
Partly due to propaganda and disinformation about the safety of vaccines, fewer and fewer parents are having their children vaccinated against diseases included in many national vaccination programmes. Why is this zo important? 

Many countries have a national vaccination program that offers vaccinations against some of the most serious and common diseases. High vaccination coverage means a well-protected population against these diseases. With huge benefits for societies. 
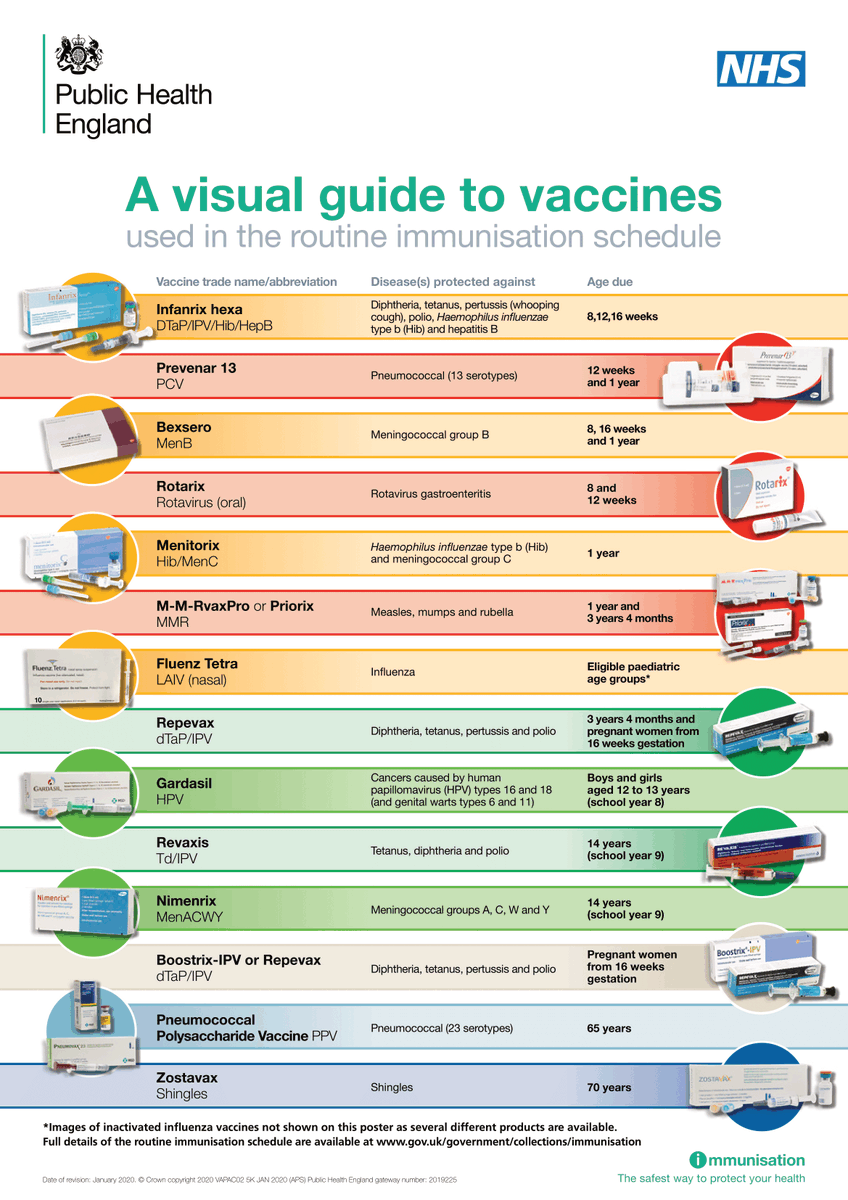
What does #vaccinationprogram consist of? The program provides the fastest and safest possible protection against diseases that can cause serious damage at a young or older age. It often starts with the first DTaP-IPV-Hib-HBV shot at the age of 3 months.
Diphtheria is a relatively unknown infectious disease caused by a bacterium. It doesn't happen very often anymore and there's a reason for that; vaccination! The disease is transmitted by coughing, touching, even through pets and food. The bacteria damages the skin and/or lungs. 

Because many people have been vaccinated, #diphtheria is very rare in many countries. However, you can still get infected. 10,000 people contracted diphtheria in the early 20th century, with 5-10% fatality and often long recovery with permanent damage. 

Diphtheria can be controlled through vaccination. Unfortunately, the bacteria is not gone and continues to infect. As soon as the vaccination rate becomes too low, it will quickly return.
news.com.au/lifestyle/heal…
news.com.au/lifestyle/heal…
Whooping cough (pertussis) is caused by a bacteria. Infection is by coughing. It is especially dangerous for young babies. 0.8% of babies who catch pertussis before 6 months old die from pneumonia or brain damage. Vaccination has much reduced this year-on-year. 

Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, but often the bacteria is no longer present by the time whooping cough is diagnosed. Treatment then no longer works. Therefore, prevention through vaccination is important.
cbc.ca/news/canada/ca…
cbc.ca/news/canada/ca…
#Tetanus (jaw clamp or wound spasm) is caused by the toxins of the bacteria Clostridium tetani. The bacteria, found everywhere, enters through an open wound. Since 1954, children receive 5 shots against tetanus toxin in the first 9 years of life.
Tetanus is absolutely terrible: cramping of the (jaw) muscles (jaw clamp), swallowing problems and breathing problems. Damage to the muscle and nervous system can lead to bone fractures, high blood pressure and cardiac arrhythmias. 

Since the toxin causes serious problems, antibiotics do not help! The reason for the 5 vaccinations is to be able to produce good memory B cells. A new vaccination, even after a wound, then ensures very rapid antibody production and the elimination of the toxin. 

Polio or poliomyelitis is caused by three types of polioviruses, transmitted from person to person through contaminated food, faeces, water or airborne droplets. The infection can lead to paralysis, especially among children who are most susceptible. 

#Polio was on the list to disappear. This has been worked on with great effort, with unfortunately still a number of places where vaccination coverage remained low. The danger was an outbreak, as in other places the vaccination rate also decreased. 

And with the #COVID-19 pandemic, partly due to reduced access to vaccines and partly due to a stream of continued misinformation about vaccines, polio outbreaks are now unfortunately a reality.
npr.org/sections/goats…
npr.org/sections/goats…
#HBV or Hepatitis B is an inflammation of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus. Transmission can occur from mother to child at birth, through sexual contact, or through contact with contaminated blood.
The problem is that if children contract HBV, there is a risk of becoming a chronic carrier of the virus and developing serious liver problems. That is why children are vaccinated against hepatitis B 3 times before their first birthday.
#Pneumococcal disease is caused by many different strains of pneumococcal bacteria. We carry these with us but usually do not get sick, but you can infect others. This is especially dangerous for young children and the elderly. 

#Pneumococci can cause middle ear, sinus infection and bronchitis. But also serious lung and meningitis and even blood poisoning. You can die from these serious forms. Babies receive 3 vaccinations against pneumococcal disease before their first birthday
People over the age of 35 are likely to have had mumps, measles, and rubella; vaccinations only started in 1980s. All 3 are RNA viruses. They are transmitted through inhalation of droplets of moisture and through direct contact with an infected person or object.
#Mumps is an inflammation of the salivary gland near the ear with a risk of meningitis and deafness. There is no treatment. Adults can also get mumps, even if they have been vaccinated. However, that chance is small. and the symptoms are much milder. 

#Measles is caused by an infectious virus. Vaccination has greatly reduced the virus. If you are vaccinated, you can still get infected, but the symptoms will be much milder. The disease starts with a cold, high fever, rash with red spots. 

Complications can arise; inflammation of the brain, rarely till 7 years after the infection. This virus weakens your immune system by attacking your memory B cells, making you very susceptible to infectious diseases, pneumonia is often a consequence.
science.org/content/articl…
science.org/content/articl…
#Rubella is also highly contagious caused by the rubella virus. It usually doesn't make you very ill. Disease symptoms are general; tired, cold and fever, then rash. A shortage of platelets, nflammation of the brain or inflammation of the joints are complications. 

Unborn children are at risk of deafness, blindness and mental developmental disorder if the mother contracts the rubella virus during pregnancy. Rubella during pregnancy can also cause a miscarriage. That's why vaccines are important.
#Meningococcal disease is caused by a bacteria called the meningococcus. There are several types; A, B, C, W and Y are the best known. We carry the bacteria in the nasopharynx without disease, but can infect others. 

Occasionally the bacteria penetrate further into the body and cause meningitis or blood poisoning. This can be very rapid and dramatic, accompanied by high fever, neck cramps or nappy pain in case of meningitis and severe bleeding in case of sepsis.
Serious consequences are epilepsy, deafness, concentration problems and eye disorders. Amputation of a limb may be necessary after severe blood poisoning. 5-10% of people die after meningitis and 20-50% of people after severe blood poisoning.
#HPV; human papillomavirus, there are different types. You hardly notice an HPV infection, but you are very contagious to someone else. Types 16 and 18 are the most dangerous; these often lead to cancer, of which cervical cancer is the best known. 

8 out of 10 people become infected with HPV at one or more times in their lives. In 10 to 20% of people, the virus gets the chance to change healthy cells. When the virus has damaged many cells, cancer can develop later. This can take ten to fifteen years. cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/6…
There is controversy about #COVID19 vaccinations. "Healthy children" are vaccinated, and "COVID-19 is not serious for children". This is completely incorrect; vaccines are there to prevent disease and to stay healthy; not only for the individual, but also for society.
In addition, #COVID19 is certainly not harmless for children. Now that the viral tropism has changed a bit and many adults have built up immunity through vaccination and/or infection, it is the young, unvaccinated, who have the serious symptoms.
And lastly, no, no vaccine or infection is preventing reinfection. However, many pathogens are slow to cause symptoms, and we do not notice. Many respiratory are fast, and symptoms are quick; but we have immunity.
npr.org/sections/healt…
npr.org/sections/healt…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










