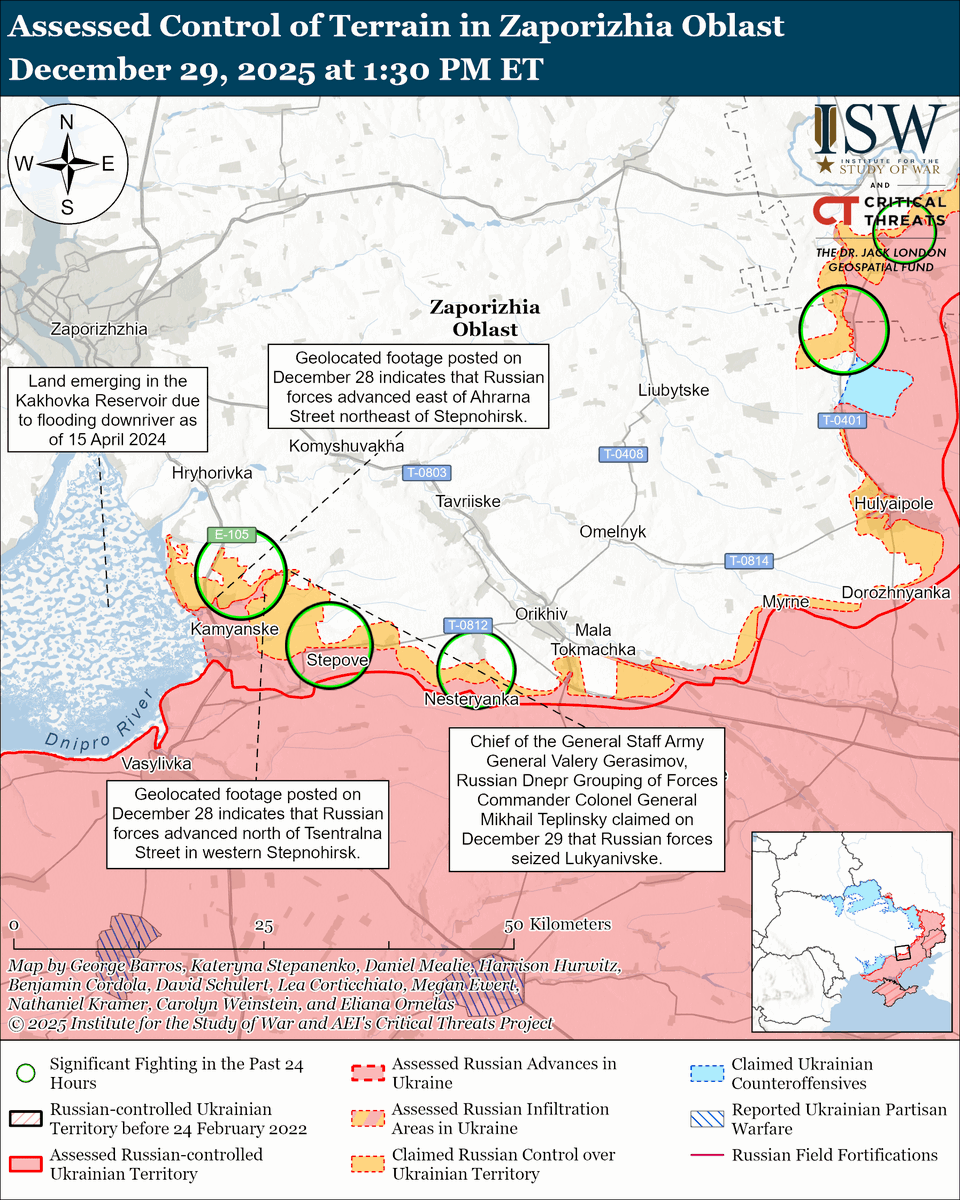
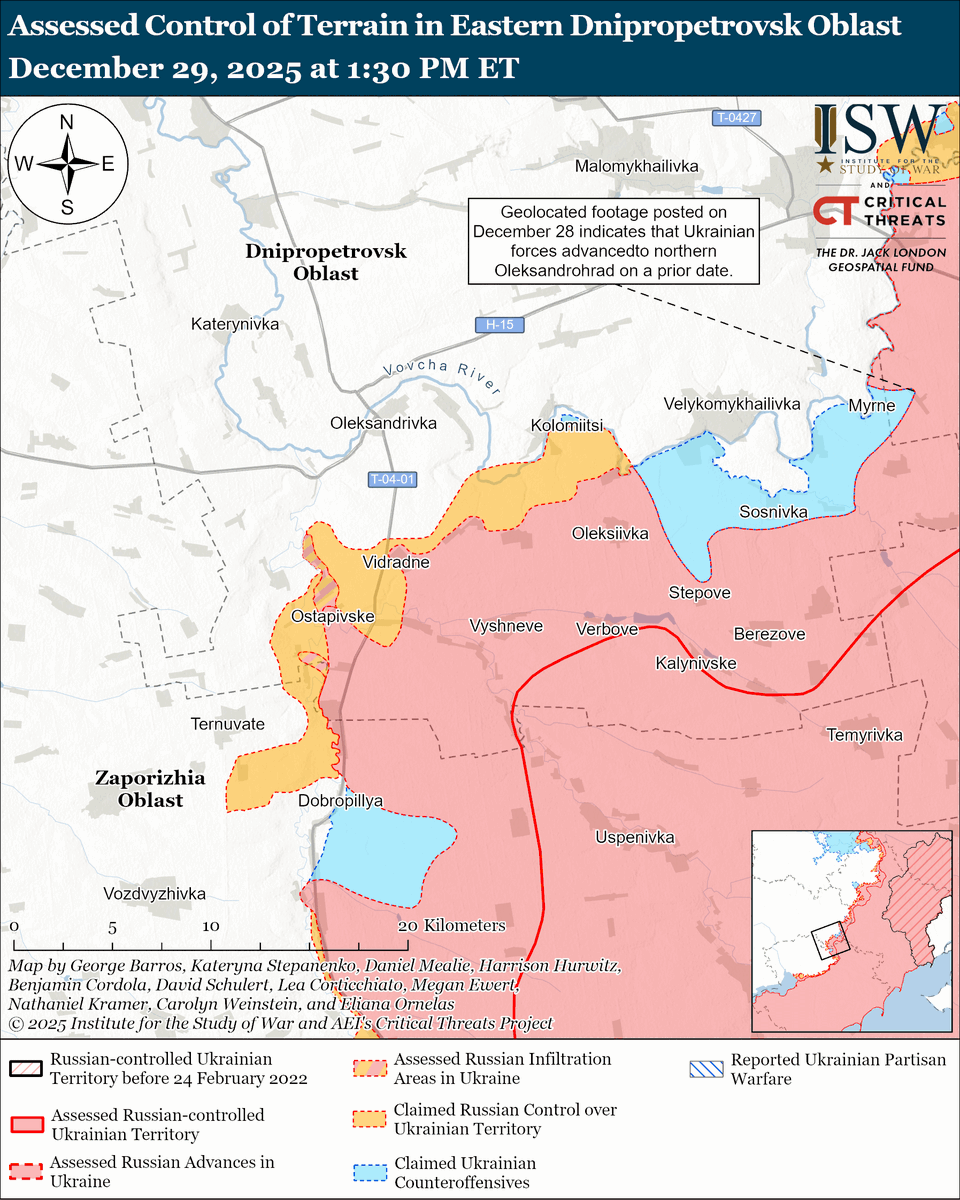
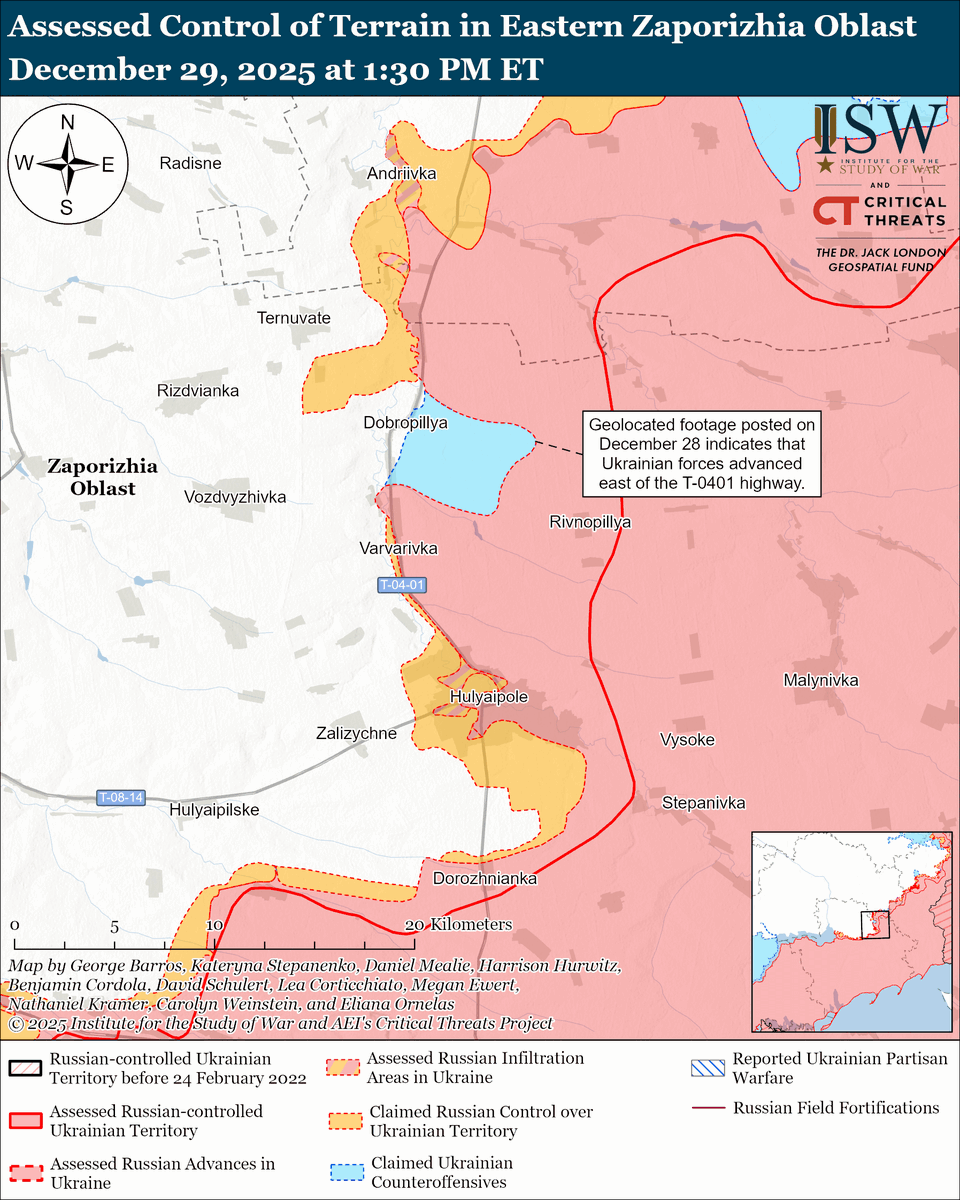
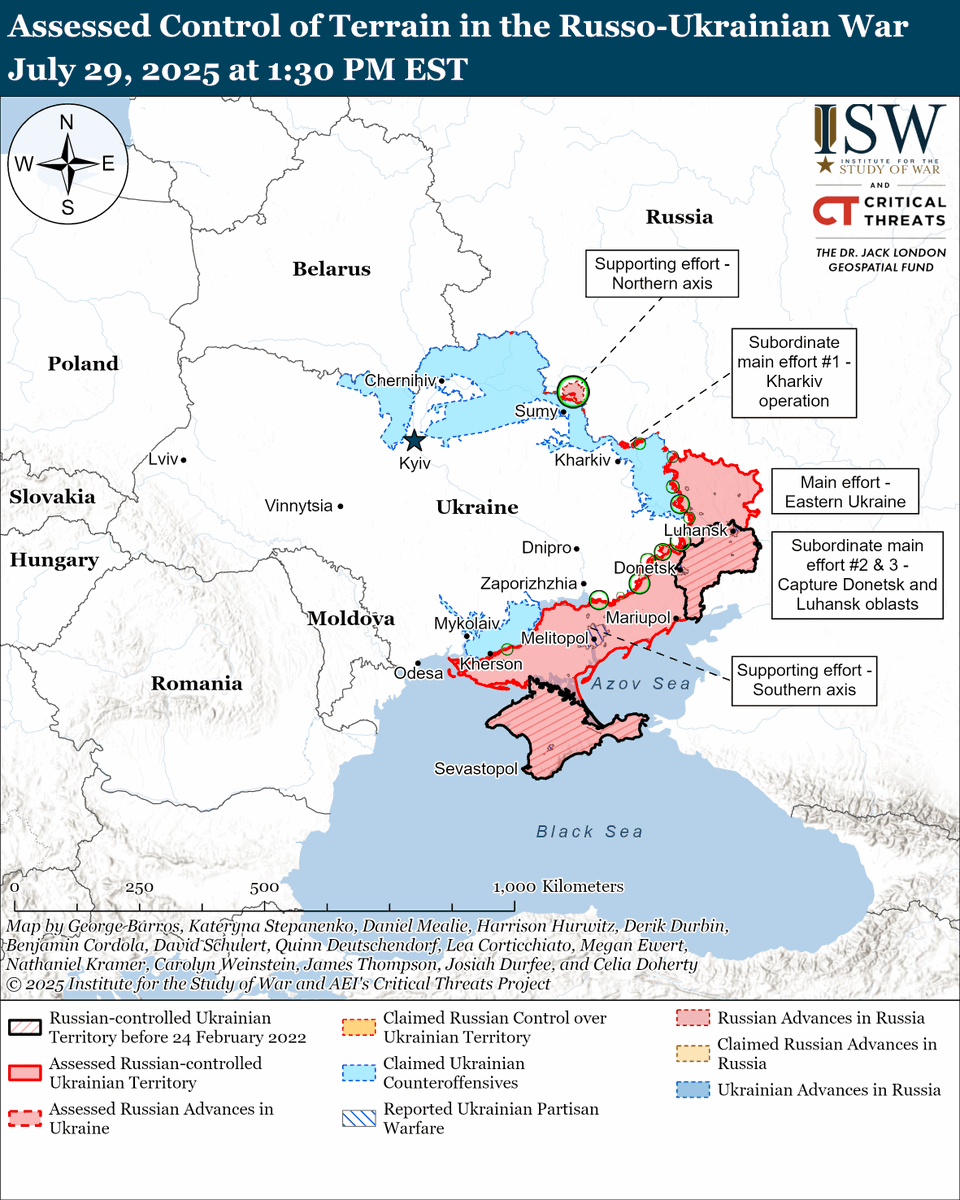
🧵#Russia likely began to run out of combat-ready forces by May 2022, forcing Russian President Vladimir #Putin to make a consequential choice between launching a volunteer recruitment campaign or ordering an unpopular involuntary reserve call-up. (1/25) isw.pub/UkrWar022623
https://twitter.com/TheStudyofWar/status/1630044611543433216
2/ The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) had likely advised Putin that he needed to declare mobilization as soon as possible to ensure that Russia had sufficient combat power to continue offensive operations past the capture of the Severodonetsk-Lysychansk line over the summer.
3/ Putin likely rejected the Russian military’s advice to order an involuntary reserve call-up because of the unpopularity of the move, the fact that he had not set informational conditions for it, and possibly also because of his growing distrust of the Russian MoD.
4/ Putin decided instead to double down on existing volunteer recruitment efforts already being conducted by ultranationalist groups and ordered the formation of new volunteer formations.
5/ Putin & his mouthpieces continued to push a narrative that the Russian “special military operation” in Ukraine was a limited campaign that would not affect the general Russian public, setting informational conditions to preclude rather than facilitate involuntary mobilization.
6/ The Kremlin had consistently outsourced voluntary recruitment efforts to support its operations abroad and during the full-scale invasion of Ukraine to ultranationalist groups & likely allowed these groups to expand their force generation campaigns over the summer.
7/ The Kremlin likely turned to these existing networks hoping to attract volunteers who ideologically support his war. ISW repeatedly observed and reported on numerous instances of Russian pro-war, nationalist milbloggers promoting recruitment and crowdfunding campaigns.
8/ These quasi-official ultranationalist groups began to increasingly recruit from the general public, reaching beyond reservists who had completed their mandatory conscript service, veterans, and contract servicemen.
9/ ISW also observed that Putin had been increasingly tolerating ultranationalist milbloggers who have become mainstream sources of frontline information since May 2022 despite their harsh criticism of the Russian military command and the progress of the war.
10/ Putin likely valued the milbloggers’ ability to recruit volunteers above maintaining the Russian MoD’s propaganda efforts or saving the reputations of Shoigu, Gerasimov, and other failed military commanders.
11/ The Kremlin, for example, tolerated and continues to tolerate former Russian officer Igor Girkin who directly criticizes Putin and his administration, likely due to Girkin’s connections to DNR and LNR volunteer formations that have generated additional volunteers for the war.
12/ Putin likely ordered the Russian MoD to form its own regional volunteer battalions to replicate the recruitment processes of the ultranationalist groups rather than ordering the involuntary reserve call-up the MoD likely recommended.
13/ The Russian MoD has historically struggled to generate volunteer forces and has instead remained reliant on conscription.
14/ The Russian MoD first attempted to form a voluntary full-scale military reserve force in February 2018 by offering individuals who had left active duty to sign military contracts.
15/ Although it is unclear how many forces this campaign generated, the Russian MoD’s August 2021 failed efforts to form the Russian Combat Army Reserve (BARS-2021) - which sought to recruit 100,000 volunteer reservists for 3-year contract service –
16/ ...suggests that the Russian MoD had likely already failed at incentivizing former servicemen to join their ranks.
The Russian MoD, in fact, appears to have abandoned the effort to recruit into the BARS system itself, delegating that effort to the ultranationalist community.
The Russian MoD, in fact, appears to have abandoned the effort to recruit into the BARS system itself, delegating that effort to the ultranationalist community.
17/ Ukraine’s sweeping counteroffensive in Kharkiv Oblast between September 6 and September 11 likely shocked Putin into realizing that he needed to order an involuntary reserve call-up.
18/ Putin likely recognized that the involuntary reserve call-up could not close the gap between Russian force requirements and available manpower in a timely fashion, however...
19/ ...and so gave the Wagner Group room to expand its recruitment of prisoners and its operations on the frontline until the mobilized personnel could arrive en masse. Putin meanwhile continued to tolerate the Russian ultranationalist community...
20/ ...which only expanded its influence in society against the backdrop of Russian military failures in Ukraine.
21/ Once the bulk of the 300,000 mobilized reservists had arrived with units in Ukraine Putin began allowing the Russian MoD to reassert its primacy over all Russian forces.
22/ Putin named Gerasimov overall theater commander on January 11, subordinating Surovikin to him. Russian MoD began actively integrating the 1st and 2nd (DNR and LNR) army corps into the conventional Russian military and is reportedly removing proxy commanders.
23/ The Russian MoD is also attempting to restrict Wagner from receiving state ammunition and stopped Wagner’s prisoner recruitment in favor of its own prisoner recruitment efforts.
24/ Putin’s clear efforts to prepare the Russian people for a protracted and painful war suggest that he has realized that only the Russian MoD can actually sustain the large mechanized forces he needs to have any hope of achieving his ambitions in Ukraine.
25/ Putin’s need for the ultranationalist community has changed but has not vanished. He no longer needs that community to draw volunteers to avoid involuntary mobilization, but he still needs it to serve as the most reliable pro-Kremlin voice supporting the war effort.
26/ #Putin may find himself facing another dilemma after another wave or two of reserve call-ups, as the pool of reservists appropriate for front-line fighting is finite. isw.pub/UkrWar022623
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh