
ICU stories (a brief one): One hour before the end of the am shift, u walk around in the ICU to make sure thinks look OK before u type your sign-out note. You spot the resp therapist & the nurse bagging the pt in Rm 306. From the hallway, u see the monitor: HR 160, RR/45, Sat 70%
This is a 30 yo pt w hx of a catastrophic brain bleed, s/p trach & PEG, admitted 2 wks ago w MDR Klebsiella UTI. Doing well, on trach mask 28%, until the episode of acute/unexpected desaturation
When u examine the pt, s/he is in extremis (accessory muscle use-tachycardic-tachypneic-diaphoretic). BP: 105/55. You grab the stethoscope that the resp therapist wears around his neck & you hear breath sounds in both sides (pt is skinny...)
The pt's lips/skin color looks like your scrubs. Actually, these are my scrubs & I am exaggerating about the color (but not too much...) 

You ask the resp therapist to add a PEEP valve to the Ambu bag but O2 sat goes only up to the high 80s-90% & drops again. What is your next step?
In a small community hospital, you don't have an army to help. In these cases, I have a very low threshold of sedating/paralyzing/connecting to the ventilator. That's exactly what we did. This "liberated" the resp therapist & the nurse to do "other stuff"...
Isn't it funny that when a pt drops the O2 sat, we take him/her off the vent? I usually try to put them back or keep them on the vent... 🤷♂️ @Thind888 has written a great piece about it. The vent waveforms sometimes can give a lot of info (but did not help in this case...)
Now what? The CXR will take at least 20-30 min. Chest CT may be not the best idea since pt is unstable. It's POCUS time! You start from the anterior L lung:
And move to the anterior R lung:
Where do you see lung sliding?
There is some movement in both sides, right? But, they don't look the same, do they? You want to be fancy & you decide to use M-mode. This is the R lung: 

How do we call the sign shown inside the M-mode yellow box?
The horizontal lines are called stratosphere (S) or barcode (BC) sign; they are the same thing. However, they should be BELOW, not above, the pleural line. So, in this case, there is no S/BC sign. But, 

under the pleural line, there are some vertical lines that are synchronous with the heartbeats. This is "lung pulse" & suggests that the parietal & visceral pleura are in touch but regional ventilation is impaired.
This 👇 was the normal L lung's M-mode for comparison. There is a "sandy" pattern below the pleural line; it is called "seashore sign": 

Since there was no strong evidence of pneumothorax on the R side, we decided to do a bronch w a single use bronchoscope (no COI) & this is what we saw: 



Not good...
After multiple mucus plugs were suctioned out from all the R lung lobes, oxygenation improved. Post-bronch chest x-ray attached: 


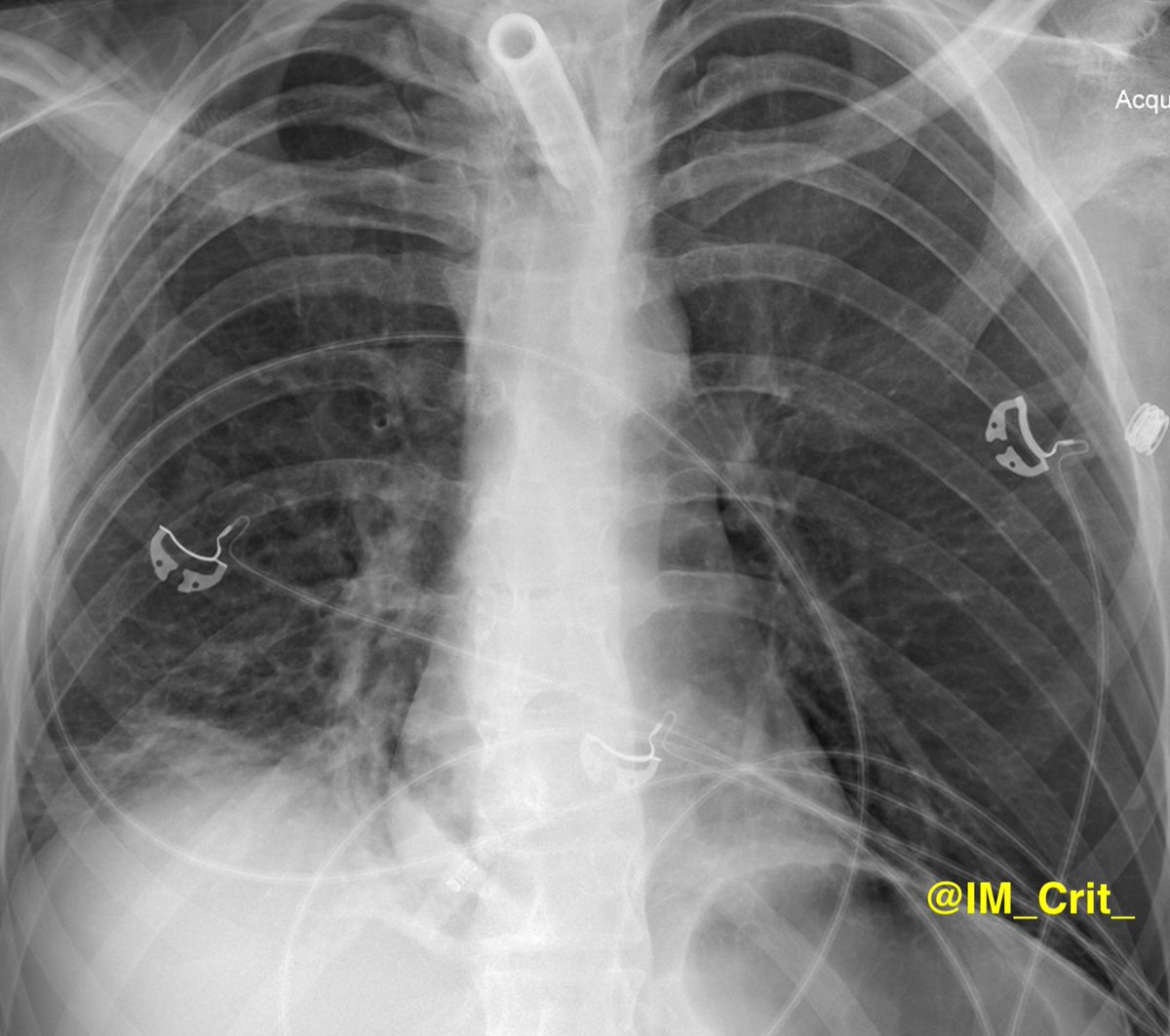
Take-home messages:
1. We tend to think that acute severe desaturation is either pneumothorax (tension, if vital signs change dramatically) or PE, but it is not unusual to find atelectasis as the underlying etiology
1. We tend to think that acute severe desaturation is either pneumothorax (tension, if vital signs change dramatically) or PE, but it is not unusual to find atelectasis as the underlying etiology
2. Lung POCUS can be very helpful but be cognizant of the limitations. It can be VERY tricky (I hope @kyliebaker888 agrees with me!)
3. Presence of lung sliding rules out pneumothorax but its absence does not equal w the presence of PTX
3. Presence of lung sliding rules out pneumothorax but its absence does not equal w the presence of PTX
4. Lung sliding is taught as an all-or-nothing phenomenon but sometimes there is SOME lung sliding (not complete absence but no presence either) and this suggests decreased regional ventilation (I think!)
5. The seashore & the lung pulse signs are helpful especially in unclear cases (ie, there is no lung sliding but no lung point to confirm PTX) but are not easy especially if you are full of adrenaline & your hand is not steady
Thanks for reading! This approach worked for me in this case but there may be better ways!
#POCUS #ECHOFIRST #POCUSpeeps #FOAMus #FOAMcc #IMPOCUS #MedTwitter #MedEd #EMBound @RJonesSonoEM @jaffa_md @katiewiskar @msiuba @NephroP @MynephCC @HeyDrNik @ICUltrasonica @khaycock2
#POCUS #ECHOFIRST #POCUSpeeps #FOAMus #FOAMcc #IMPOCUS #MedTwitter #MedEd #EMBound @RJonesSonoEM @jaffa_md @katiewiskar @msiuba @NephroP @MynephCC @HeyDrNik @ICUltrasonica @khaycock2
@NickjohnsonMD @nickmmark @pocusmeded @POCUSClub @thepocusatlas @TaotePOCUS @pocusfoamed @cianmcdermott @ImagenCardiaca @cjosephy @KalagaraHari @UAlberta_ICU @UAB_Sono @critconcepts @MegriMohammed @emily_fri @icmteaching @curromir @iceman_ex @Thind888 #MedStudentTwitter
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









