1/Radiologist not answering the phone?Just want a quick read on that stat head CT?
Here's a little help on how to do it yourself w/a #tweetorial on how to read a head CT!
#medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medstudenttwitter #medstudent #neurorad #radres @MedTweetorials #neurosurgery
Here's a little help on how to do it yourself w/a #tweetorial on how to read a head CT!
#medtwitter #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medstudenttwitter #medstudent #neurorad #radres @MedTweetorials #neurosurgery
2/In bread & butter neuroimaging—CT is the bread—maybe a little bland, not super exciting—but necessary & you can get a lot of nutrition out of it. MRI is like the butter—everyone loves it, it makes everything better, & it packs a lot of calories. Today, we start w/the bread! 

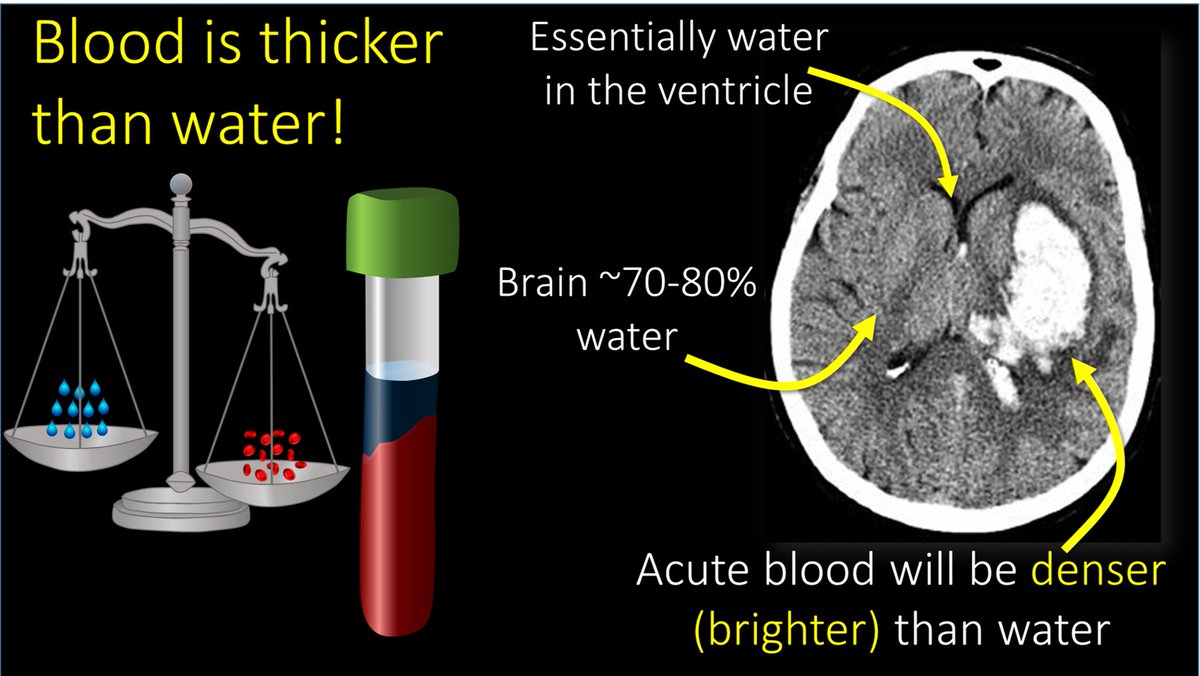
3/The most important thing to look for on a head CT is blood. Blood is Bright on a head CT—both start w/B. Blood is bright bc for all it’s Nobel prizes, all CT is is a density measurement—and blood is denser (thicker) than water and denser things are brighter on CT 
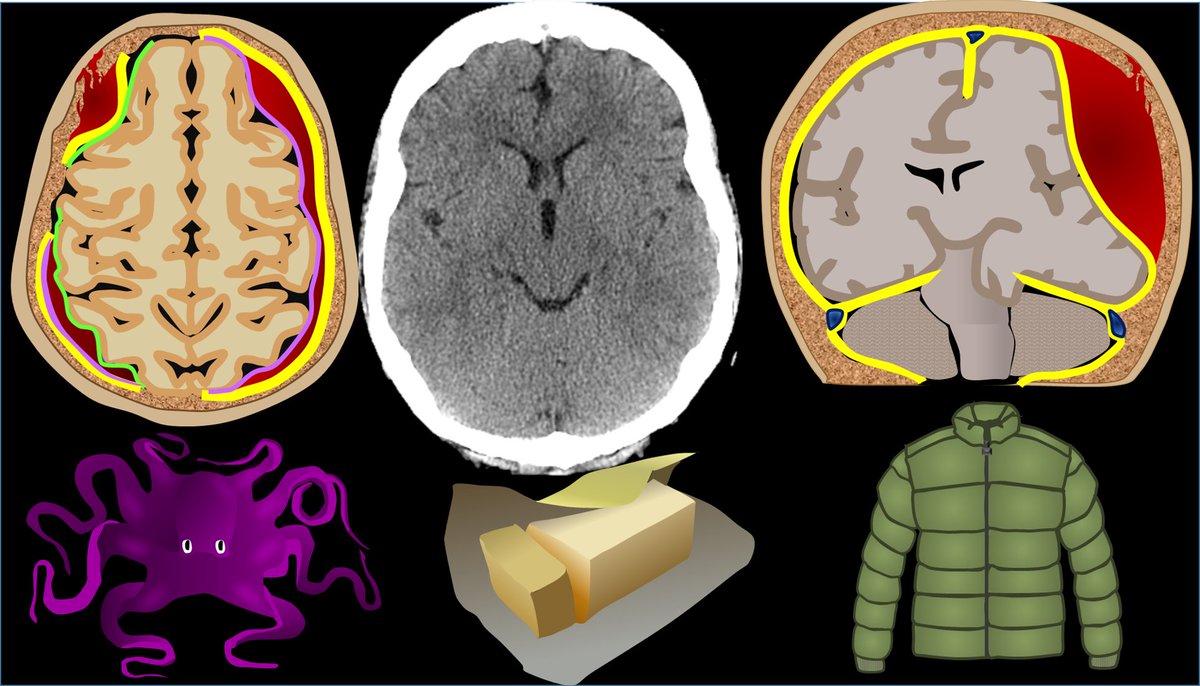
4/Once you see blood, the next question is—where is it? To know this, we need to know meningeal layers. Outer most layer is the dura mater. I remember it bc dura mater is DURAble. It is thick like a winter coat. Like a winter coat, it doesn’t hug the curves & hides rolls of fat. 

5/Inner most layer is the pia mater. It is thin and hugs the curves of the brain like an adult onsie. I remember it bc pee-ah mater is just a few letters away from pee-jay mater—so it sounds like adult onsie PJs 

6/In between these two layers is the arachnoid. It is called that because it contains web like septations like a spider’s web (ARACHnoid like ARACHnophobia). So now you know the meningeal layers. I remember the order bc the meninges “P-A-D” the brain—Pia/Arachnoid/Dura 

7/Blood can be anywhere in these layers. EPIdural is beside the dura, or outside all layers. SUBdural is below the dura, but still outside pia & arachnoid. SUBarachnoid is below both dura & arachnoid. I’m skipping intraparenchymal hemorrhage here bc that is relatively obvious. 

8/Each of these types of hemorrhage has a unique look on CT. Epidural hemorrhage is called “lentiform” bc it is convex out like a lens or a pregnant belly. Subdural hemorrhage wraps around the brain like a crescent. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is curvy between gyri like a snake 

9/So why is intracranial hemorrhage so dangerous? You won’t exsanguinate from intracranial hemorrhage like a retroperitoneal bleed. The reason intracranial hemorrhage is so dangerous is bc the calvarium is a closed space with no give for anything extra. 
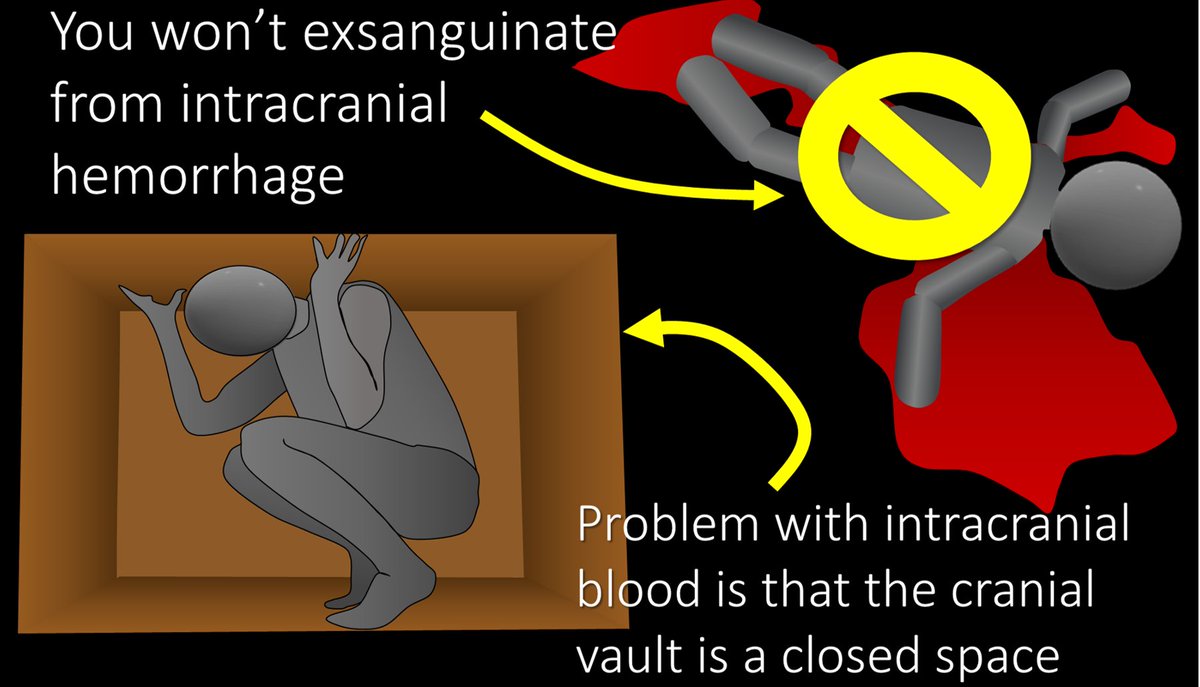
10/So when you add something extra like blood, the calvarium won’t give, and something else has to—and that’s the brain. Blood will push on the brain causing damage from the associated mass effect. 

11/Let’s talk about mass effect. Symmetry is beautiful—that’s why Denzel Washington is such the epitome of beauty bc he is perfectly symmetry. The brain on a CT should be symmetric. A CT tech once told me he could make all the findings on CTs bc all he did was look for asymmetry. 

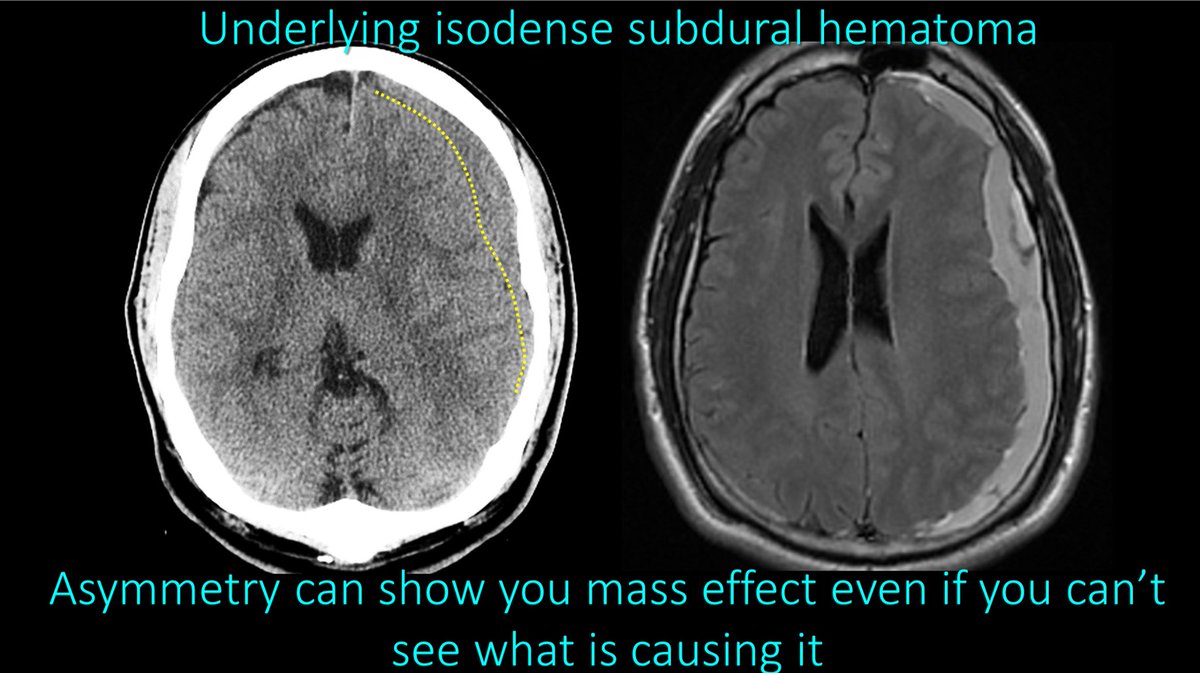
12/So on every CT you should look for symmetry—and things that are asymmetric are BAD. If you can’t draw a line down the middle have each side be a mirror image—something is wrong. 

13/This asymmetry was from an subdural hemorrhage that was the same density as brain—making it difficult to visualize, but you could tell it was there from the asymmetry it caused. Mass effect causes asymmetry 
14/Mass effect can cause brain to herniate into wrong compartments. There are 2 main herniation types. Subfalcine herniation is where one side slides under the falx to the other side. On CT, we call this midline shift—how much one side shifts under the midline to the other side 

15/Next is transtentorial herniation—where the supratentorial compartment herniates through the tentorium that separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum. We see this on CT by effacement of the basilar cisterns—which are CSF spaces at the base of the brain. 

16/The two most important cisterns for herniation are the suprasellar cistern—which looks like a pentagon—and the ambient/quadrigeminal cistern that look like the mouth of a semi-evil smiley face with the lateral and third ventricles as the eyes and nose. 

17/With transtentorial herniation, we are looking for that pentagon to become a triangle or that smiley to get a Bell’s palsy—with part of it missing. If you see either of those, there is transtentorial herniation. 

18/The final thing to look for on a head CT is a stroke. We see this as loss of gray-white differentiation. Normally, the interface between gray and white matter is crisp and looks like long octopus arms of white matter reaching out into the gray matter. 

19/With a stroke, this interface gets blurred. It is like some took a painting that had a clear line between the white and gray matter and just smeared the white matter into the gray matter. If I see anywhere where the white matter looks smeared into the gray, I call an infarct 

20/So now you know the basics of head CTs! Hopefully now your reads of the bread of neuroimaging will go smoothly like butter! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















