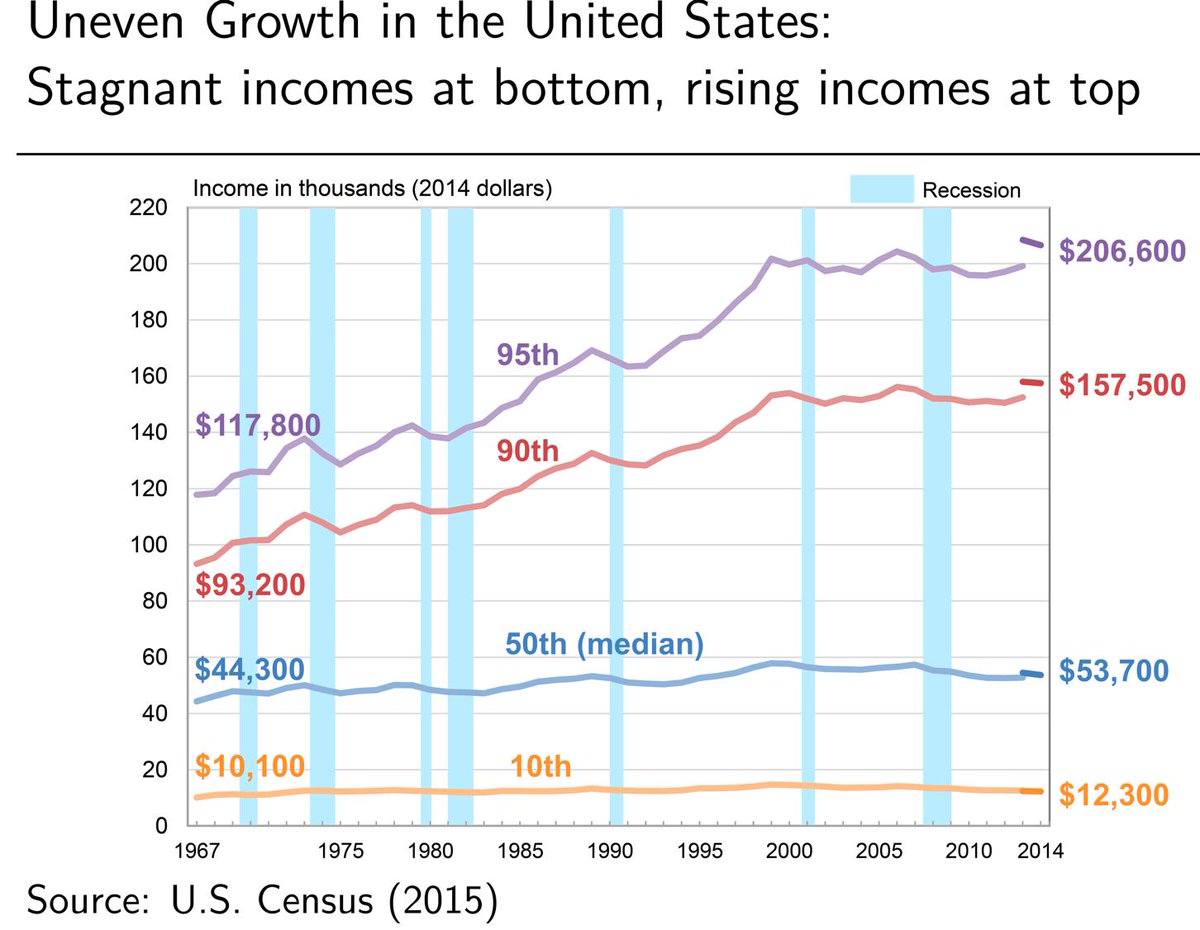
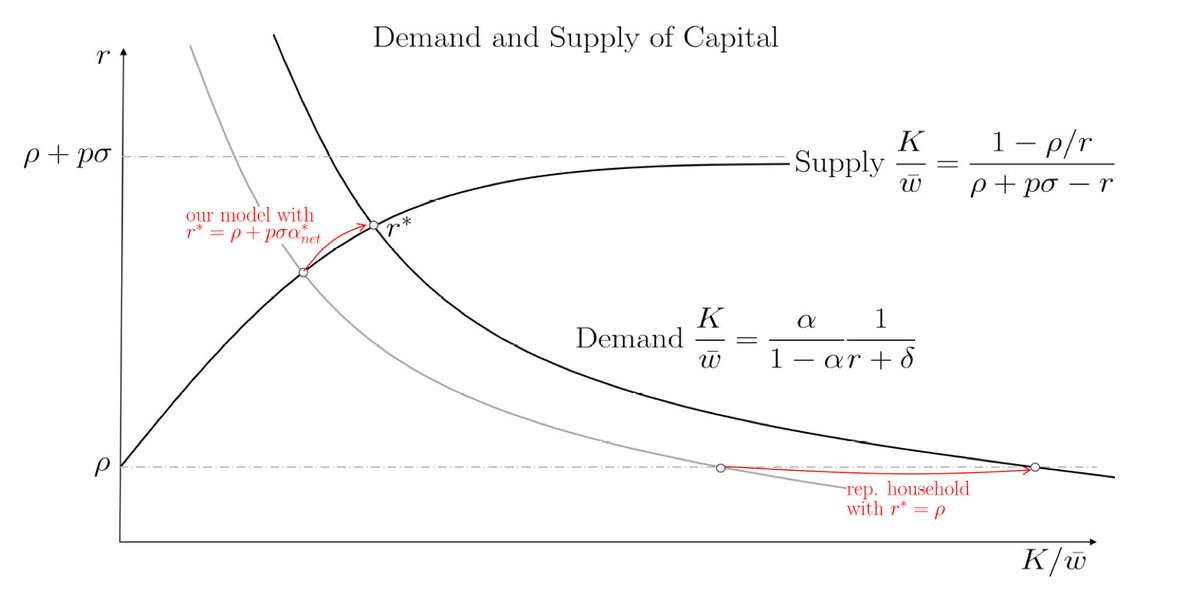
Can't stop thinking about this:
"Wir reden von Armut" - "We're talking about poverty"
said Robert Habeck, German vice chancellor and economic minister of economy and climate @BMWK
No, he was not reflecting on the fate of 2 million who have fled Ukraine in as many weeks, ...
"Wir reden von Armut" - "We're talking about poverty"
said Robert Habeck, German vice chancellor and economic minister of economy and climate @BMWK
No, he was not reflecting on the fate of 2 million who have fled Ukraine in as many weeks, ...
https://twitter.com/ben_moll/status/1502372887109459971
clutching on to a plastic bag with what's left of their life's possessions.
He also wasn't talking about Mariupol's residents destined to die of starvation & dehydration, or shelling.
He was reflecting on the ~0.5-6% (I'm generous*) hit to annual GDP per capita in Germany, ...
He also wasn't talking about Mariupol's residents destined to die of starvation & dehydration, or shelling.
He was reflecting on the ~0.5-6% (I'm generous*) hit to annual GDP per capita in Germany, ...
Europe's economic powerhouse.
These reflections came with no accompanying numbers or analysis,
against the backdrop of strong support of tougher sanctions across 🇩🇪 population,
and surely were well heard in Moscow.
My guess: history will judge these words harshly.
These reflections came with no accompanying numbers or analysis,
against the backdrop of strong support of tougher sanctions across 🇩🇪 population,
and surely were well heard in Moscow.
My guess: history will judge these words harshly.
*one way in which this is generous is that this range includes the 'disaster' estimates out there that I don't think are likely.
the other is that these numbers use the wrong counterfactual (status-quo). Not acting now will bite later, and the price will most likely be higher.
the other is that these numbers use the wrong counterfactual (status-quo). Not acting now will bite later, and the price will most likely be higher.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh