
P/E ratio is a financial metric that compares a company's stock price to its earnings per share. It's used to evaluate the relative value of a stock and assess its potential for growth.
A P/E ratio of 15, for example, means that the stock's price is 15 times its earnings per share. A higher P/E ratio indicates that investors are paying more for each rupee of earnings.
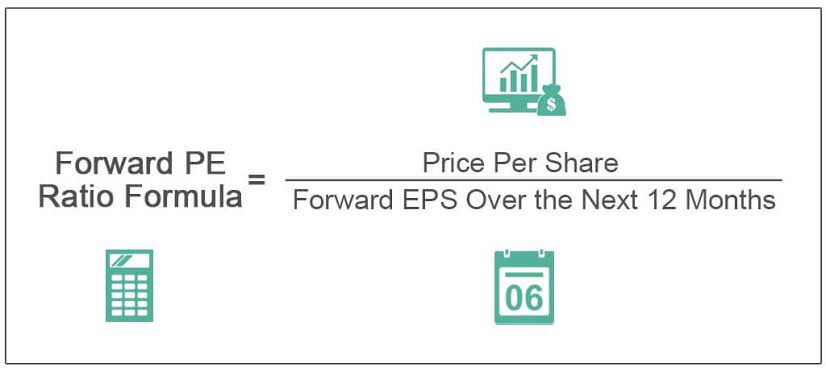
The forward P/E ratio, also known as the forward price-to-earnings ratio, is a measure of a company's valuation based on its future earnings potential. It is calculated by dividing the current stock price by the estimated earnings per share (EPS) for the next 12 months. 
Its important because it helps investors determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued based on its future earnings potential. A lower forward P/E ratio indicates that a stock may be undervalued, while a higher ratio may indicate that it's overvalued. #valuation
To calculate the forward P/E ratio, you need to know the current stock price and the company's estimated EPS for the next 12 months. The formula is: Forward P/E = Current Stock Price / Estimated EPS for Next 12 Months. #calculation 
It's important to note that the forward P/E ratio should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics and analysis to make a more informed investment decision. Other metrics such as P/B ratio, P/S ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio should also be considered. #diversify
When comparing companies within same industry, it's imp to consider the growth rate of company. A company with a higher forward P/E ratio but a higher growth rate may still be a more attractive investment than a company vt a lower forward P/E ratio & lower growth rate. #growth
It's important to consider the economic environment when evaluating a company's forward P/E ratio.A company with a high forward P/E ratio during an economic downturn may be considered overvalued,while the same ratio during an economic upturn may be considered undervalued. #macro
Keep in mind that forward P/E ratios are based on estimates and projections, and actual earnings may differ. This means that the ratio may change as the company releases actual earnings results and analysts adjust their estimates. #uncertainty
Lastly, it’s important to understand that forward P/E ratios are not a perfect indicator of a stock's value, and should not be used as the sole basis for making an investment decision. It should be used along with other analysis, research and due diligence.
Another thing to consider is the industry average, if a company has a forward P/E ratio that is significantly higher or lower than the industry average, it may indicate that the company is overvalued or undervalued relative to its peers.
The trailing P/E ratio is a valuation ratio calculated by dividing the current market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS) over the last 12 months. It shows how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings. 

The key difference between the two is that the trailing P/E ratio is based on historical earnings, while the forward P/E ratio is based on projected earnings. 

While the trailing P/E ratio gives a sense of the company's past performance, the forward P/E ratio helps to predict how the company's future earnings may change. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh







