#Ramayana-Hindu Culture spread throughout Asia via the Rama Story. It travelled by sea and land to China, Tibet, Turkestan, Java, Sumatra, Malaya, Burma, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and Cambodia.
#Thread
1/26
#Thread
1/26

Most countries have adapted Rama Story acc. to their own culture with a local setting; the Indian names are used for important towns, sites, mountains, rivers, and lakes.
The adoption of Valmiki Story in Asian countries was selective and influenced by local values
2/26
The adoption of Valmiki Story in Asian countries was selective and influenced by local values
2/26

In China, The Buddhist work Mahavibhasa (150ce) is oldest record of Ramayana. Hsuan Tsang stated "There is a book called the Rāmāyaṇa...[it] explains only two topics: namely Rāvana carrying Sītā off by violence and Rāma recovering Sītā and returning."
pic @CliosChronicles
3/26
pic @CliosChronicles
3/26

Rama story in China exists in the form of two Jätaka tales: of an unnamed king called the Anamaka Jātakam, and the Nidana of King Ten-Luxuries, called the Dasarata Katha
The Buddhist who brought Rama story to China has transformed it into Buddhist describing Buddha as Rama
4/26
The Buddhist who brought Rama story to China has transformed it into Buddhist describing Buddha as Rama
4/26

Rama's enemy is his own maternal uncle, who usurps his throne. His wife is abducted by Naga. Rama retires to forest instead of war. In the end, serpent and uncle dies. King's wife proves her chastity by entering into earth
5/26
5/26

In Tibet, there is another version other than 2 chinese versions. In this version, Sita is shown as daughter of Ravana, who was thrown into sea, found by farmers given to Janaka later destroys her father. Obviously, this is not in orig. Ramayana or Ramcharitmanas
6/26
6/26
https://twitter.com/Advaidism/status/1283255506547572736
East Turkestan
Rāma story in East Turkestan dates back from the ninth century A.D. The Rāmāyaṇa of East Turkestan, unlike the Tibetan Rāmāyana, does not have the Uttara Kanda
7/26
Rāma story in East Turkestan dates back from the ninth century A.D. The Rāmāyaṇa of East Turkestan, unlike the Tibetan Rāmāyana, does not have the Uttara Kanda
7/26

Vietnam
The Annamites have given it a local orientation. Champa, kingdom of 10-heads (Ravana) and Annam kingdom of the Ten-chariots (Dasaratha) were enemies. the Champa king abducts Annamite king's wife. Annammite builds a causeway across the sea and recovers the Queen.
8/26
The Annamites have given it a local orientation. Champa, kingdom of 10-heads (Ravana) and Annam kingdom of the Ten-chariots (Dasaratha) were enemies. the Champa king abducts Annamite king's wife. Annammite builds a causeway across the sea and recovers the Queen.
8/26
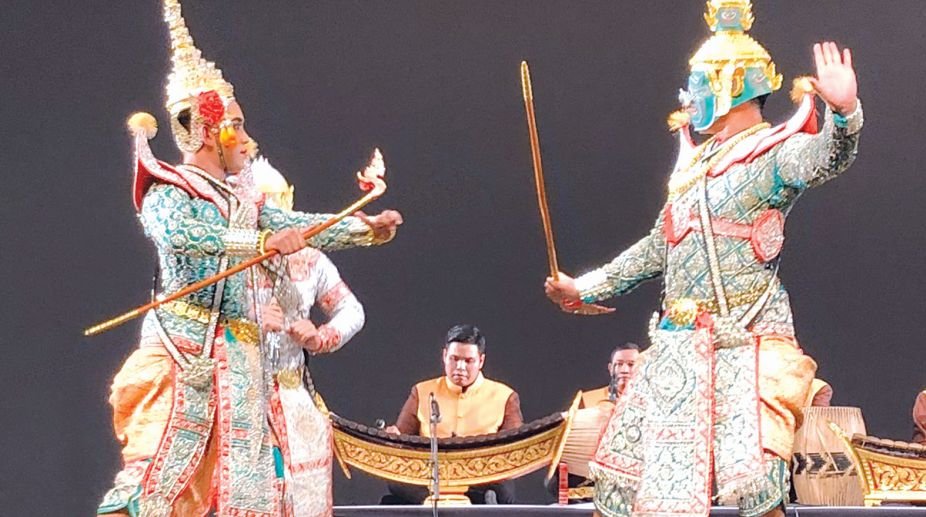

Indonesia
The several literary versions in Indonesia are the Kākāwin Rāmāyaṇa, the Serat Ram, the Javanese Uttara Kanda (existing as a separate work), the Carit Rāmāyaṇa, the Serät Kända, and the Rama Kling.
9/26
The several literary versions in Indonesia are the Kākāwin Rāmāyaṇa, the Serat Ram, the Javanese Uttara Kanda (existing as a separate work), the Carit Rāmāyaṇa, the Serät Kända, and the Rama Kling.
9/26

The Javanese Kakawin Ramayana, a story from Kashmir (5th ce) doesn;t have Bala Kanda and Uttra Kanda. Since Kakawin closely follow Valmiki Ramayana, it must be based on version of Rama story b4 1st and last kand were added to Valmiki's Ramayana
10/26
10/26

The other Javanese ver. 'Serät Kända' has interesting part, Mandodari is wife of Dasaratha, later given away to Ravana, Sita is the daughter of Mandodari in Serat Kanda unlike Tibetan. Sita is banished for drawing Ravana portrait.
Sita gives birth to only one son
11/26
Sita gives birth to only one son
11/26
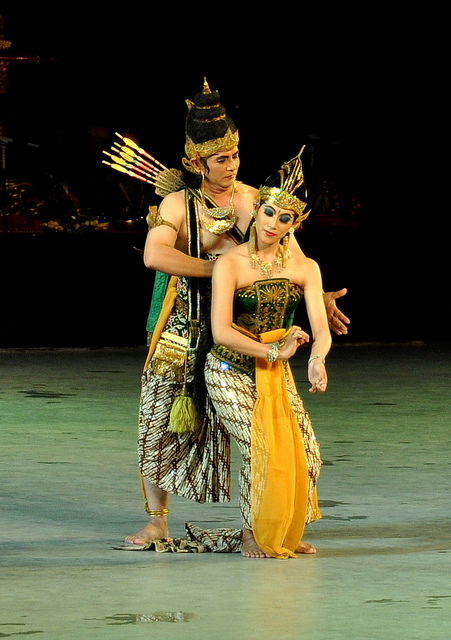

In another story 'Maiyarab' in javanese ver Serat, Rama goes to underworld and meets his 2 sons and war takes place between father and sons.
12/26
12/26
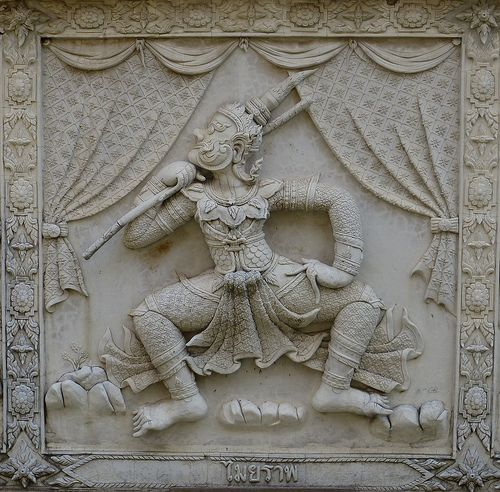

Malaya Ramayan called Hikayat Seri Ram is based completely on Serat Kanda with many musIim legends.
13/26
13/26
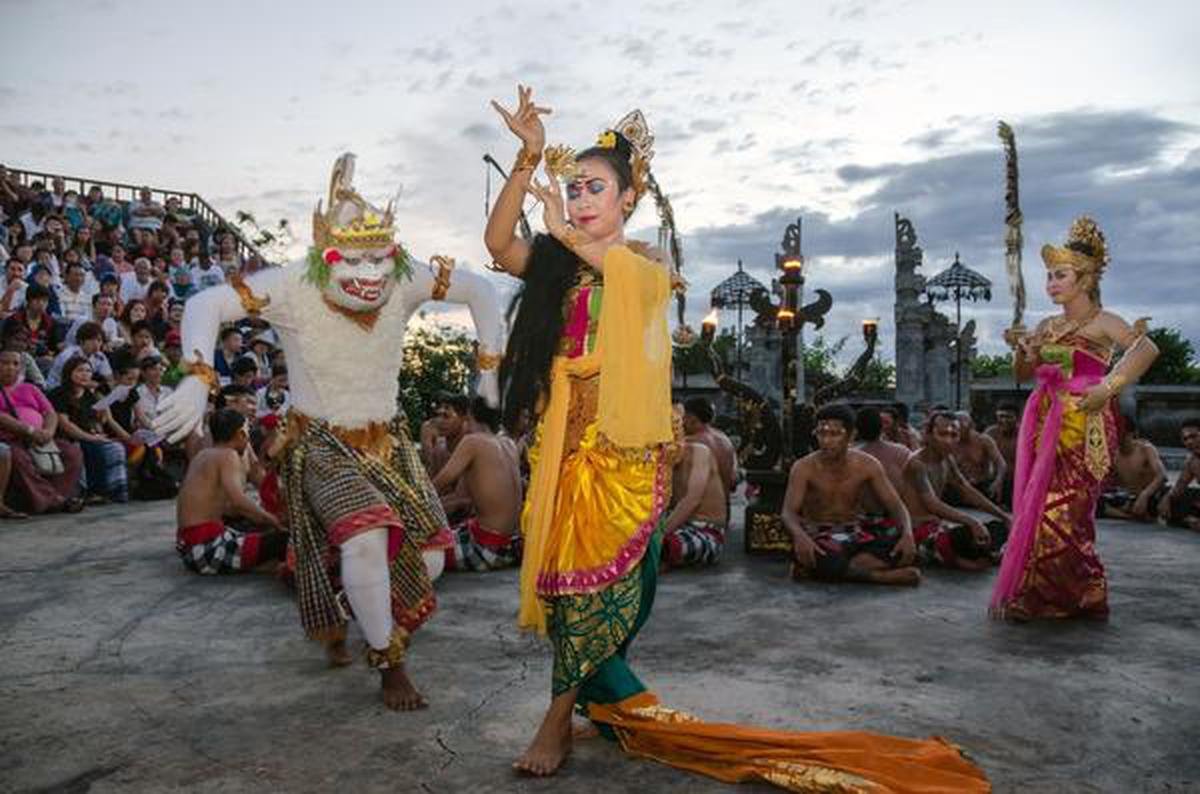

Cambodian Rama story 'Riemkerr' differs considerably from Valmiki Ramayana and somewhat closure to Thai Ramayana. Riemkerr ends with the union of Rama and Sita.
14/26

14/26


Thai Rama Story in literary form was written in 1798-1809 ce. in verse form for staging of masked play 'Khon'. This ver. also doesn't tally with Valmiki's ver. Sita in Thai Ramakirti is daughter of Ravana, banished for drawing portrait, bears one son, fight b/w father son
15/26
15/26
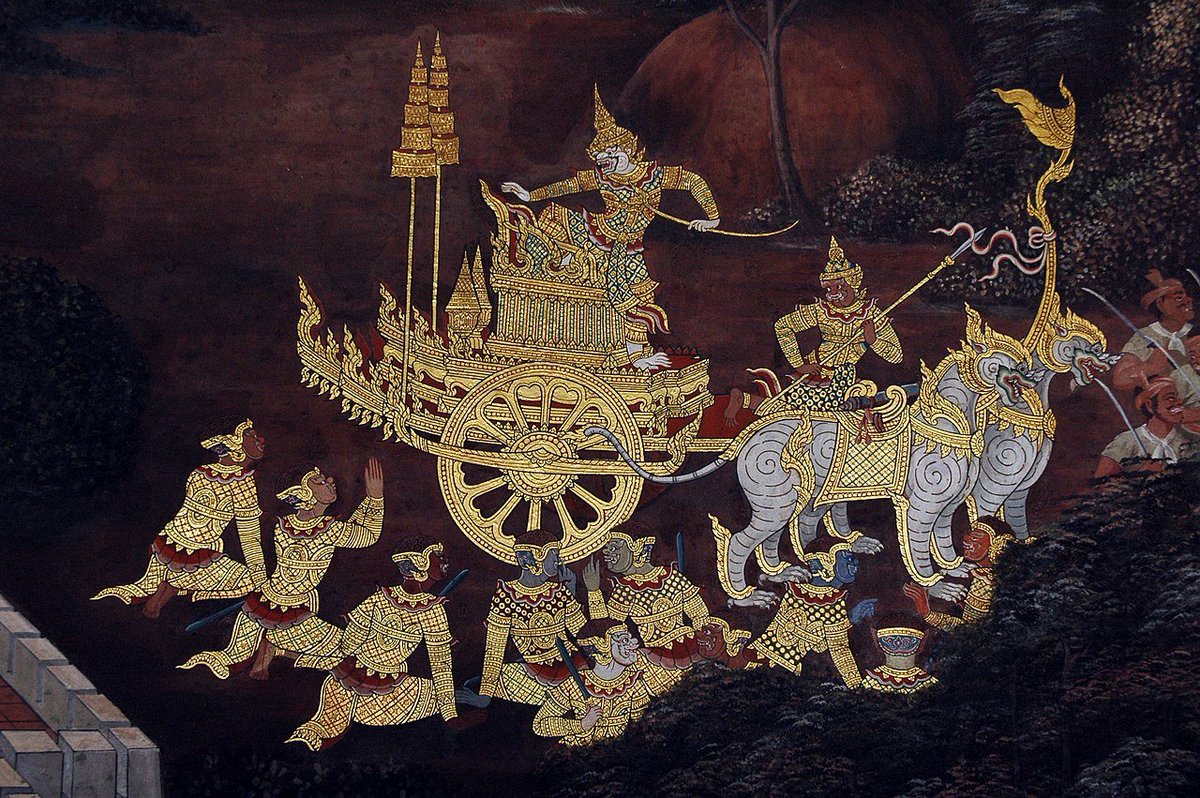

In Laotian literature, a tale of Dasratha and a tale of Rama is found in Mandu-Pakron. The Dasratha tale deals with Rama exile and Tale of Rama describes Sita's abduction ensuing a war.
This version some what agrees with Valmiki's Ramayana.
16/26

This version some what agrees with Valmiki's Ramayana.
16/26


In Burmese Ramayana, Ranava sends a stag to lead Rama away from Sita. The story has local setting in connection to healing herb which Hanumana brings from Mount Popa instead from Himalayas
Pic blogs.bl.uk/asian-and-afri…
17/26

Pic blogs.bl.uk/asian-and-afri…
17/26


This background of the diversity of the Rama story within India itself, it is possible now to account for the non-Välmiki elements of the Rāma story in Asia. Most of these non-Välmīki episodes are traceable to India in the regional Rāmāyaṇas,
18/26
18/26
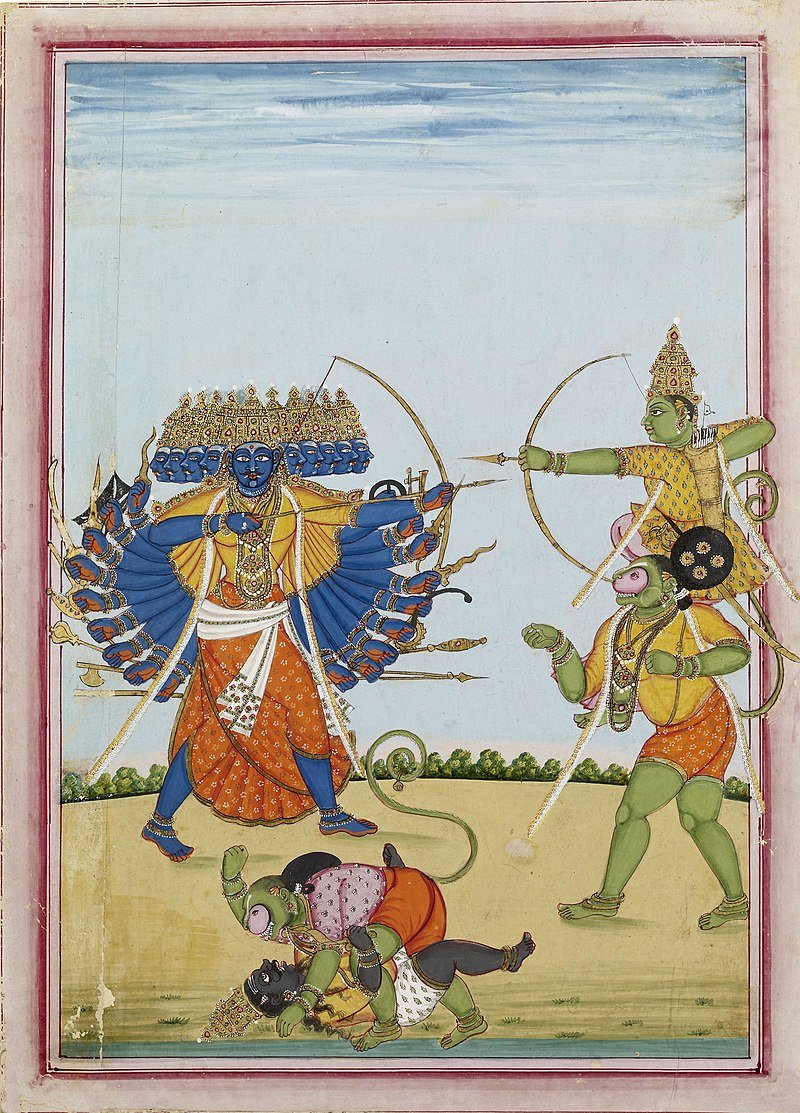

The regional versions contain most of the important non-Valmiki elements of the Asian version:
1. Parentage of Sitä (Kashmiri Rāmāyaṇa);
2. Recognition of Ravana's qualities (Jain and Kamban Rāmāyaṇas)
3. Episode of Maiyarab (Bengāli Rāmāyaṇa of Krittibāsa);
19/26
1. Parentage of Sitä (Kashmiri Rāmāyaṇa);
2. Recognition of Ravana's qualities (Jain and Kamban Rāmāyaṇas)
3. Episode of Maiyarab (Bengāli Rāmāyaṇa of Krittibāsa);
19/26
4. Reason for the second banishment of Sitä (Jain Rāmāyaṇa, Bengāli Rāmāyaṇa of Krittibāsa and Kashmiri Rāmāyaṇa)
5. miraculous creation of Sita's second son (Käshmiri Rāmāyaṇa);
Rāma's war with his sons (Bengali Rāmāyaṇa of Chandravati and Kashmiri Rāmāyaṇa)
20/26
5. miraculous creation of Sita's second son (Käshmiri Rāmāyaṇa);
Rāma's war with his sons (Bengali Rāmāyaṇa of Chandravati and Kashmiri Rāmāyaṇa)
20/26
6. the final union of Rama and Sītā (Bhavabhūti's Uttara- ramacharita).
21/26
21/26
The Välmīki Rāmāyaṇa depicts Hindu dharma of personal life, family life, and social order. As regards personal and family life, the Välmīki Rāmāyaṇa creates ideal human characters in Räma, Lakṣmaṇa, Bharata, Kausalya, and Sītā.
22/26
22/26
It emphasizes the ideal relationships between father and sons, between brothers, and between husband and wife.
Valmiki Rāmāyaṇa lays down the character of an ideal woman and man. Rāma and Sīta are the Hindu ideals of the Perfect Man and the Perfect Woman.
23/26
Valmiki Rāmāyaṇa lays down the character of an ideal woman and man. Rāma and Sīta are the Hindu ideals of the Perfect Man and the Perfect Woman.
23/26
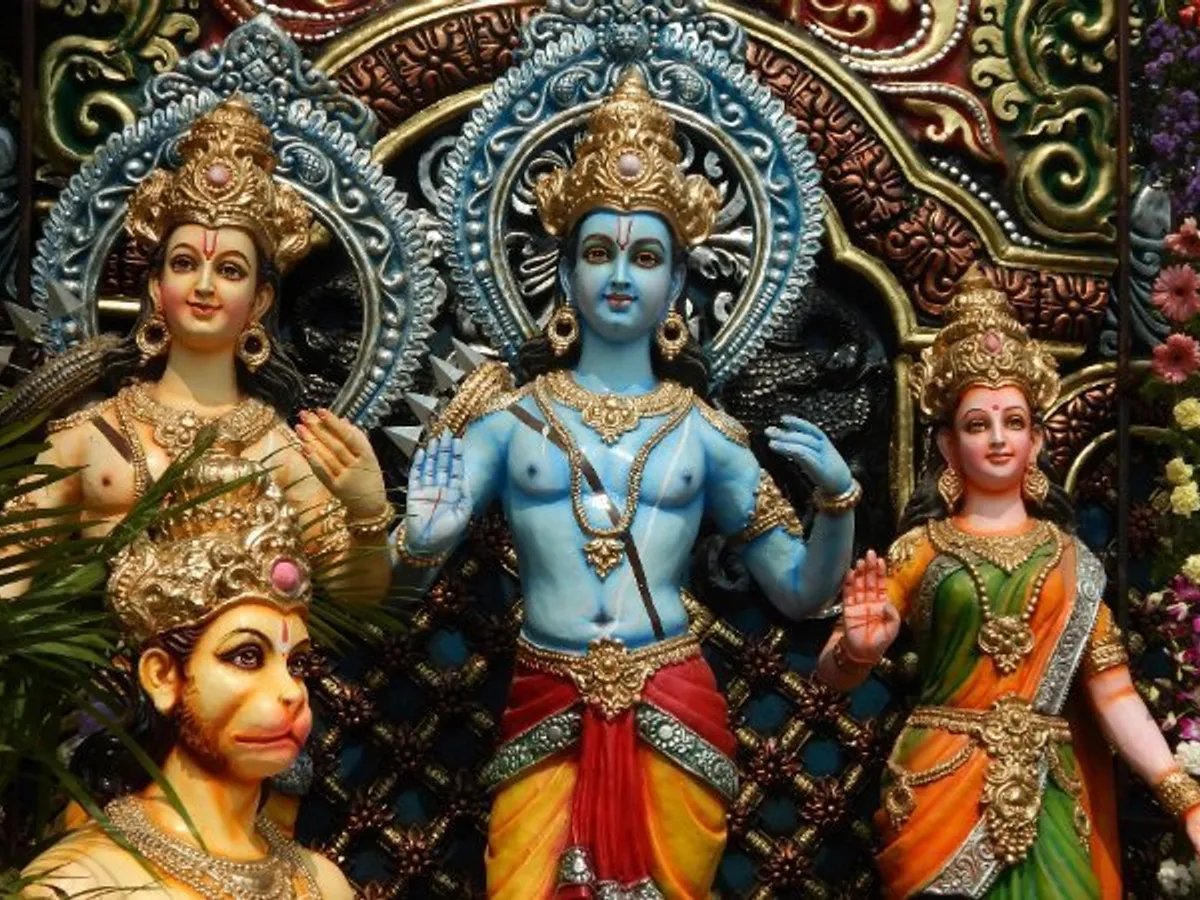
The Valmiki Rāmāyaṇa also depicts the Hindu ideal of a perfect life of righteousness. To live right a person has to undergo sorrow, suffering, trial, and endurance
24/26
24/26

Src
jstor.org/stable/2942721
The Journal of Asian Studies
Vol. 30, No. 1 (Nov., 1970), pp. 5-20
jstor.org/stable/4527910
Disclaimer : none of the information or pic in this #Thread is mine.
25/26
jstor.org/stable/2942721
The Journal of Asian Studies
Vol. 30, No. 1 (Nov., 1970), pp. 5-20
jstor.org/stable/4527910
Disclaimer : none of the information or pic in this #Thread is mine.
25/26
I hope you've found this thread helpful.
Follow me @GemsOfINDOLOGY for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
26/26
Follow me @GemsOfINDOLOGY for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
26/26
https://twitter.com/GemsOfINDOLOGY/status/1593263552030068736
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




















