1/Do questions about brainstem anatomy cause you to suddenly get a case of locked in syndrome?!
Do you try to localize the lesion or just wait for the MR?
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you w/brainstem #anatomy & localization!
#medtwitter #meded #neurotwitter #neurorad #radres
Do you try to localize the lesion or just wait for the MR?
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you w/brainstem #anatomy & localization!
#medtwitter #meded #neurotwitter #neurorad #radres
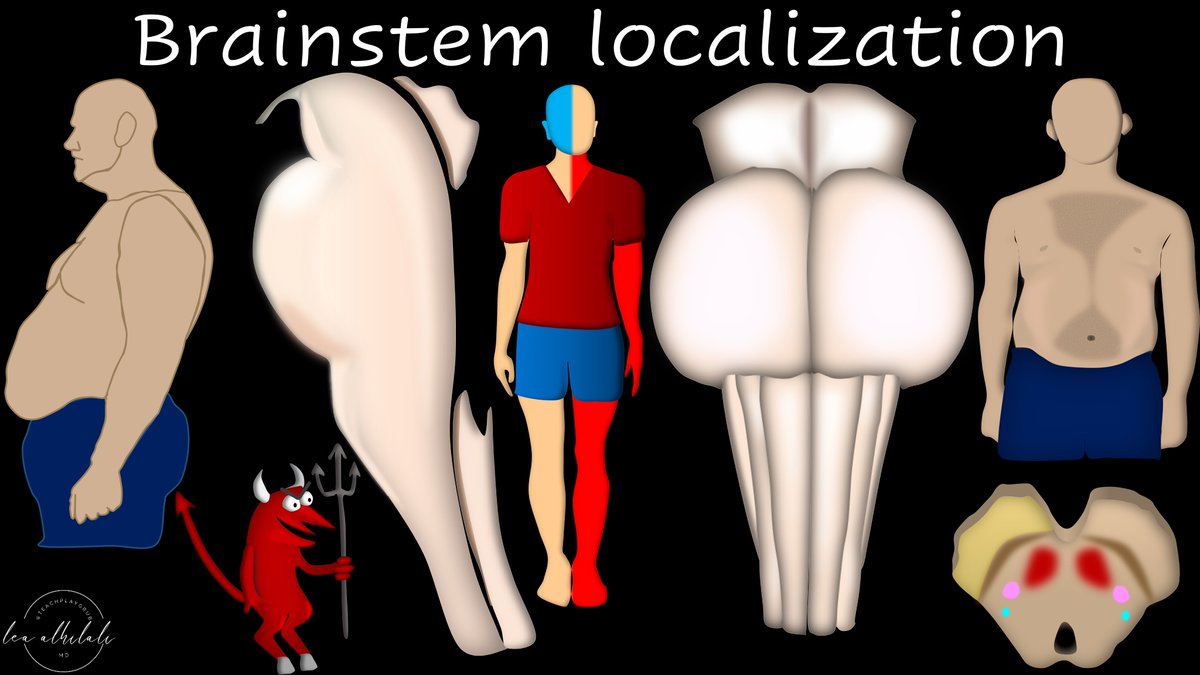
2/First some basic gross anatomy.
Brainstem from the side looks like a "dad bod"--the body you get after you have kids & the kids wear you down & you don’t exercise anymore.
Head & shoulders are the midbrain, potbelly is the pons, & fat thighs are the medulla
Brainstem from the side looks like a "dad bod"--the body you get after you have kids & the kids wear you down & you don’t exercise anymore.
Head & shoulders are the midbrain, potbelly is the pons, & fat thighs are the medulla

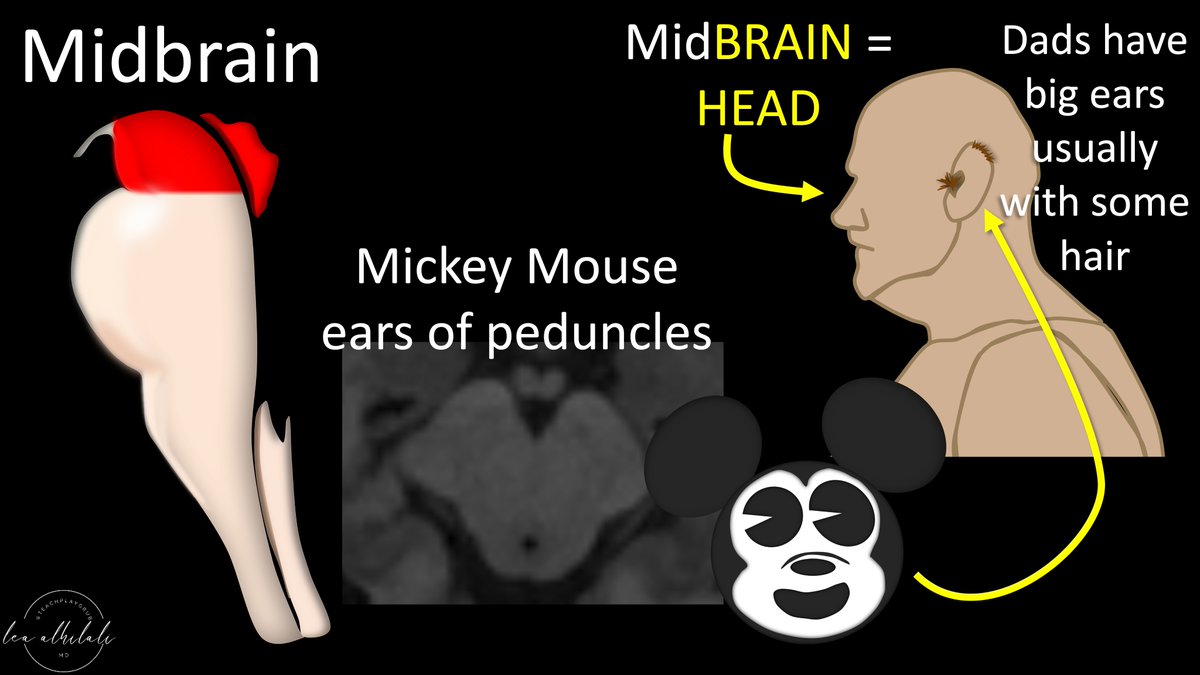
3/Midbrain is the head & shoulders.
This makes sense b/c the name “midbrain”—brain should be in the head.
Midbrain also has the cerebral peduncles which look like classic Mickey Mouse ears—and dads classically have big, usually hairy, ears
This makes sense b/c the name “midbrain”—brain should be in the head.
Midbrain also has the cerebral peduncles which look like classic Mickey Mouse ears—and dads classically have big, usually hairy, ears
4/Back of the midbrain has 2 bumps—superior & inferior colliculi (parts of vision & auditory pathways, respectively)
You can see these bumps on the dad bod too
Back of the balding head is the superior colliculus & the buffalo hump associated w/his obesity is inferior colliculus
You can see these bumps on the dad bod too
Back of the balding head is the superior colliculus & the buffalo hump associated w/his obesity is inferior colliculus

5/Next is the pons.
Dad's potbelly is the basis pontis.
Dad’s butt is the facial colliculus—where the facial nerve bulges out as it goes around, behind the 6th nerve nucleus.
Facial colliculus looks like two little baby butt cheeks on the axial images as well!
Dad's potbelly is the basis pontis.
Dad’s butt is the facial colliculus—where the facial nerve bulges out as it goes around, behind the 6th nerve nucleus.
Facial colliculus looks like two little baby butt cheeks on the axial images as well!

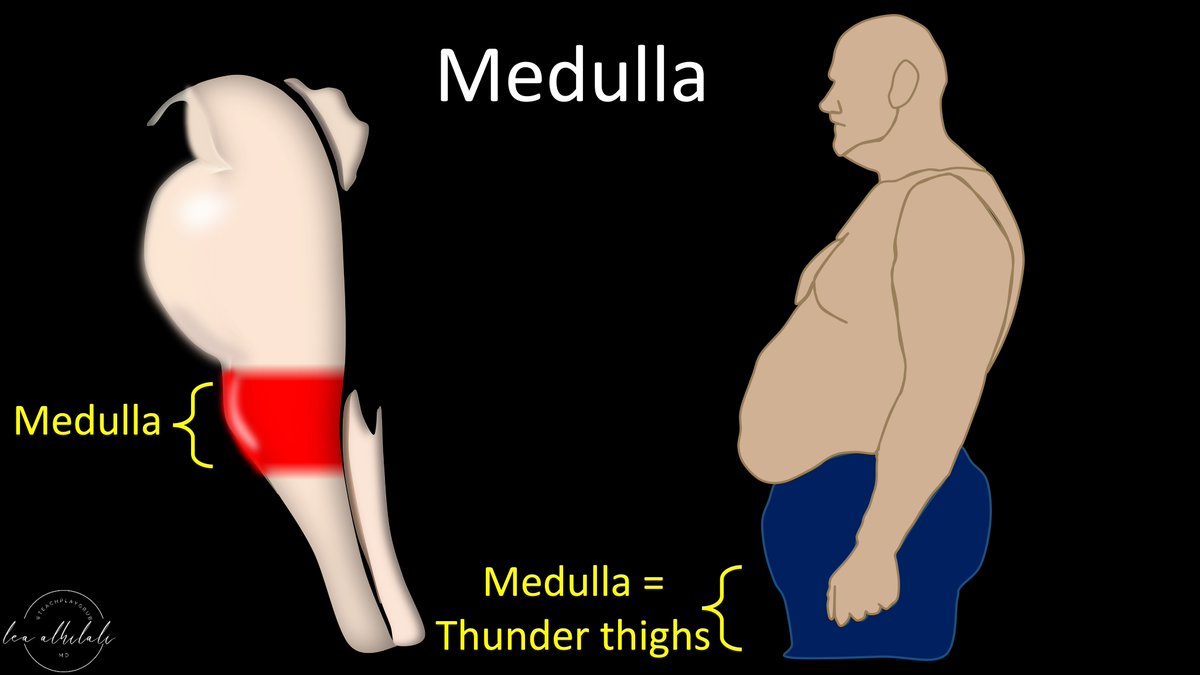
6/Finally, is the medulla.
This is the dad’s thunder thighs before heading down into the thinner legs of the spinal cord.
This is the dad’s thunder thighs before heading down into the thinner legs of the spinal cord.
7/You can see this dad bod when you at the brainstem from the front too.
You have the head of the midbrain, which then bulges as you go down into the pons/potbelly.
It then narrows as it goes down into the medulla/hips
You have the head of the midbrain, which then bulges as you go down into the pons/potbelly.
It then narrows as it goes down into the medulla/hips

8/The hallmark of a brainstem lesion/syndrome is:
1. IPSILATERAL cranial nerve deficit
2. CONTRALATERAL body deficit (be it weakness, sensory loss, or ataxia)
This is key to remember, in order to recognize a clinical presentation as a brainstem syndrome
1. IPSILATERAL cranial nerve deficit
2. CONTRALATERAL body deficit (be it weakness, sensory loss, or ataxia)
This is key to remember, in order to recognize a clinical presentation as a brainstem syndrome

9/You can remember this split b/c commonly your head wants to do one thing (work out) but your body feels like doing another (relaxing).
So it is not uncommon that things in the head & neck (cranial nerves) will be the opposite of the body
So it is not uncommon that things in the head & neck (cranial nerves) will be the opposite of the body

10/This is true not only for motor (ie, exercising), but also for sensory
Often your head has certain feelings that do not match up w/the feelings in your heart/body
This split between the head & body (opposite side involvement) is key for recognizing brainstem syndromes
Often your head has certain feelings that do not match up w/the feelings in your heart/body
This split between the head & body (opposite side involvement) is key for recognizing brainstem syndromes

11/Now for localization!
The brainstem is basically a highway between the brain & spinal cord.
Motor information is traveling south on the highway to the cord & sensory information is traveling north from the cord to the brain
The brainstem is basically a highway between the brain & spinal cord.
Motor information is traveling south on the highway to the cord & sensory information is traveling north from the cord to the brain

12/Like any highway, there are on ramps & off ramps.
Motor information exits at the off ramps & sensory information comes in through the on ramps.
These on-ramps & exits in the brainstem are the cranial nerves (CNs)
Motor information exits at the off ramps & sensory information comes in through the on ramps.
These on-ramps & exits in the brainstem are the cranial nerves (CNs)

13/On a highway, we know where we are by what exit we are near—they act like mile markers.
We localize how far we are on the highway by what exit we are coming to.
Same w/the brainstem. We know where we are in the brainstem by which exit (or cranial nerve) we are near
We localize how far we are on the highway by what exit we are coming to.
Same w/the brainstem. We know where we are in the brainstem by which exit (or cranial nerve) we are near

14/We know where the CN exits are located in the brainstem using the rule of 4s:
There are 4 CNs in each section (medulla, pons & above the pons)
Counting up from 12, we can see that:
9-12 are in the medulla
5-8 in the pons
3 & 4 in the midbrain (1&2 are supratentorial)
There are 4 CNs in each section (medulla, pons & above the pons)
Counting up from 12, we can see that:
9-12 are in the medulla
5-8 in the pons
3 & 4 in the midbrain (1&2 are supratentorial)

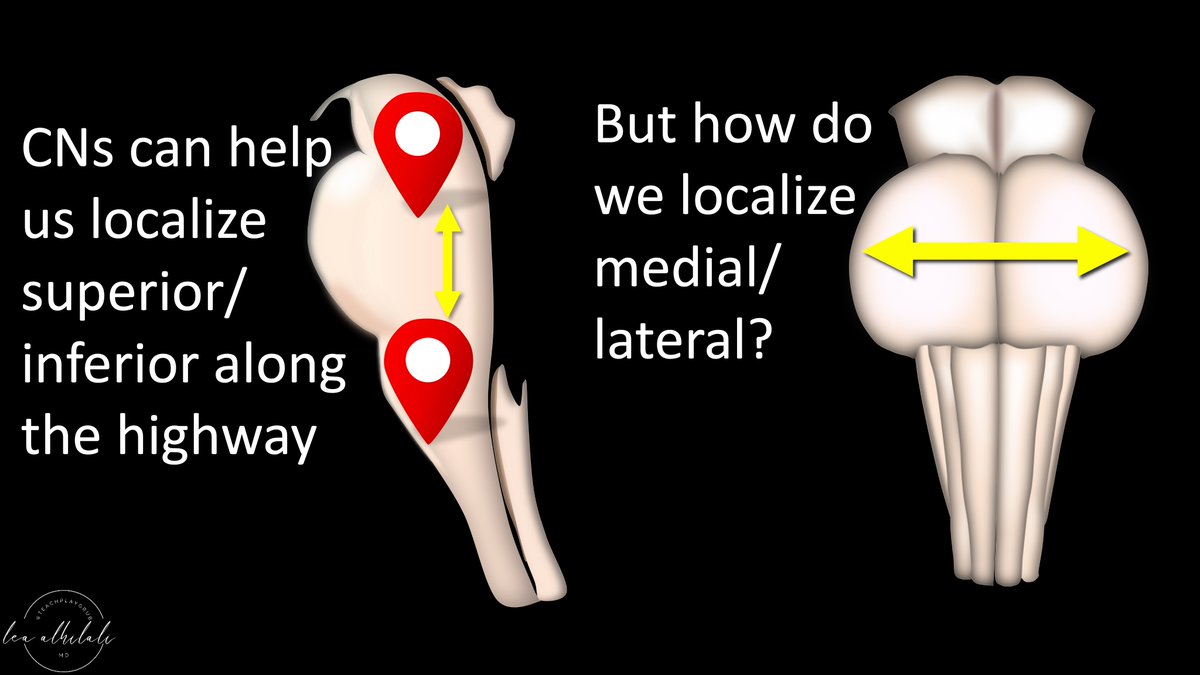
15/Determining which CN is involved by a lesion & then using the rule of 4s can tell us where a lesion is in the brainstem from top to bottom.
But how do we localize in the transverse plane (medial or lateral, anterior or posterior)?
But how do we localize in the transverse plane (medial or lateral, anterior or posterior)?
16/We can do this by determining whether a lesion involves the motor tracts or the two major sensory tracts:
Medial lemniscus (located, well, medially)
Spinothalamic tract located laterally
Medial lemniscus (located, well, medially)
Spinothalamic tract located laterally

17/Motor is anterior. Motor involvement tells you if the lesion is anterior or posterior
Medial lemniscus is medial, so its involvement suggests medial location, while spinothalamic injury suggests lateral location
Together w/CN involvement, you can now localize in 3 planes
Medial lemniscus is medial, so its involvement suggests medial location, while spinothalamic injury suggests lateral location
Together w/CN involvement, you can now localize in 3 planes

18/You can remember motor is anterior b/c that’s where motors are usually in a car.
So motor involvement equals an anterior lesion, while sparing of it suggests a more posterior location
So motor involvement equals an anterior lesion, while sparing of it suggests a more posterior location

19/How to remember which sensory deficits are medial & which are lateral?
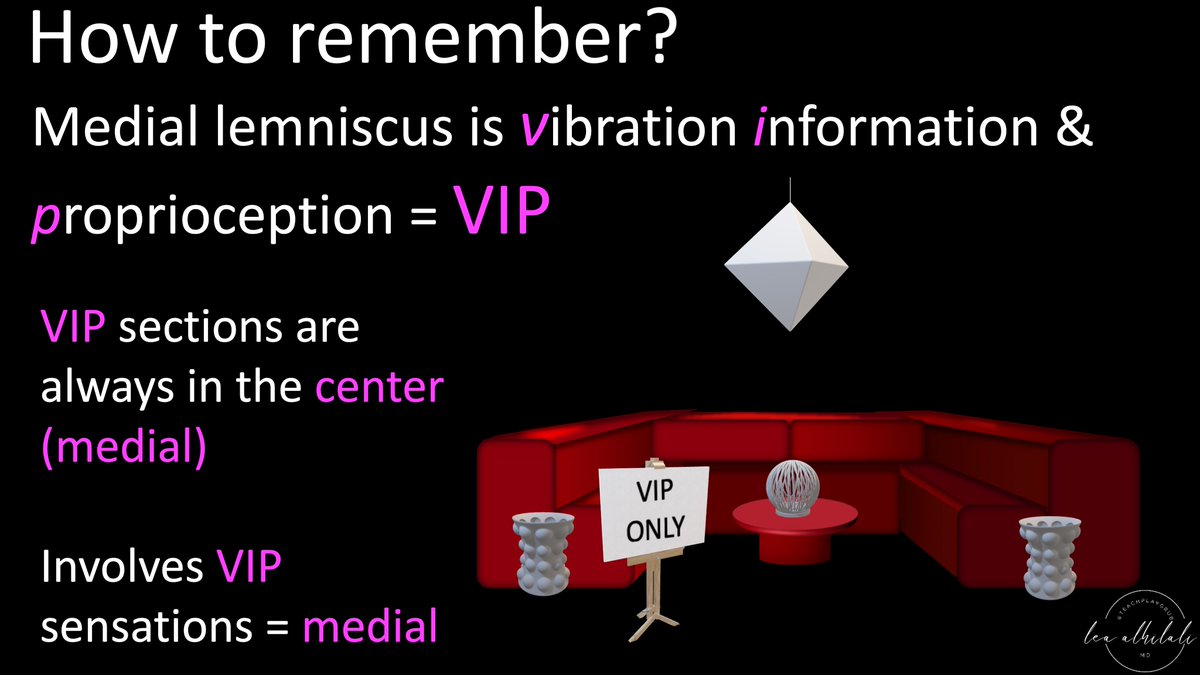
Well, medial lemniscus is vibration information & proprioception. I abbreviate it VIP—& all VIPs are the center of attention (center = medial)
So vibration & proprioception loss indicates medial location
Well, medial lemniscus is vibration information & proprioception. I abbreviate it VIP—& all VIPs are the center of attention (center = medial)
So vibration & proprioception loss indicates medial location
20/Spinothalamic is pain & temperature
You can remember that w/hot temperatures, the 1st thing that burns is the skin or periphery—so temperature is peripheral or lateral
Same w/pain—it's always your extremities (or periphery) that get hurt first, so pain is peripheral/lateral
You can remember that w/hot temperatures, the 1st thing that burns is the skin or periphery—so temperature is peripheral or lateral
Same w/pain—it's always your extremities (or periphery) that get hurt first, so pain is peripheral/lateral

21/CN involvement also indicates medial or lateral position.
CNs located medially innervate medial structures.
CNs located laterally in the brainstem innervate lateral structures.
So yourself ask—does the CN involved innervate medial or lateral structures?
CNs located medially innervate medial structures.
CNs located laterally in the brainstem innervate lateral structures.
So yourself ask—does the CN involved innervate medial or lateral structures?

22/Medial structures are eyes & tongue
All other CNs innervate a lateral object (lat face, ear, parotid, carotid, abdom viscera, shoulder musc)
If CN innervates eyes/tongue, it’s found medial in the brainstem—& is also divisible into 12
Opposite is true for lateral located CNs
All other CNs innervate a lateral object (lat face, ear, parotid, carotid, abdom viscera, shoulder musc)
If CN innervates eyes/tongue, it’s found medial in the brainstem—& is also divisible into 12
Opposite is true for lateral located CNs

23/So for every brainstem lesion, do 3 things:
(1) Find where it is along the length of the brainstem using CN involvement
(2) Determine if it’s ant or post based on whether motor is involved
(3) Determine if it’s med or lat based on type of sensory deficit & CN involvement
(1) Find where it is along the length of the brainstem using CN involvement
(2) Determine if it’s ant or post based on whether motor is involved
(3) Determine if it’s med or lat based on type of sensory deficit & CN involvement

24/Now you can localize brainstem lesions in all 3 planes based on their clinical presentation!
Hopefully now when confronted w/a brainstem syndrome, you will no longer be locked in, but instead handle it like a VIP!
Hopefully now when confronted w/a brainstem syndrome, you will no longer be locked in, but instead handle it like a VIP!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















