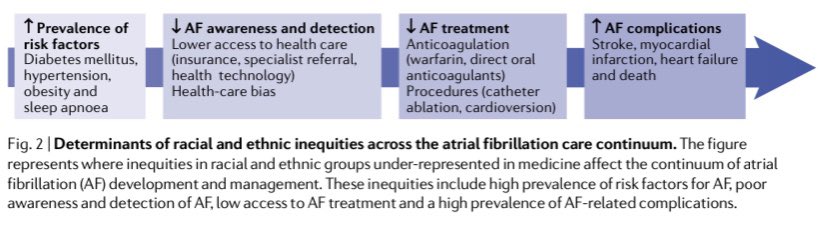
1/ 🧵 NEW Paper!
As part of a special issue on 💊 costs & access, we wrote a broad review on “Pursuing #Pharmacoequity - Determinants, Drivers, and Pathways to Progress.
We talk social & health policy, research, patient & prescriber factors. 👇🏾👇🏾
Link: tinyurl.com/nvtamek8
As part of a special issue on 💊 costs & access, we wrote a broad review on “Pursuing #Pharmacoequity - Determinants, Drivers, and Pathways to Progress.
We talk social & health policy, research, patient & prescriber factors. 👇🏾👇🏾
Link: tinyurl.com/nvtamek8

2/ Understanding the multilevel determinants that influence equitable access to medications (and trying to do so in <5000 words (!) was the goal of our review.
With so many factors out there, we know we only began to scratch the surface.
read.dukeupress.edu/jhppl/article/…
#Pharmacoequity
With so many factors out there, we know we only began to scratch the surface.
read.dukeupress.edu/jhppl/article/…
#Pharmacoequity

3/ A few topics we discussed:
🔴 Public transportation & geographic access to pharmacies
🔴 Income and wealth inequities
🔴 Research representation
🔴 Health insurance coverage (e.g., ACA & Medicare Part D)
🔴 Clinician bias & trustworthiness
🔴 Patient primary language
🔴 Public transportation & geographic access to pharmacies
🔴 Income and wealth inequities
🔴 Research representation
🔴 Health insurance coverage (e.g., ACA & Medicare Part D)
🔴 Clinician bias & trustworthiness
🔴 Patient primary language
4/ Along with the drivers, we discuss some possible solutions:
🟢 Decreasing cost of drugs
🟢 Provide low-cost drug coverage for uninsured & under-insured
🟢 Reduce geographic barriers to pharmacies
🟢 Engage community in developing interventions to increase pharmacoequity
🟢 Decreasing cost of drugs
🟢 Provide low-cost drug coverage for uninsured & under-insured
🟢 Reduce geographic barriers to pharmacies
🟢 Engage community in developing interventions to increase pharmacoequity

5/5 This #Pharmacoequity review was a definite labor of love.
Amazing to work with rockstar med students @rohanchalasani & @sudkrish who led the paper, and get pharmacy (@Sudamonas & Dr. Terri Newman) and legal (@S_Delaney) expertise while writing this.
read.dukeupress.edu/jhppl/article/…
Amazing to work with rockstar med students @rohanchalasani & @sudkrish who led the paper, and get pharmacy (@Sudamonas & Dr. Terri Newman) and legal (@S_Delaney) expertise while writing this.
read.dukeupress.edu/jhppl/article/…

P.S. One of the best parts about writing this was we had to be extremely thoughtful about our citations.
More than ever we need more work that helps to place 💊 policy in the historical context of the writing from these amazing authors.
#Pharmacoequity
tinyurl.com/nvtamek8
More than ever we need more work that helps to place 💊 policy in the historical context of the writing from these amazing authors.
#Pharmacoequity
tinyurl.com/nvtamek8

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh