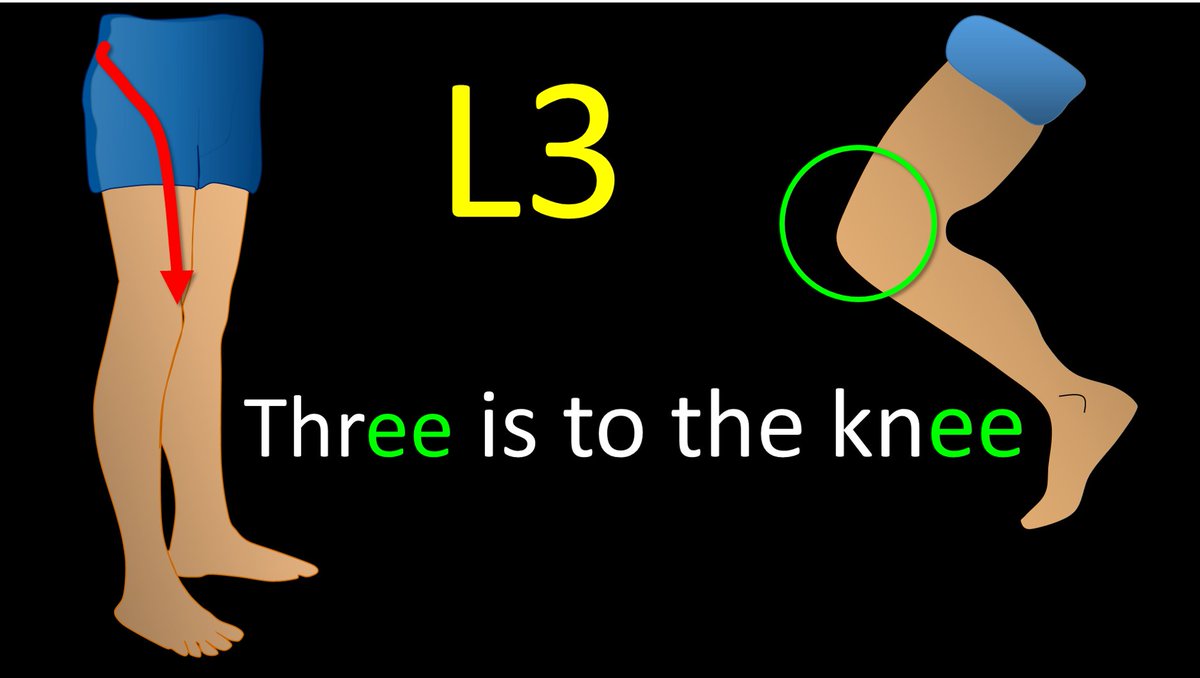
1/”Tell me where it hurts.” How back pain radiates can tell you where the lesion is—if you know where to look!
A 🧵about how to remember lumbar radicular pain distributions. #medstudenttwitter #medtwitter #radres #FOAMed #FOAMrad #neurorad #Meded #backpain #spine #Neurosurgery
A 🧵about how to remember lumbar radicular pain distributions. #medstudenttwitter #medtwitter #radres #FOAMed #FOAMrad #neurorad #Meded #backpain #spine #Neurosurgery
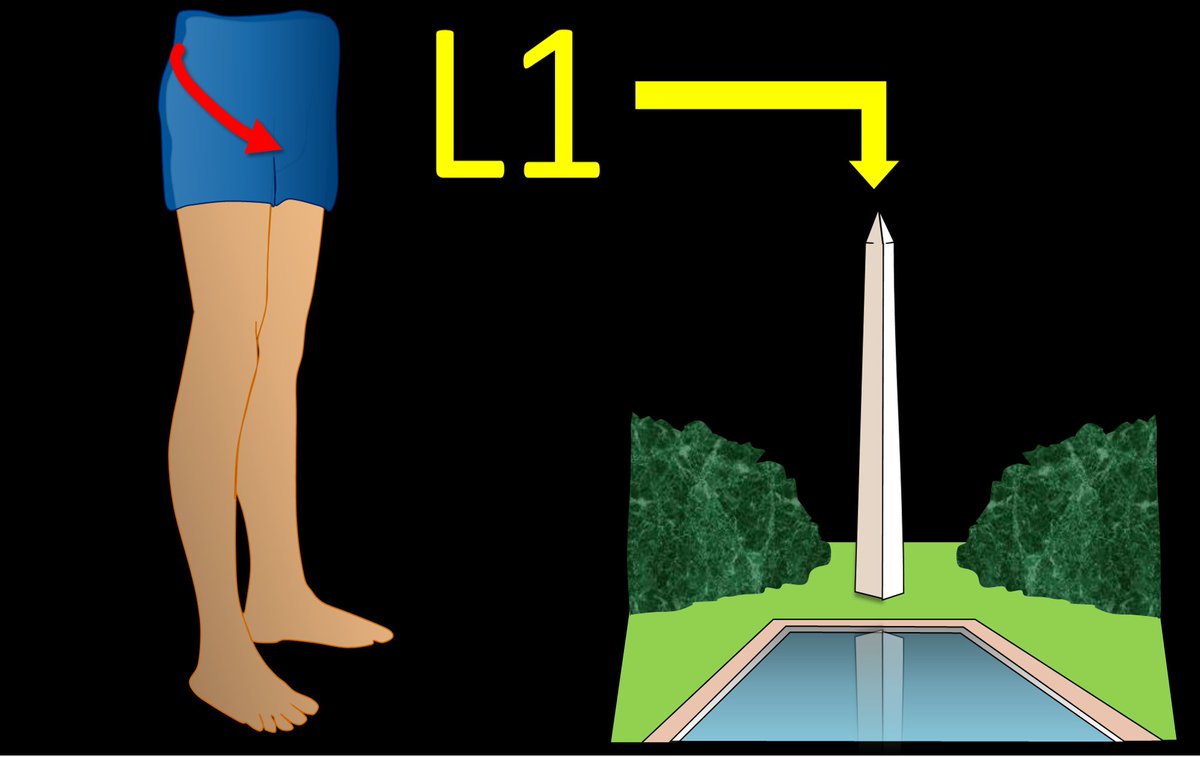
2/Let’s start with L1. L1 radiates to the groin. I remember that b/c the number 1 is, well, um…phallic. So the phallic number 1 radiates to the groin. 
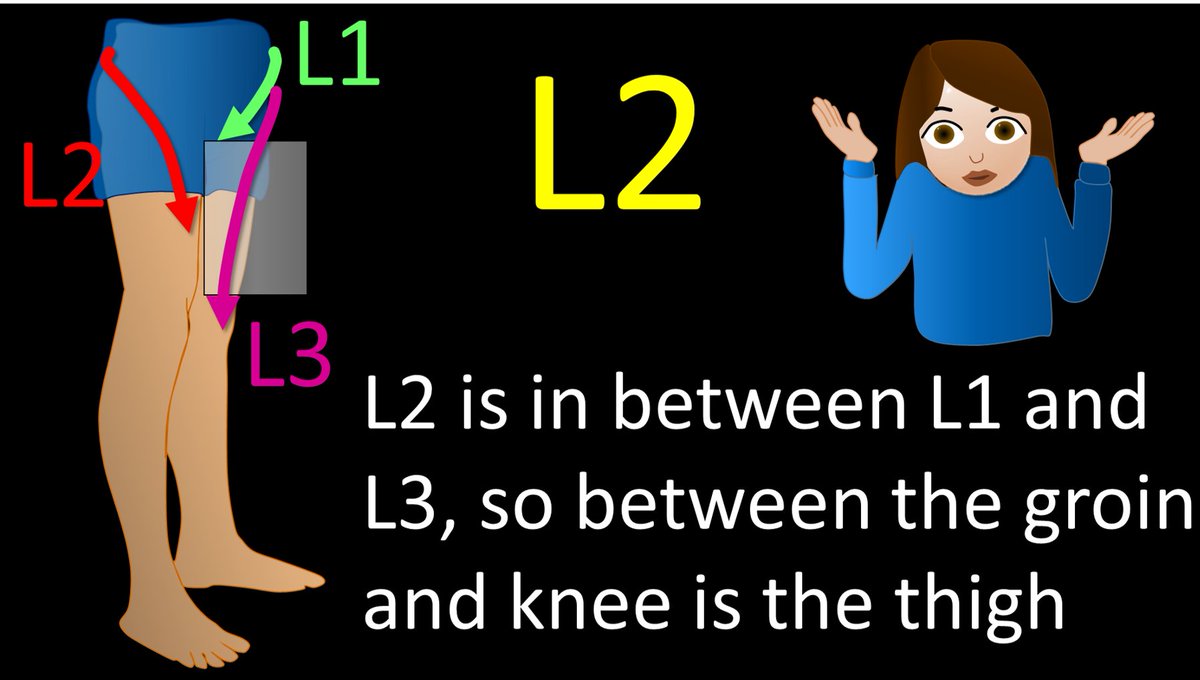
4/Ok, back to L2. Two is the number between 1 and 3, so the distribution of L2 is between the distributions of L1 and L3—and between the groin and knee is the thigh. L2 radiates to the thigh. It’s not the catchiest way to remember it, but it works. 
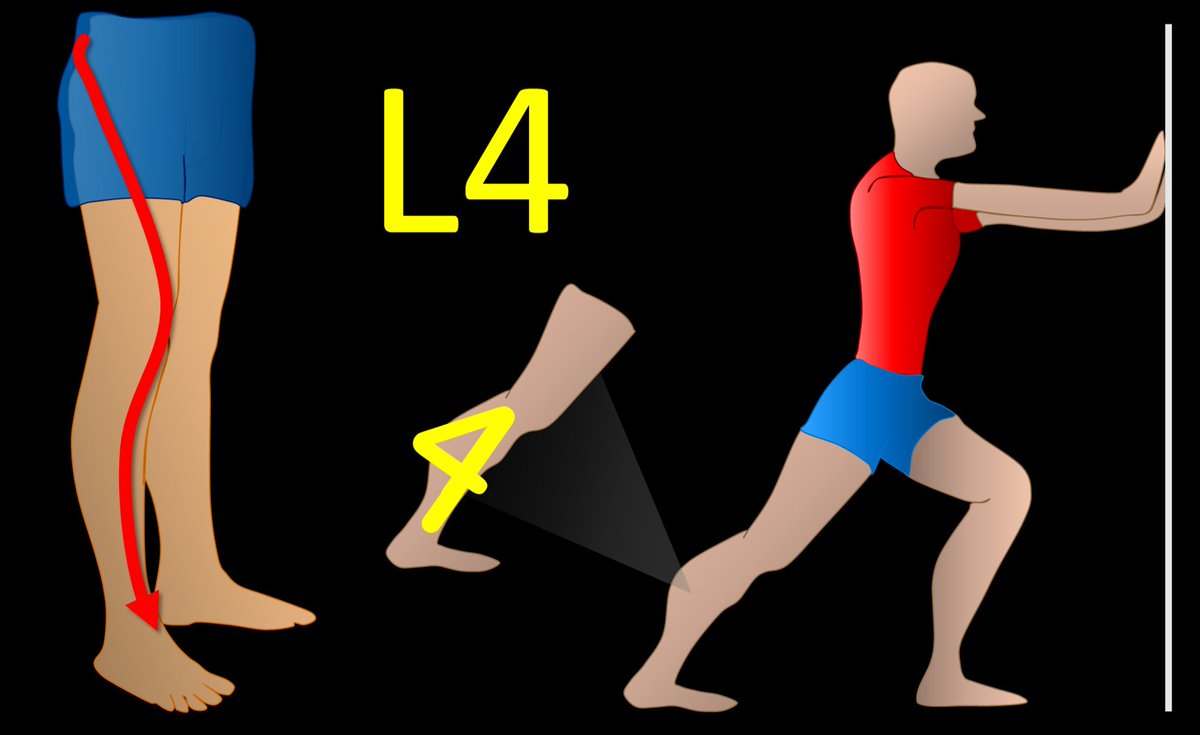
5/L4 radiates to the calf. I remember this bc the number 4 looks like the calf, with the top part of the 4 looking like a bulging gastroc & the bottom part of the four is the rest of the calf connecting to the ankle. Don’t we all wish we had bulging gastrocs like the number 4! 
6/L5 radiates to the big toe. So I have the little rhyme “Five is to the big guy!” L5 is also foot drop. So I remember big guys are heavy, and heavy gravity = drop. If I hear the history “foot drop,” I never stop looking until I have traced out the entire L5 nerve root. 

7/Finally, S1 radiates to the side of the foot. I remember this bc both S1 & Side start w/S.
So now you know where in the lumbar spine to look when a patient says the pain radiates down the leg & hopefully remembering the lumbar radicular distributions won’t cause you any pain!
So now you know where in the lumbar spine to look when a patient says the pain radiates down the leg & hopefully remembering the lumbar radicular distributions won’t cause you any pain!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh