1/To be or not 2b?? That is the question!
Do you have questions about how to remember cervical lymph node anatomy & levels?
Here’s a #tweetorial to show you how--#Superbowl weekend edition!
#medtwitter #meded #neurorad #HNrad #FOAMed #FOAMrad #radres #radtwitter #ENT #radiology
Do you have questions about how to remember cervical lymph node anatomy & levels?
Here’s a #tweetorial to show you how--#Superbowl weekend edition!
#medtwitter #meded #neurorad #HNrad #FOAMed #FOAMrad #radres #radtwitter #ENT #radiology

2/Google cervical lymph node anatomy & you always get this anatomic picture w/the head flung back like a model posing.
But unless you live in LA, your patients don’t look like this & understanding anatomy from this image is difficult
But unless you live in LA, your patients don’t look like this & understanding anatomy from this image is difficult

3/First, you need to know how lymph node drainage works in the neck.
Nodes drain like rivers—smaller streams drain into larger rivers.
In the neck, there are outer circle nodes (peripheral) & inner circle nodes—both drain into the large river of the deep cervical nodes
Nodes drain like rivers—smaller streams drain into larger rivers.
In the neck, there are outer circle nodes (peripheral) & inner circle nodes—both drain into the large river of the deep cervical nodes
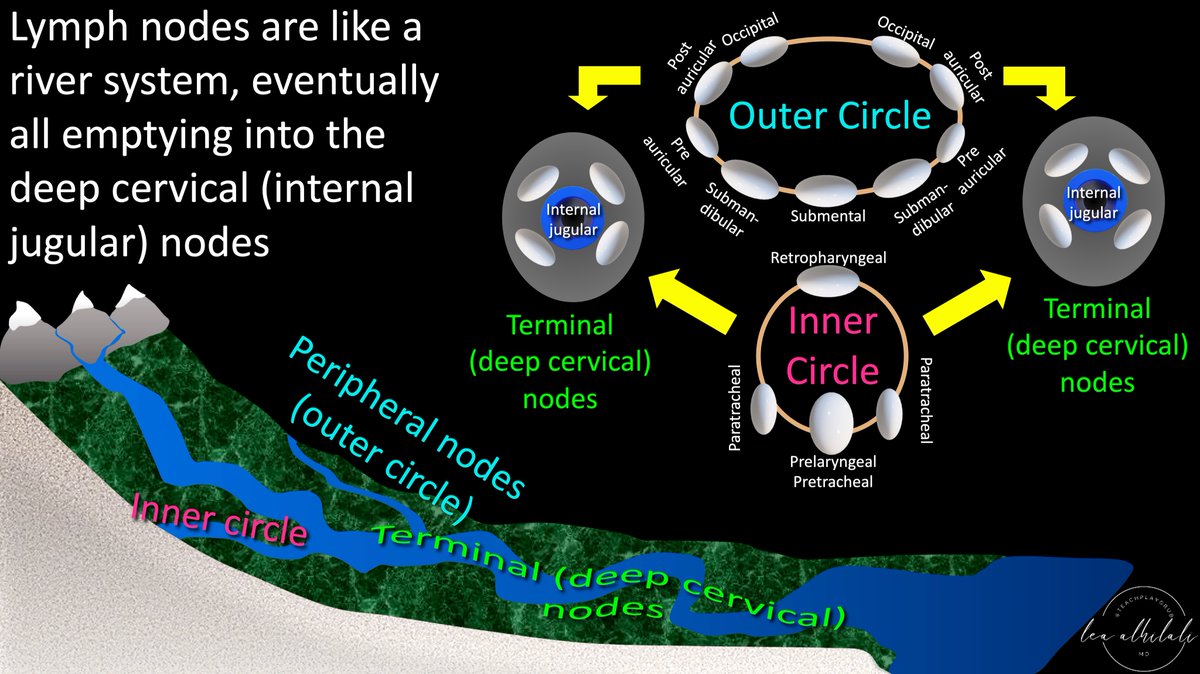
4/Think of it like football. Teams are in 2 different conferences like the NFL (outer circle & inner circle, like NFC & AFC). They’re separate, but eventually meet in the end at the Superbowl! Internal jugular nodes are the superbowl where inner & outer circle drainage meet 

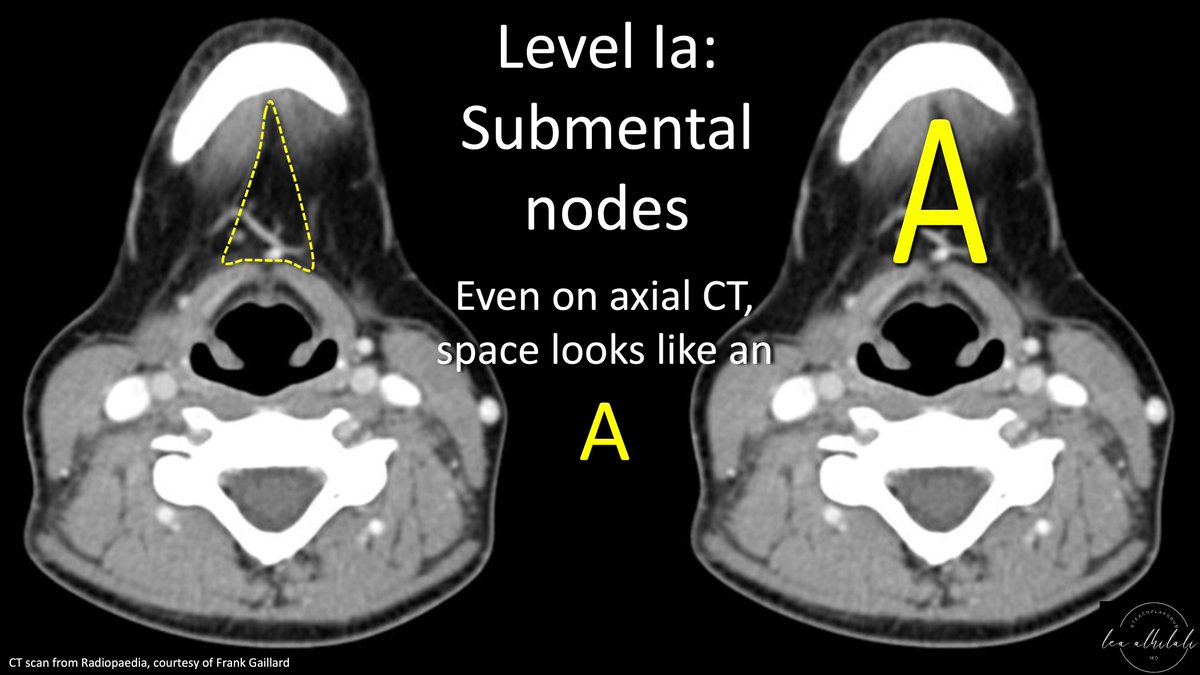
5/First are submental nodes (menton=chin in French), so they’re behind the chin. They’re the nodes between the anterior bellies of the digastric below the floor of mouth.
The space between the anterior bellies looks like a capital A—so you can remember 1A lives in an A space
The space between the anterior bellies looks like a capital A—so you can remember 1A lives in an A space

6/Even on axial CT slices, the space between the anterior bellies looks like an A. So if you see a node inside this A, you know its 1A! 
7/Next are submandibular nodes. They start where 1A ends—from the anterior digastric belly laterally to the mandible/platysma
They circle around the submandibular gland—hence the name
This space along the edge, circling around the submandibular gland looks like a lower-case b
They circle around the submandibular gland—hence the name
This space along the edge, circling around the submandibular gland looks like a lower-case b

8/On axial CT, you can see how this space makes a lower-case b:
Running straight along the mandible before circling around to encompass the submandibular gland.
Running straight along the mandible before circling around to encompass the submandibular gland.

9/Next are upper jugular nodes.
Behind the submandibular gland, these are sandwiched between the medial carotid and medial border of the sternocleidomastoid.
Bread is SCM and medial carotid. Sandwich filling is the lymph nodes
Behind the submandibular gland, these are sandwiched between the medial carotid and medial border of the sternocleidomastoid.
Bread is SCM and medial carotid. Sandwich filling is the lymph nodes

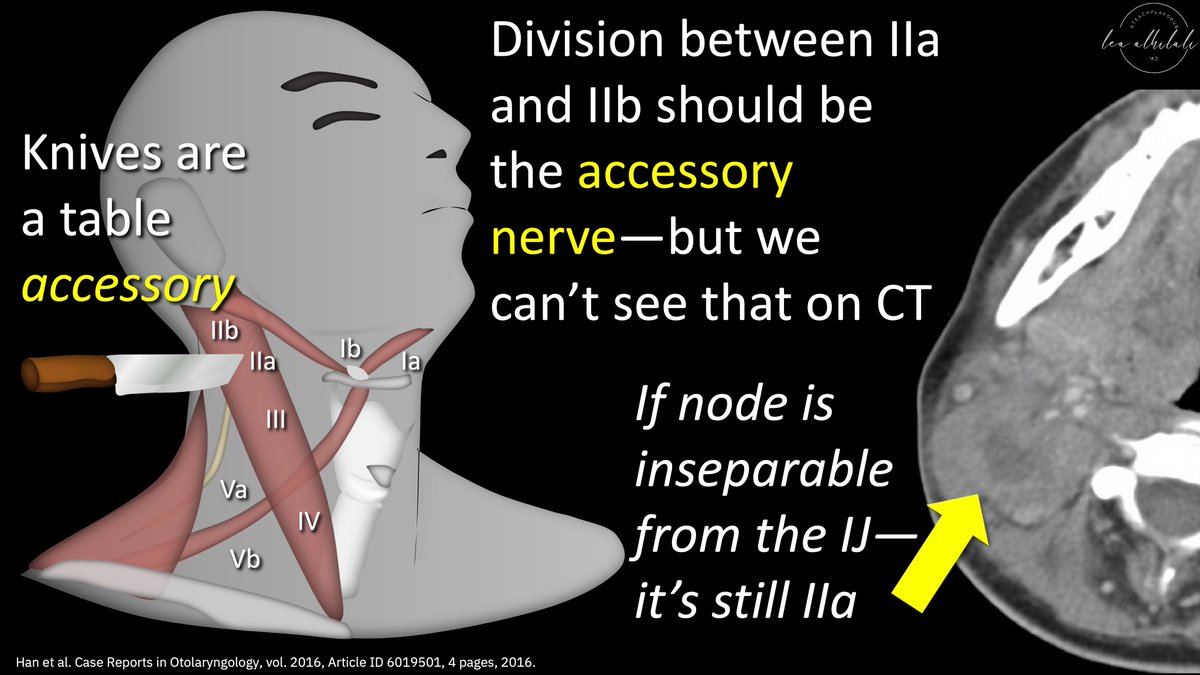
10/Level 2 is divided in 2. It’s divided into 2a & 2b at a plane along the posterior jugular vein—like cutting a sandwich in half
It’s easy to remember the jugular as the dividing landmark b/c if you’re cutting in someone’s neck—well, some might say you’re going for the JUGULAR
It’s easy to remember the jugular as the dividing landmark b/c if you’re cutting in someone’s neck—well, some might say you’re going for the JUGULAR

11/The dividing line is actually the accessory nerve—remember this b/c knives are a table accessory!
But we can’t see the accessory nerve on conventional images, so the post. jugular is used as a surrogate
If the node is inseparable from the posterior IJ, then it’s still 2a
But we can’t see the accessory nerve on conventional images, so the post. jugular is used as a surrogate
If the node is inseparable from the posterior IJ, then it’s still 2a
12/Jugulodigastic is the highest level 2 node. Some call it the sentinel node bc it’s the 1st deep node to see drainage from nose & mouth
Bc it sees so many antigens as a result, it may act like a sentinel & overreact (get enlarged). So we give it leeway & let it get upto 1.5cm
Bc it sees so many antigens as a result, it may act like a sentinel & overreact (get enlarged). So we give it leeway & let it get upto 1.5cm

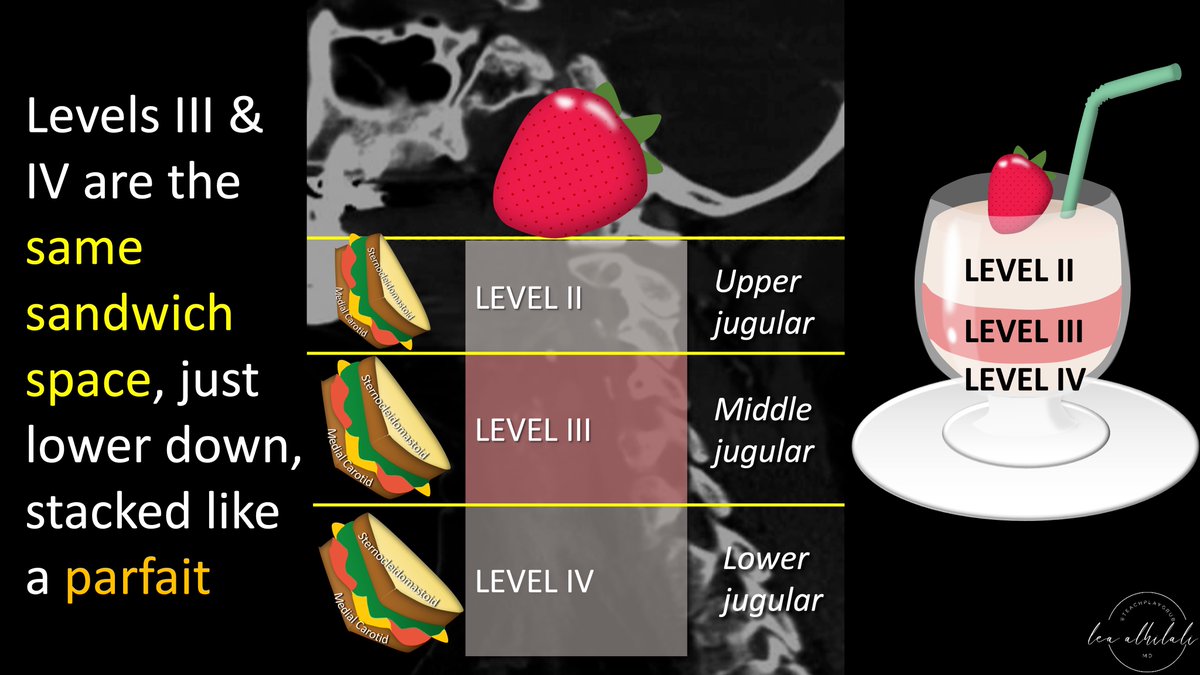
13/Levels 3 & 4 are the same sandwich space as level 2 (between medial carotid & medial SCM), but just lower down in the neck.
Think of them like a stacked parfait—all the same space, just different levels in the neck. Calvarium is the cherry on top!
Think of them like a stacked parfait—all the same space, just different levels in the neck. Calvarium is the cherry on top!
14/ 3 landmarks divide the sandwich space into its 3 levels: C1, hyoid, & cricoid:
C1 is the first landmark bc it’s number 1!
Hyoid comes next b/c the hy-oid is hi-gher than the cricoid
Cricoid is last—remember, cri-coid cri-es. You cry w/the larynx which is lower in the neck
C1 is the first landmark bc it’s number 1!
Hyoid comes next b/c the hy-oid is hi-gher than the cricoid
Cricoid is last—remember, cri-coid cri-es. You cry w/the larynx which is lower in the neck

15/Next are posterior triangle nodes. These are behind level 2, between posterior SCM & trapezius
I think this area looks like a mullet on the back of the neck
I remember level 5 is in the mullet bc mullets are business in the front, during the day, & party after 5! 5 = mullet
I think this area looks like a mullet on the back of the neck
I remember level 5 is in the mullet bc mullets are business in the front, during the day, & party after 5! 5 = mullet

16/Next are central compartment nodes.
These encompass two central nodes: anterior jugular in the front & paratracheal in the back.
A backwards number 6 outlines these regions, with its circle coming around the back of the thyroid where paratracheal nodes lie.
These encompass two central nodes: anterior jugular in the front & paratracheal in the back.
A backwards number 6 outlines these regions, with its circle coming around the back of the thyroid where paratracheal nodes lie.

17/So now you know how to remember the main lymph node levels in the neck.
You will never again have to ask the question “2b or not 2b?!”
You will never again have to ask the question “2b or not 2b?!”

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















