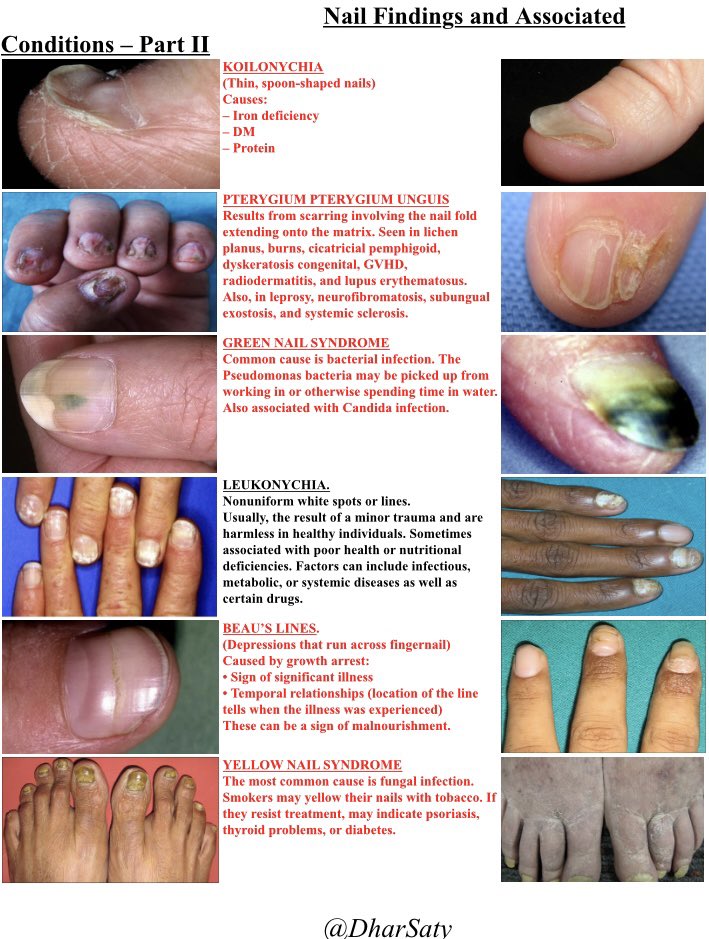
4-chloro-N-(2-furyl-methyl)-5-sulfamoyl-anthranilic acid, member of the sulfa’s. Potent natriuretic drug, inhibits Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
Direct Vd effects results in its therapeutic effectiveness in the Rx of acute pulm edema.
/2
Direct Vd effects results in its therapeutic effectiveness in the Rx of acute pulm edema.
/2

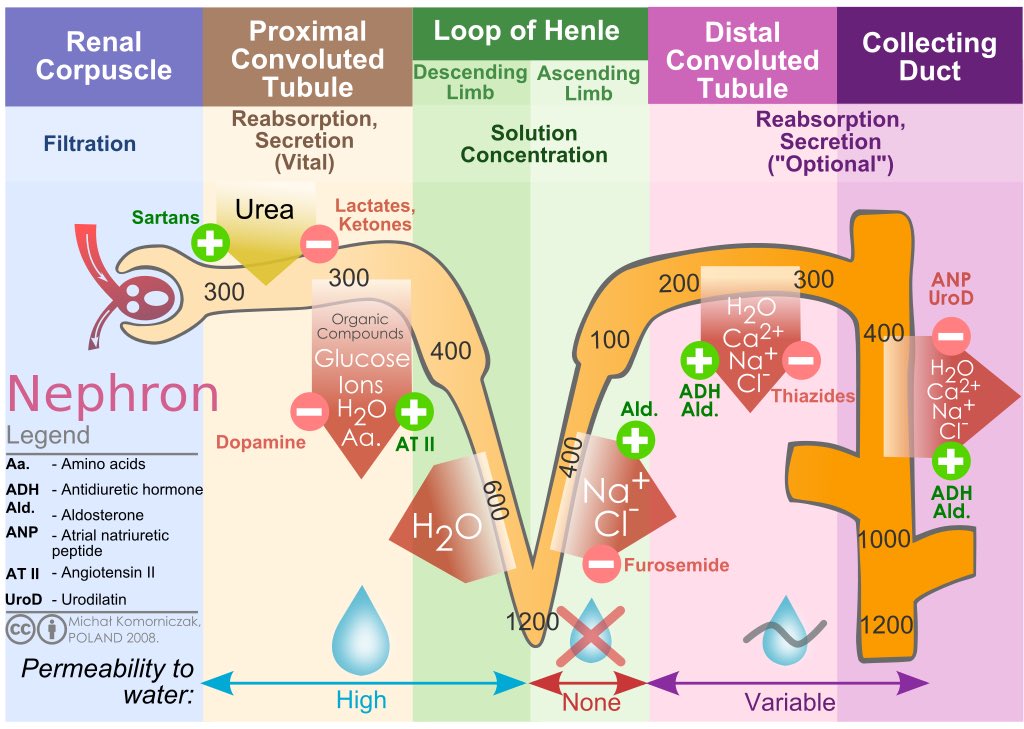
Vasodilation leads to reduced responsiveness to vasoconstrictors, such as angiotensin II and noradrenaline, and decreased production of endogenous natriuretic hormones with vasoconstricting properties.
/3
/3

Furosemide strongly binds to plasma proteins (91–99%), particularly to anionic sites on albumin. Severe hypoalbuminemia might impair diuretic effectiveness, owing to impaired delivery to the kidney, and albumin administration might enhance natriuresis.
/4
/4

Renal actions peak within 1 h after oral & within 5 min after IV administration. The half-time (T½) ranges from 0.5–2 h, but can be ⬆️ in renal failure. The duration of natriuretic effect is supposedly ∼6 h after oral & ∼2 h after single-dose IV administration, but can vary.
/5
/5
Furosemide increases kaliuresis indirectly by promoting K+ secretion by increased distal tubular fluid flow.
The ratio of equipotent doses of furosemide-to-bumetanide is 40:1 in normal individuals, that ratio declines as kidney dysfunction progresses
/6
The ratio of equipotent doses of furosemide-to-bumetanide is 40:1 in normal individuals, that ratio declines as kidney dysfunction progresses
/6
A bolus IV results in a strong natriuresis with FENa in healthy individuals >25% with peak Na+ excretion of ∼5 mmol/min.
Should not be given- rapid IV push. There are no data related to the optimal time of a single IV dose, the reasonable is 20- 40 mg over 5 min.
/7
Should not be given- rapid IV push. There are no data related to the optimal time of a single IV dose, the reasonable is 20- 40 mg over 5 min.
/7

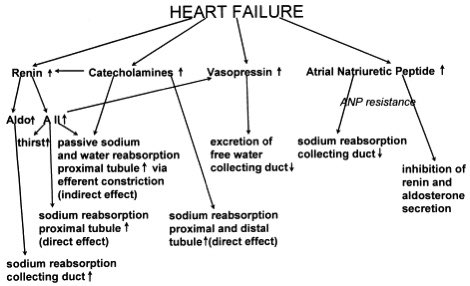
A large study in HF patients was unable to demonstrate that continuous IV furosemide was more effective in ⬇️ volume overload than bolus IV. However, continuous IV therapy may be less ototoxic than bolus therapy & maintains a sustained effective rate of diuretic excretion.
/8
/8
Deafness/tinnitus appear to result from ⬆️ serum concentration, which inhibit an Na-K-2Cl isoform.This transport protein, which is different from that expressed along the thick ALH, is expressed by the stria vascularis & participates in secretion of potassium-rich endolymph.
/9
/9
IV Furosemide in Acute HF
The initial dose of IV should be approx 2-2.5 times the patient's home oral dose.
If there is little or no response, the dose should be x2 at two-hour intervals, PRN, up to the max recommended doses.
/10
The initial dose of IV should be approx 2-2.5 times the patient's home oral dose.
If there is little or no response, the dose should be x2 at two-hour intervals, PRN, up to the max recommended doses.
/10

Doses higher than the "maximum effective dose" often produce further diuresis, with less Na excretion/mg of diuretic administered.
Pts who do not have an adequate response to a maximal IV dose are unlikely to respond to another loop diuretic since their MOI are similar.
/11
Pts who do not have an adequate response to a maximal IV dose are unlikely to respond to another loop diuretic since their MOI are similar.
/11

Repetitive admins ➡️ short-term (braking phenomenon, acute diuretic resistance) & long-term (chronic resistance) adaptations- mechanisms not known. The braking phen. is the ⬇️ in the response after the first dose & is a physiological response to avoid ECFV contraction.
/12
/12
Causes of diuretic resistance:
- Delayed absorption.
- Reduced secretion into the tubular lumen (its site of action).
- Compensatory retention of Na after the effective period of the diuretic.
- Hypertrophy & hyperplasia of epithelial cells of the DCT.
/13
- Delayed absorption.
- Reduced secretion into the tubular lumen (its site of action).
- Compensatory retention of Na after the effective period of the diuretic.
- Hypertrophy & hyperplasia of epithelial cells of the DCT.
/13
Approach to resistance:
-Assess compliance- salt & med intake.
-Discontinue NSAIDs.
-Adjust the dose of the meds in pts with renal impairment.
-Switch to IV to overcome impaired absorption.
-Continuous IV may succeed.
-Combine with other diuretics preferably a thiazides.
/14
-Assess compliance- salt & med intake.
-Discontinue NSAIDs.
-Adjust the dose of the meds in pts with renal impairment.
-Switch to IV to overcome impaired absorption.
-Continuous IV may succeed.
-Combine with other diuretics preferably a thiazides.
/14
References:
journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.11…
cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/14/8/1…
pmj.bmj.com/content/79/931…
uptodate.com/contents/mecha…
ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/HY…
/15
@threadreaderapp please “unroll”
journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.11…
cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/14/8/1…
pmj.bmj.com/content/79/931…
uptodate.com/contents/mecha…
ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/HY…
/15
@threadreaderapp please “unroll”
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh