1/When it comes to brachial plexus pathology, you shouldn’t have to wing it! A #tweetorial to help you figure out #brachialplexus injuries
#medtwitter #meded #neurosurgery #orthotwitter #orthopedics #neurorad #radres #medstudent #FOAMed #FOAMrad #spine #radiology #neurotwitter
#medtwitter #meded #neurosurgery #orthotwitter #orthopedics #neurorad #radres #medstudent #FOAMed #FOAMrad #spine #radiology #neurotwitter
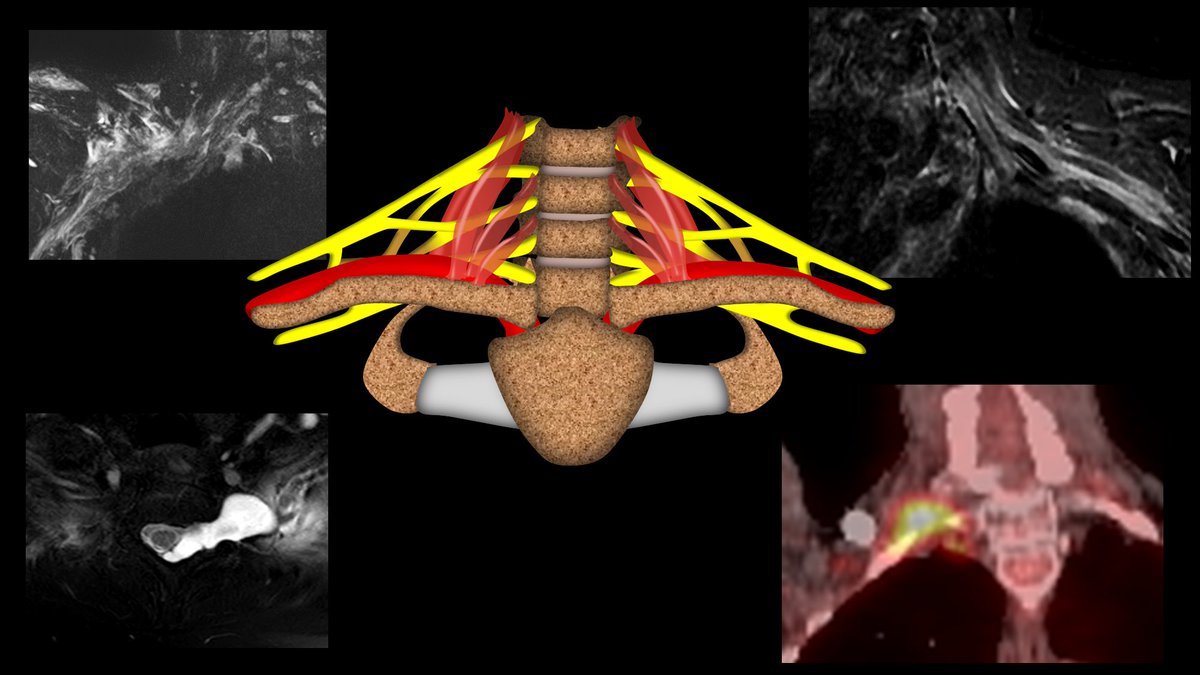
2/When it comes to brachial plexus injuries, the most important distinction to make is whether it is a pre or post ganglionic injury. Pre ganglionic injuries are nerve root avulsions from the spinal cord and cannot be repaired, while most post ganglionic injuries can be repaired 

3/It’s like repairing a house. If there’s a structural flaw at the beginning, before you’ve even built it, you won’t even try to build it, you’ll just scrap the design (preganglionic). But if there’s damage after the house is built, you can salvage it w/repair (postganglionic) 

4/Preganglionic injuries often have an associated pseudomeningocele. This is bc when you rip the nerve root out, you also rip the dura—like pulling the cork out of a champagne bottle—and CSF will leak, creating a collection. 

5/Another sign of a preganglionic injury is that there is no identifiable nerve root. B/c the nerve root has been ripped out and retracted, you will not see it in the thecal sac. The nerve root sleeve will also be empty—an empty shell of where the nerve root used to be. 

6/For plexus injuries, remember, the plexus is how cervical nerve roots jump down to the arm—kind of like a bungee jumper—tied to the top while jumping down to the bottom. So all the bad things that can happen to a bungee jumper can help us remember what harms the brachial plexus 

7/First problem on the way down—the bungee cord attachment rips off—and you are left free falling 😬. This is like a preganglionic injury. And just like what happens to the jumper when the cord attachment rips off--there is no salvage w/this type of injury 

8/Remember, for preganglionic injuries, look to see if the nerve root is missing and look for the characteristic pseudomeningocele. 

9/Next problem on the way down—getting hit by external objects flying through the air. This is like radiation therapy—it comes flying from outside to hit the brachial plexus. 

10/Radiation plexopathy will show long segment or diffuse thickening or enhancement of the plexus, but there won’t be an identifiable focal mass. Where you see the thickening depends on the cancer treated. Head & neck XRT will affect higher, while lung XRT will affect lower. 

11/Next problem on the way down—crashing into something in the vicinity. This is like trauma. The brachial plexus can crash into the clavicle in front of it, like crashing into the rocks below. It can also be stretched as well. 

12/Three main things to look for w/traumatic plexus injury. (1) Edema will usually indicate injury. (2) Thickening could hide a neuroma in continuity, so it needs follow up, (3) Discontinuity—nerve is disrupted. Postganglionic disruptions can possibly be repaired w/microsurgery 

13/Where the injury occurs determines if it can be repaired. The Nagano injury zones show that while we knew we couldn’t repair preganglionic injuries, post ganglionic injuries not past the foramen are too difficult to repair. So if it’s not out of the foramen, it’s foregone! 

14/Finally, the jumper can get eaten by something—this is involvement by tumor. It can be an intrinsic tumor like a schwannoma, or metastases from something like breast, but most commonly, it is direct invasion by a Pancoast lung tumor. 

15/A tumor can be differentiated from radiation changes by seeing a focal mass. Because Pancoast lung tumors come from below, they usually affect the lower nerve roots, C7 and T1. 

16/So now you can remember the brachial plexus pathologies by remembering the unfortunate things that can happen to a bungee jumper on the way down. So while brachial plexus injuries may cause winging—when it comes to diagnosing these injuries, you won’t have to wing it! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















