1/Time to FESS up! Do you understand functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)?
If you read sinus CTs, you must know what they’re doing to make the helpful findings
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you!
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #FOAMrad #radres #neurorad #HNrad #radtwitter
If you read sinus CTs, you must know what they’re doing to make the helpful findings
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you!
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #FOAMrad #radres #neurorad #HNrad #radtwitter
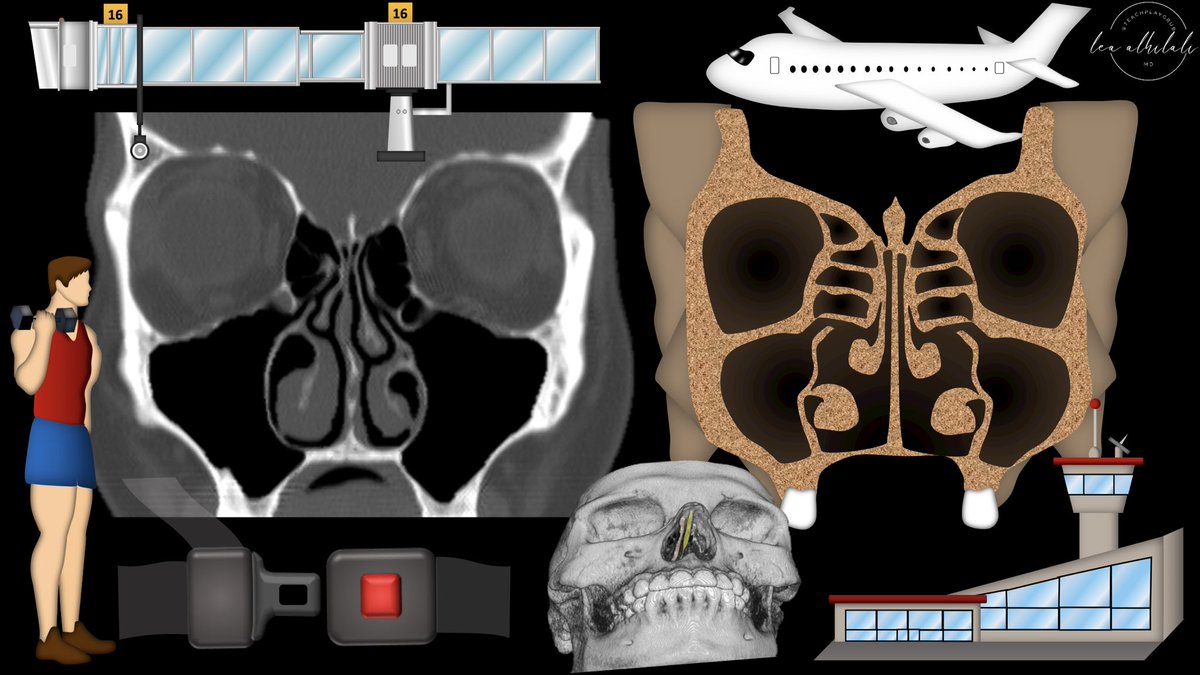
2/The first step is to insert the endoscope into the nasal cavity.
The first two structures encountered are the nasal septum and the inferior turbinate.
The first two structures encountered are the nasal septum and the inferior turbinate.

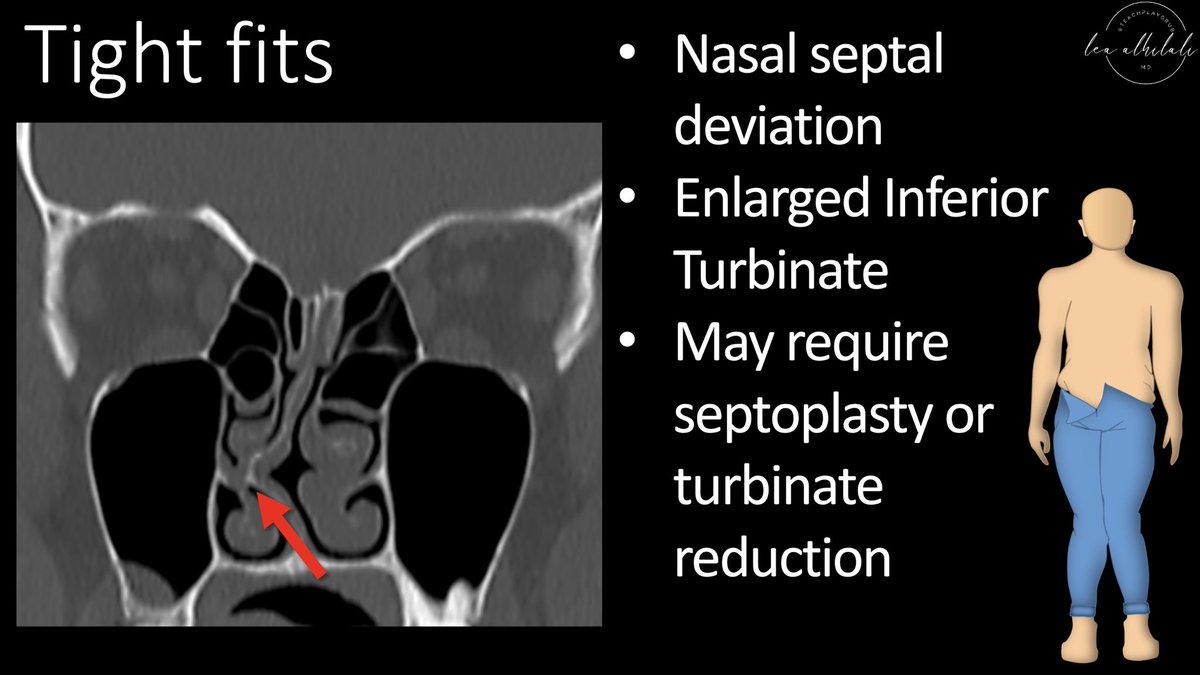
3/So on every sinus CT you read, the first question is whether there is enough room to insert the scope. Will it go in smoothly or will it be a tight fit? 

4/Prominent nasal septal deviation or enlarged turbinates can make it difficult. It is important to alert the surgeon to these. This may require a septoplasty or turbinate reduction in addition to the FESS, and you want them to be aware ahead of time 
5/Next step is advancing the endoscope to the middle turbinate. It is an important landmark in FESS. Previously, FESS would often fail b/c of adhesions occurring after surgery between the mid turbinate & lateral nasal cavity wall—causing a new obstruction 

6/So now, to prevent this, the middle turbinate is medialized.
A suture used to tie the turbinate to the nasal septum—keeping it medial, like a seat belt holding you in place.
Eventually, scar will make the positioning permanent.
A suture used to tie the turbinate to the nasal septum—keeping it medial, like a seat belt holding you in place.
Eventually, scar will make the positioning permanent.

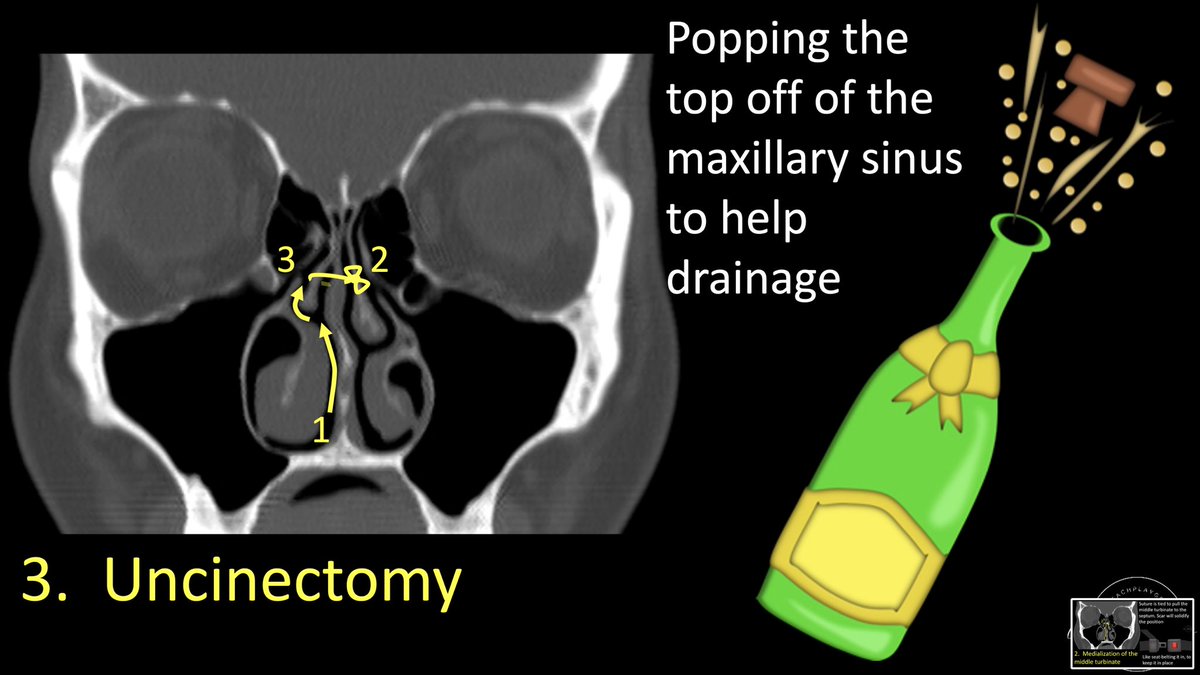
7/Next step is an uncinectomy. This step is used to open up the drainage pathway of the maxillary sinus—like popping the cork off champagne to open it up.
To understand how this works, you have to understand how the maxillary sinus drains
To understand how this works, you have to understand how the maxillary sinus drains
8/Maxillary sinus cavity is the antrum.
Think of the movement of mucus like the movement of travelers.
Antrum is like the airport—where all the people congregate, waiting to move out to their final destination. Mucus needs to leave the antrum
Think of the movement of mucus like the movement of travelers.
Antrum is like the airport—where all the people congregate, waiting to move out to their final destination. Mucus needs to leave the antrum

9/The first door to exit the antrum is the ostium. Think of it like the airport gate to enter a plane. It lets you out of the airport—but you aren’t on the plane yet. 

10/Just like an airport gate leads you out of the airport into a long hallway—the jetway—the ostium opens to a hallway-like structure called the infundibulum. Just how you must walk down a jetway to get to the plane, you must go through the infundibulum before you can truly leave 

11/The end of the infundibulum is the hiatus semilunaris—just like how the jetway ends in the door of the plane.
This is the exit that finally allows you to leave the maxillary sinus drainage pathway—just how entering the airplane finally allows you to take off.
This is the exit that finally allows you to leave the maxillary sinus drainage pathway—just how entering the airplane finally allows you to take off.

12/The hiatus semilunaris opens into the middle meatus—a space in the nasal cavity that is a common meeting point for many drainage pathways. Think of it like the jet plane. People from many different places come together on one plane & now can head off to their final destination 

13/Here is a summary of the maxillary sinus drainage—from the airport (antrum), you exit through the gate (ostium), before traversing down a jetway (infundibulum) to go through the jet door (hiatus semilunaris), that lets you join your fellow travelers on the jet (middle meatus) 

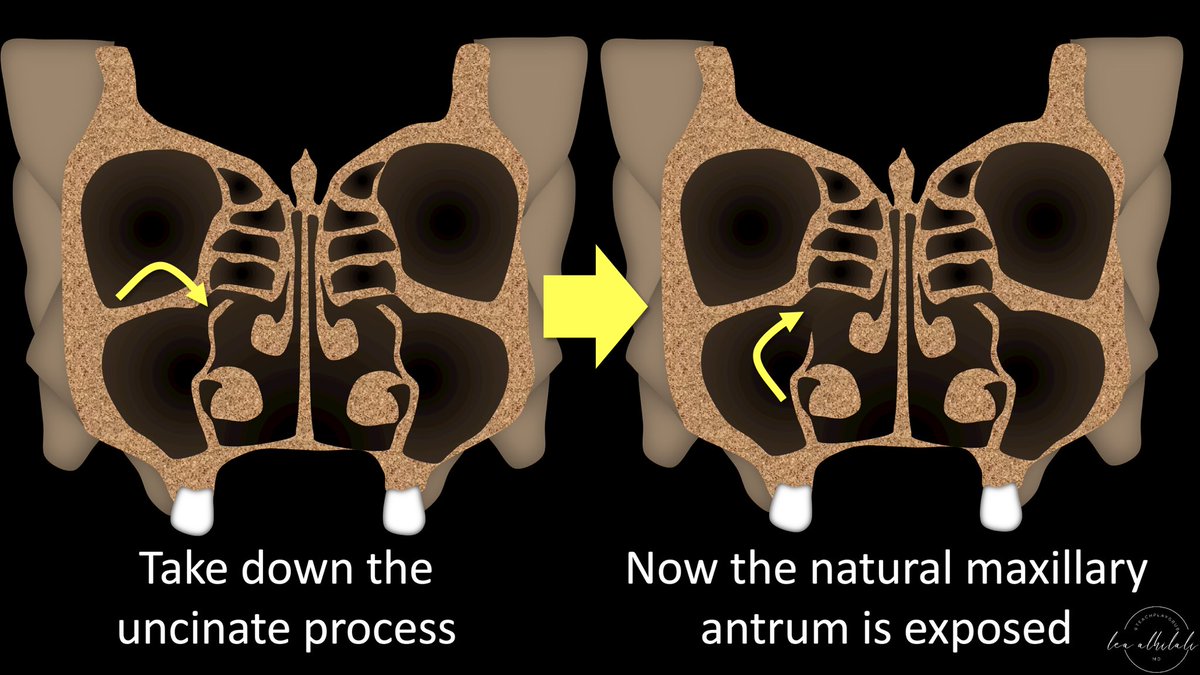
14/Uncinate process is the wall helping to create this drainage pathway. It must be taken off to expose, or open up, the door of the natural maxillary ostium 

15/Taking down the uncinate process exposes the natural maxillary ostium
You must be careful to alert the surgeon to findings that would increase the risk of violating the orbit when they take down the uncinate, such as an atelectactic uncinate process against the orbit
You must be careful to alert the surgeon to findings that would increase the risk of violating the orbit when they take down the uncinate, such as an atelectactic uncinate process against the orbit
16/The ostium is the natural endpoint for the mucociliary flow in the maxillary sinus.
Mucus will be propelled towards the ostium—so if the ostium is opened up, more mucus flow can get through.
How much to open it up?
Mucus will be propelled towards the ostium—so if the ostium is opened up, more mucus flow can get through.
How much to open it up?

17/Minimum is a uncinectomy (just taking down the uncinate).
This can further be enlarged front to back in a type 1 sinusotomy—or enlarged both front to back & up and down for a type 2 sinosotomy.
Largest is a type 3 sinosotomy—usually for polyposis
This can further be enlarged front to back in a type 1 sinusotomy—or enlarged both front to back & up and down for a type 2 sinosotomy.
Largest is a type 3 sinosotomy—usually for polyposis

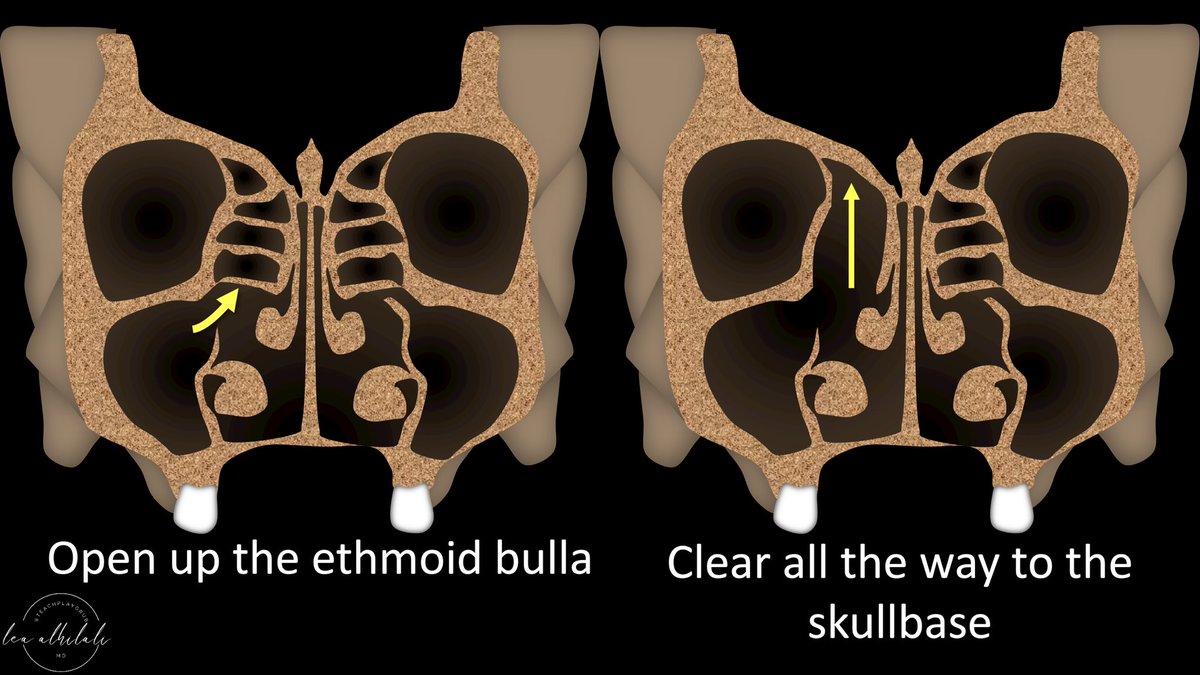
18/Next is an ethmoidectomy.
Anterior ethmoid air cells have to be cleared all the way to the skull base.
So mention any findings that could increase risk of perforation of the skull base, such as a deep cribiform plate.
Anterior ethmoid air cells have to be cleared all the way to the skull base.
So mention any findings that could increase risk of perforation of the skull base, such as a deep cribiform plate.
19/If the disease is only involving the anterior drainage, these four steps make up the steps of FESS.
Posterior disease requires more extensive surgery, but that’s for another tweetorial, I must conFESS!
Posterior disease requires more extensive surgery, but that’s for another tweetorial, I must conFESS!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















