTML, JS, CSS along with other media like videos, images, etc.
Now the browser will interpret these files and start to visually render them onto the screen.
Note server will only send the files not the rendered ones.
21/
Now the browser will interpret these files and start to visually render them onto the screen.
Note server will only send the files not the rendered ones.
21/
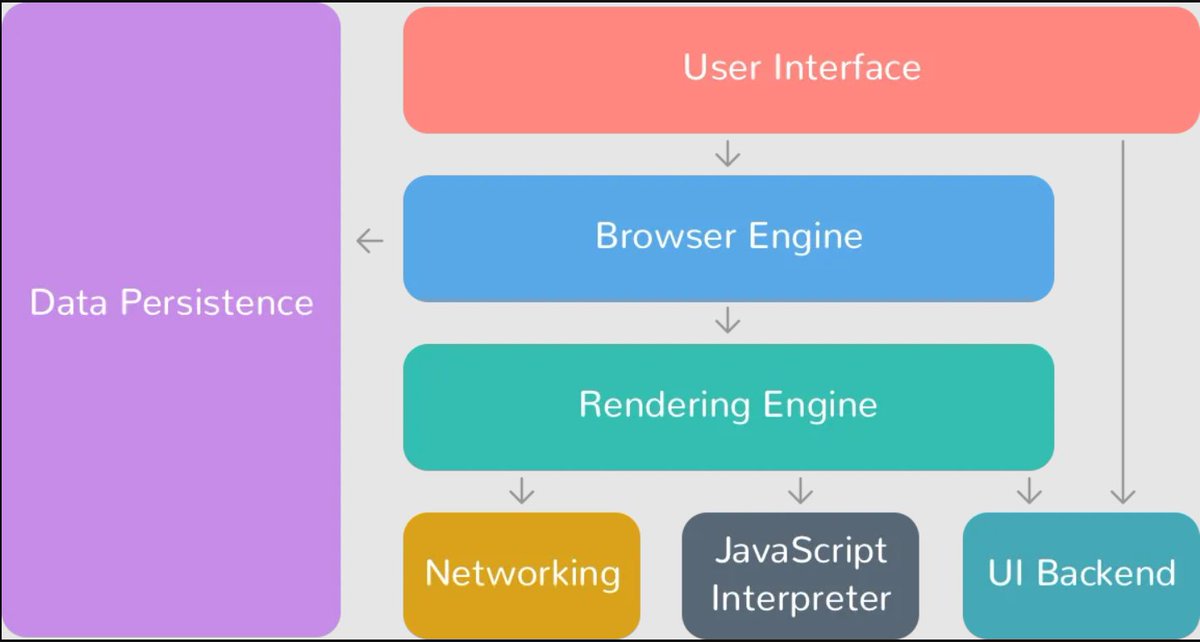
The browser will start with HTML interpretation, then add images and videos if any, and then using CSS it will build the layout of the site and starts styling with fonts and colors
Nowadays browsers are so fast, we can't even realize under the hood this is really happening
22/
Nowadays browsers are so fast, we can't even realize under the hood this is really happening
22/

Browsers also do many other things, Like stores some of the information securely, check sites for viruses.
It also remembers the sites you visited and keeps a copy of them in a data cache so that the next time you visit the same site it would be faster to load.
23/
It also remembers the sites you visited and keeps a copy of them in a data cache so that the next time you visit the same site it would be faster to load.
23/
Well, you have converted the most basic thing that happens in our day-to-day life yet we don't notice it under our eyes.
Kudos to you 🎉for making it this far.
That brings an end to this thread
24/
Kudos to you 🎉for making it this far.
That brings an end to this thread
24/
Resources:
Video: by @treehouse
Overview on HTTP protocol -> developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web…
HTTP request and response headers ->
developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web…
25/
Video: by @treehouse
Overview on HTTP protocol -> developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web…
HTTP request and response headers ->
developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web…
25/
This thread is part of a Web3 Developer roadmap, Please have a look at it -> 0xviking.hashnode.dev/ultimate-roadm…
Thank you for reading till here.
I am a budding developer in web3, Started #21DaysOfLearnandShare to learn more and share.
If you like the content,
✅Like the first post
✅RETWEETS are appreciated
✅Please follow @0xViking for more such content
Thanks again
0xViking
I am a budding developer in web3, Started #21DaysOfLearnandShare to learn more and share.
If you like the content,
✅Like the first post
✅RETWEETS are appreciated
✅Please follow @0xViking for more such content
Thanks again
0xViking
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh