1/If all you know is: To Zanzibar By Motor Car—then you don’t even know half of facial nerve anatomy—literally!
Here’s a #tweetorial on the facial nerve anatomy you don’t know!
#medtwitter #neurotwitter #neurorad #radres #meded #FOAMed #neurosurgery #neurology #radtwitter
Here’s a #tweetorial on the facial nerve anatomy you don’t know!
#medtwitter #neurotwitter #neurorad #radres #meded #FOAMed #neurosurgery #neurology #radtwitter

2/On coronal MRI sequences, the brainstem in the region of the facial nerve looks like a bodybuilder.
But it looks like one of those body builders who concentrates only on upper body workouts, so they are huge up top (the pons) & but have chicken legs (the medulla)
But it looks like one of those body builders who concentrates only on upper body workouts, so they are huge up top (the pons) & but have chicken legs (the medulla)

3/Facial nerve comes out in this region from between the pons & medulla.
It looks like a weightlifting belt, coming out from the waist between the giant pons upper body & the medulla chicken legs
It looks like a weightlifting belt, coming out from the waist between the giant pons upper body & the medulla chicken legs

4/Intracranial segments of the facial nerve follow the stages of life.
To begin, you are born. So is the facial nerve.
It leaves the pons at the root exit point—just as you exit your mother’s womb at birth
To begin, you are born. So is the facial nerve.
It leaves the pons at the root exit point—just as you exit your mother’s womb at birth

5/Next is the attached segment. This is the next stage of life
Just like after birth, you are very attached to your mother in childhood, so too is the facial nerve “attached” to the pons after its birth, like a little kid
It runs closely along the pons undersurface at first
Just like after birth, you are very attached to your mother in childhood, so too is the facial nerve “attached” to the pons after its birth, like a little kid
It runs closely along the pons undersurface at first

6/Next stage of life is when you must finally leave the safety of clinging to your parents
So too must the facial nerve leave the undersurface of the pons. This is called the root detachment point
You can remember this b/c most teenagers are very cool & “detached” at this age
So too must the facial nerve leave the undersurface of the pons. This is called the root detachment point
You can remember this b/c most teenagers are very cool & “detached” at this age

7/Next is stage of life is transitional.
After leaving for college, you’re not quite independent—you still go home & do your laundry & beg for money! So it’s a “transitional zone” for you
Same for facial nerve—initially it’s “transitional” between central & peripheral myelin
After leaving for college, you’re not quite independent—you still go home & do your laundry & beg for money! So it’s a “transitional zone” for you
Same for facial nerve—initially it’s “transitional” between central & peripheral myelin

8/Finally is the cisternal segment. This is the stage of life when you’re finally mature & go out on your own
Same for the facial nerve. It’s left the central myelin of its pontine mama behind & is now fully peripheral myelin. It’s ready to go out & meet CN VIII in the IAC
Same for the facial nerve. It’s left the central myelin of its pontine mama behind & is now fully peripheral myelin. It’s ready to go out & meet CN VIII in the IAC

9/The full course of the facial nerve is best seen on coronal images
On the axial images, you can see the portions after it has left the pons (root detachment point, transitional zone & cisternal segment)
You can’t see more proximally b/c this is covered by the pons on axials
On the axial images, you can see the portions after it has left the pons (root detachment point, transitional zone & cisternal segment)
You can’t see more proximally b/c this is covered by the pons on axials

10/It’s important to know this anatomy so you can look for compression of the facial nerve in this region.
Most often it’s compression from a vessel (microvascular compression).
Microvascular compression can lead to hemifacial spasm
Most often it’s compression from a vessel (microvascular compression).
Microvascular compression can lead to hemifacial spasm
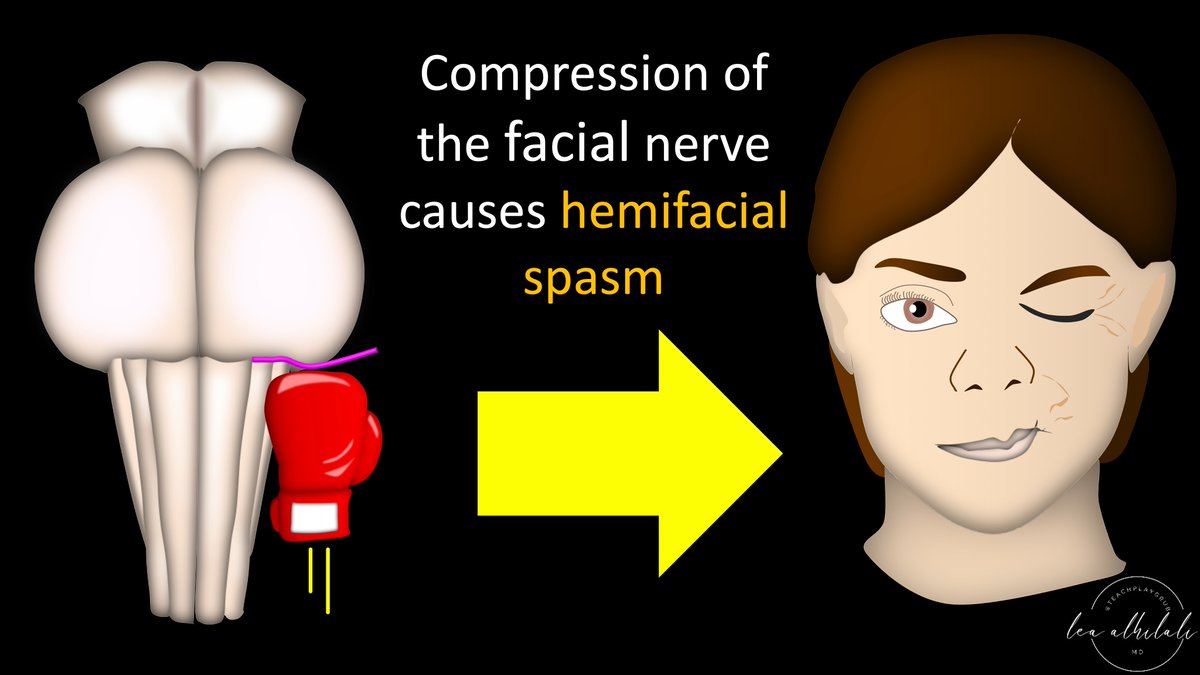
11/This is most common in the transitional zone b/c central myelin is vulnerable & here central myelin is out in the cistern
It’s like how kids are most likely to get into trouble in the college years—b/c you’re still a kid, but now exposed to more temptations/real world danger
It’s like how kids are most likely to get into trouble in the college years—b/c you’re still a kid, but now exposed to more temptations/real world danger

12/You can see compression of the transitional zone on the axial images b/c the transitional zone is after the nerve has left from under the pons
So always look for vessels compressing the nerve right next to pons—like bad influences bringing you trouble during the college years
So always look for vessels compressing the nerve right next to pons—like bad influences bringing you trouble during the college years

13/Besides the college years, the next most common time to get into trouble is your childhood. Same w/the facial nerve
Next most common place for microvascular compression is the attached segment. Even though its under the roof of its pontine mama, it can still get punched
Next most common place for microvascular compression is the attached segment. Even though its under the roof of its pontine mama, it can still get punched

14/But you can’t see this area on axial images b/c it’s hidden under the pons!
Most common cause of a failed decompression is that transitional zone compression is relieved but attached segment compression is missed
So always check coronals for attached segment compression!
Most common cause of a failed decompression is that transitional zone compression is relieved but attached segment compression is missed
So always check coronals for attached segment compression!

15/So now you know the intracranial facial nerve by remembering how its segments follow the stages of life—& you know where to look for compression by remembering which stages of life are vulnerable to trouble
Hopefully this will keep you out of trouble w/facial nerve anatomy!
Hopefully this will keep you out of trouble w/facial nerve anatomy!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















