
🧵Private/Public key pairs.
My first ever thread on #crypto with #Private and #Public keys and how they work.
My first ever thread on #crypto with #Private and #Public keys and how they work.
1/ I am going to do a general overview skipping all the complex math so that its easy to understand. A private and public key pair control access to a wallet. This can be a custodial wallet on an exchange, a hot wallet or even a cold wallet.
2/ The major difference is that a private and public key pair created on an exchange is controlled by that exchange. You have no control over that Custodial Wallet other than what that exchange allows you. A software or hardware wallet gives you control over your keys.
3/ The cryptocurrency itself never leaves the blockchain. Its always alive on the blockchain. All you control is moving that crypto into a public crypto address for which you control the private keys that control access to the public address. 

4/ The private key is a random 256 bit number. Depending on the blockchain, it can be 256 binary or hexadecimal number. Its just a number. When you create a wallet, you get a seed phrase that is 12 or 24 words.
5/ Those words use a system called BIP39 to translate that 256 bit number into a mnemonic of 12 or 24 words. These come form and represent the private key. This means you can take your private seed phase and use it in any wallet that supports BIP39 protocol. 

6/ You can take the seed phrase from Trust Wallet and use it in Exodus wallet or Metamask and vice versa. As long as those wallets use the same BIP39 protocol. That private key is like a password for access to that public address on the blockchain which holds all that crypto.
7/ Another easy way to think of the relationship of the private key and public key is to used email. You have a public email address that you can give out to anyone and get email.
8/ Only you have the password to get into that email to account. The public key is like the email address and the private key is like your email password.
9/ The public address is generated from the 256 bit private key. Its just another 256 bit number generated from a special algorithm called an Elliptical Curve Algorithm. This uses some random generated numbers to extrapolate the public key number. 
10/ The public key is used to generate a public address after it gets hashed. This varies by blockchain for the creation of the public address from the public key. Bitcoin uses SHA256 to hash it then takes that and hashes it with another algorithm to get a public address. 

11/ Then it adds the bc1 on the beginning for the full address. The Ethereum blockchain uses Keccak256 to has the public key and takes the first 40 bytes and adds the 0x to the beginning. 

12/ When you create a wallet, you make the private key and public key pair. The private key is your 12 or 24 word seed phase. The public key is used to generate the public address for that wallet. Then you can send crypto to that public address.
13/ One benefit is that a private key can be used with the algorithm to come up with many public keys. This is used often today to generate a new public key for each transaction. This help provide privacy as you are not always using the same public address over and over.
14/ The crypto doesn't go into your wallet. It goes into that public address that lives on the blockchain and you have a private key seed phase to control that public address.
15/ This is an important concept because if a wallet is ever destroyed like a hardware wallet or you break your phone with your software wallet on it, you can go get a new one and use your seed phase to recover access to that public address where your crypto is stored.
16/ This is also important because, if you lose your seed phrase, you lose control of your crypto. Anyone who gets that seed phrase can take control of that public address and move your crypto anywhere they wish.
17/ When you create a transaction, you sign it with your private key. This is done through a digital signature algorithm. No one ever sees your private key but you.
18/ Anyone who has your public key and use it to verify that signature, but can't see your private key from that public key. 

19/ When you create a message, it is signed with your private key and then encrypted with the receivers public key so only they can access that transaction or message. Only the receiver can decrypt that message using their private key as it was encrypted with their public key. 
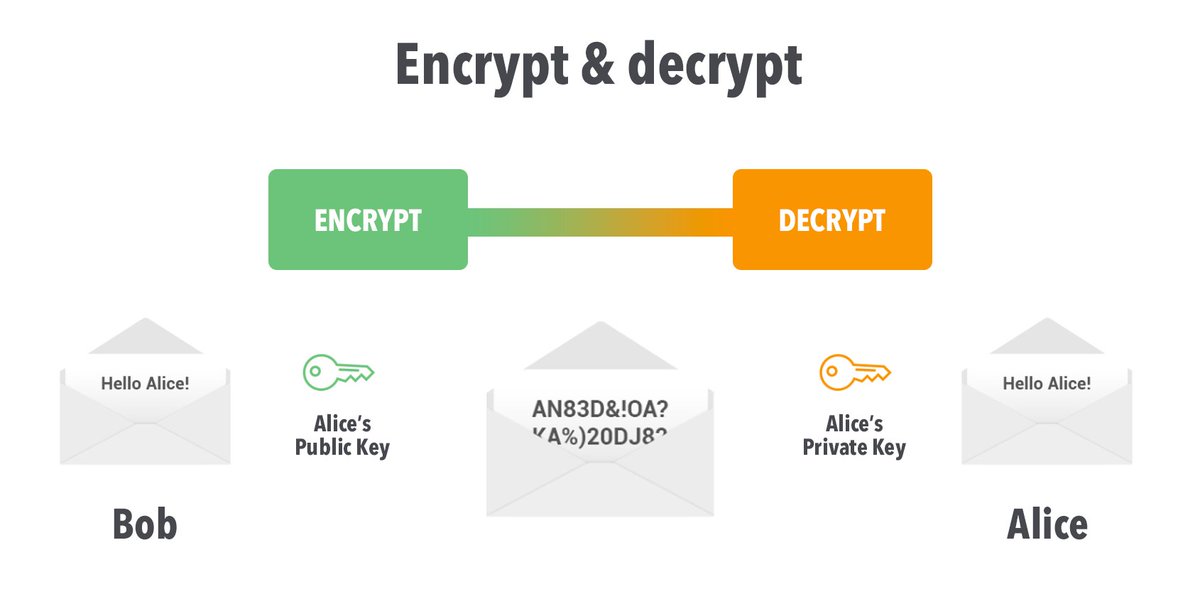
20/ This is the basics of Private Key and Public keys in cryptocurrencies. Its also how you control the access to your crypto my controlling you private key seed phrase. It also shows how those keys are used to create and receive transactions.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh











