1/Ready for a throwdown? MMA fights get a lot of attention, but MMA (middle meningeal art) & dural blood supply doesn’t get the attention it deserves.
A #tweetorial on dural vascular #anatomy
#neurosurgery #neurorad #Neurointervention #radres #medtwitter #neurotwitter #meded
A #tweetorial on dural vascular #anatomy
#neurosurgery #neurorad #Neurointervention #radres #medtwitter #neurotwitter #meded

2/Everyone knows about the blood supply to the brain. Circle of Willis anatomy is king and loved by everyone, while the vascular anatomy of the blood supply to the dura is the poor, wicked step child of vascular anatomy that is often forgotten 

3/But dural vascular anatomy & supply are important, especially now that MMA embolizations are common for chronic recurrent subdurals. It also important for understanding dural arteriovenous fistulas as well. 

4/Although we talk about individual vessels feeding the dura, it should actually be thought of more as a vascular network. Anastomoses among the dural vessels are common and plentiful, as is often seen with external carotid networks. 

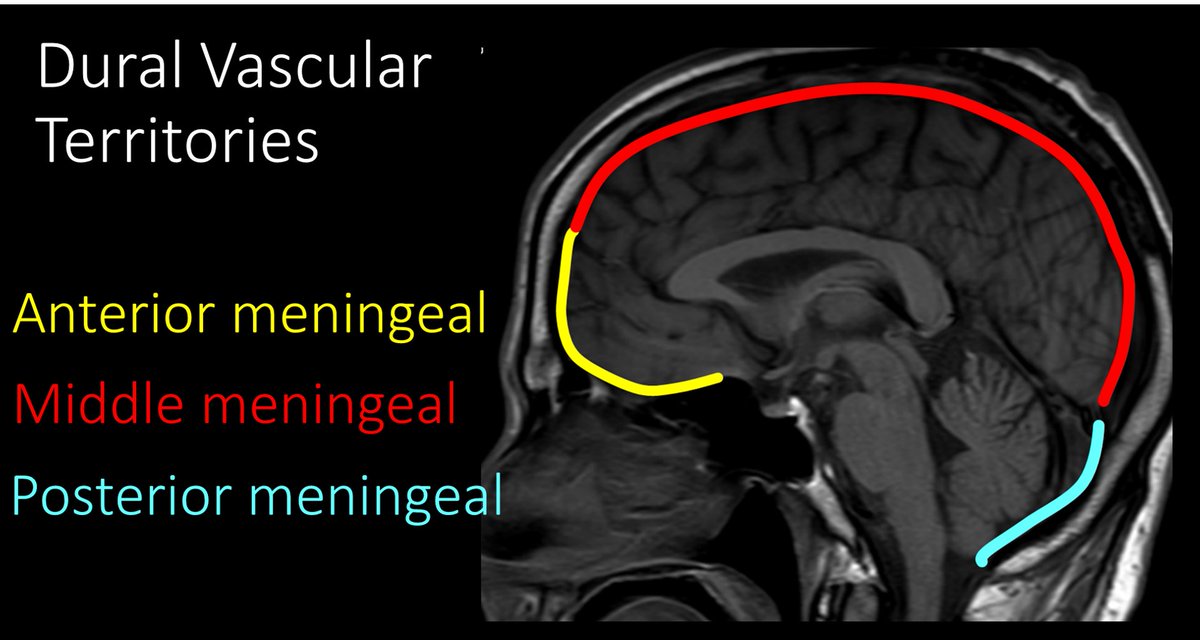
5/The largest & most important dural vessel is the middle meningeal artery or MMA. It arises from the internal maxillary artery or IMAX. I remember that b/c Mortal Kombat & other MMA type fighting is commonly shown in IMAX theaters. 

6/MMA enters at foramen spinosum.
At the skullbase, foramen ovale & spinosum together look like a high heel shoe footprint
Spinosum is the heel of the footprint. I remember this b/c that’s the high heel spike and SPinosum & SPike sound alike. I always look for this footprint
At the skullbase, foramen ovale & spinosum together look like a high heel shoe footprint
Spinosum is the heel of the footprint. I remember this b/c that’s the high heel spike and SPinosum & SPike sound alike. I always look for this footprint

7/After spinosum, the MMA takes a sharp, corkscrew-like turn lateral & anterior following the curvature of the middle cranial fossa.
This gives it a very characteristic angiographic appearance—always look for the sharp turn.
I remember that the artery SPINs after SPINosum
This gives it a very characteristic angiographic appearance—always look for the sharp turn.
I remember that the artery SPINs after SPINosum

8/MMA immediately gives off a tiny petrous branch and then splits into anterior (frontal) & posterior (parietal) divisions. I think it looks like an MMA fighter celebrating their victory with their two arms in the air 

9/Post division is smaller & has branches covering the posterior convexity. Its territory is draped over the back of the calvarium the way MMA fighters drape flags over their backs after winning. So it covers the back of the calvarium like the flag covers the MMA fighter’s back 

10/Ant division is larger & has branches that anastomose to the contralateral MMA. You can remember this b/c opposing MMA fighters touch gloves before the fight, and gloves are out in front. So ant division touches the opposite side like opponents touching gloves before a fight 

11/Anterior division passes under the pterion, a junction of four calvarial bones. This renders it vulnerable to trauma & resulting epidural hemorrhage. This is easy to remember—the forward facing or anterior part of an MMA fighter (his face) is very vulnerable to injury 

12/Posterior meningeal artery is much smaller than the MMA. It arises from the ascending pharyngeal artery and supplies the dura to the posterior fossa. It also has anastomoses with the posterior division of the MMA. 
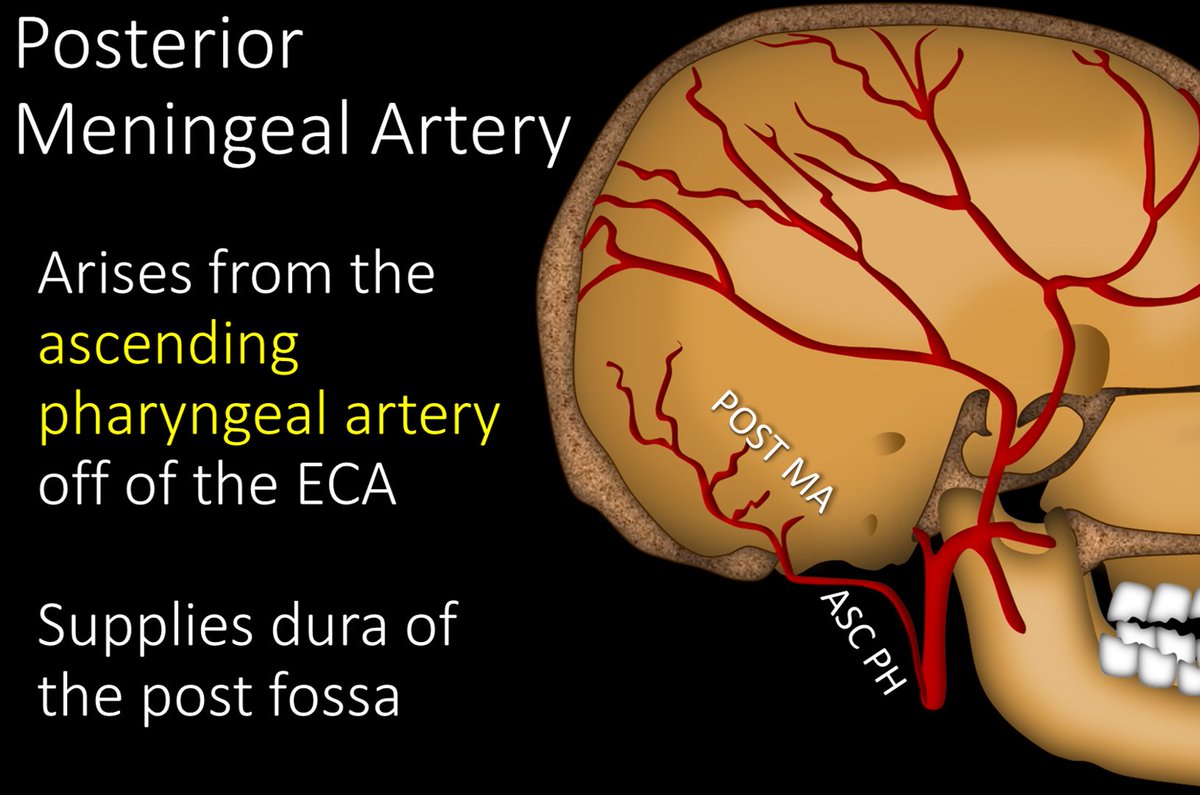
13/You can remember its origin bc TONSILS are in the PHARYNX, so the ascending PHARYNGEAL supplies the dural around the cerebellar TONSILS (posterior fossa) 

14/Anterior meningeal artery is also much smaller than the MMA. It arises from both the anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries. It supplies the dura of the anterior cranial fossa. It has many anastomoses with the frontal branches of the MMA 

15/You can remember its origin bc the anterior meningeal artery supplies the dura overlying the ethmoids, so it would make sense it arises from the ethmoidal arteries 

16/Uniquely, as it ascends, the anterior meningeal artery actually runs in the wall of the anterior superior sagittal sinus. It is the only named artery to run in the wall of a sinus. 

17/Now you know the anatomy of the major arterial supply to the dura & their territories. So the next time someone questions you about dural blood supply, you can attack it MMA style! 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















