TODAY we have the #FOMC meeting.
The expectations are 10.7% for no rate hike (0 points) and 89.3% for a 25-point hike. In this thread, we'll explore why and how the Federal Reserve uses interest rates as a tool, other tools and the history behind it, and some examples 👇
The expectations are 10.7% for no rate hike (0 points) and 89.3% for a 25-point hike. In this thread, we'll explore why and how the Federal Reserve uses interest rates as a tool, other tools and the history behind it, and some examples 👇

Before we continue, if you would like to learn more about what the FOMC is doing and the impacted on the market. You can read my thread from yesterday. Just follow the link:
https://twitter.com/cryptovoes/status/1638122771636002818
The #Fed uses interest rates as a key tool in managing the US economy. By changing interest rates, the Fed can influence borrowing, spending, and inflation, helping to stabilize the economy and achieve its dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability. 

The history of using interest rates as a tool dates back to the 20th century. The Federal Reserve Act of 1913 established the Fed as the US central bank, with the power to influence interest rates and maintain financial stability. #FederalReserveAct 

When the Fed raises interest rates, it becomes more expensive for banks, businesses, and individuals to borrow money. This can slow down economic growth, reduce inflation, and ultimately help to achieve the Fed's objectives. 
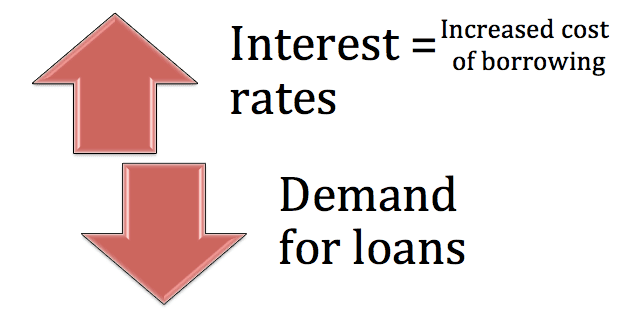
The opposite is also true: when the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, which can stimulate spending, investment, and economic growth. This was seen during the Great Recession, when the Fed cut rates to near-zero levels to counteract the downturn. 

One famous example of interest rate policy is the Volcker Shock in the early 1980s. Fed Chairman Paul Volcker aggressively raised interest rates to combat high inflation, causing a recession but ultimately taming inflation and setting the stage for a long period of growth, but... 

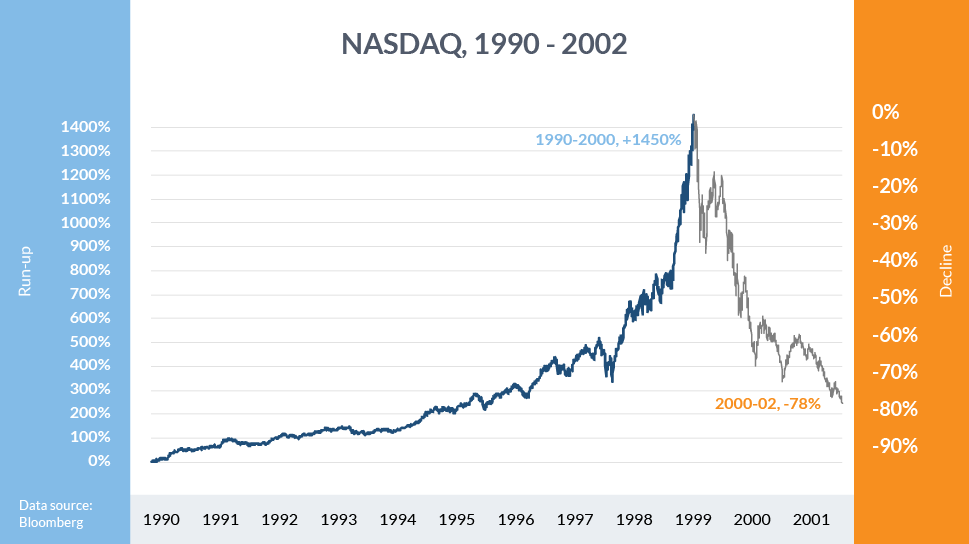
The use of interest rates as a tool can have unintended consequences. For example, in the late 1990s, this Fed's low-interest-rate policy contributed to the dot-com bubble, which burst in 2000 and led to one of the biggest recessions. 
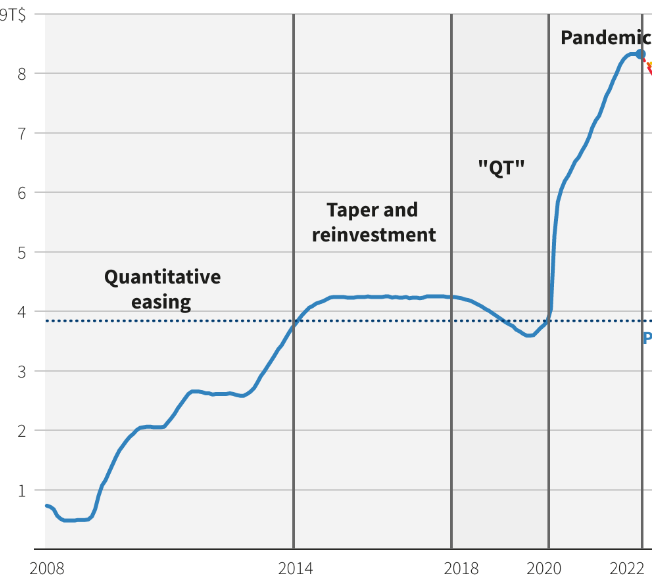
In recent years, the Fed has relied on other tools alongside interest rates, such as quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT). Let's explore what they are and how they work.
Quantitative easing is when a central bank creates new money and uses it to buy government bonds or other financial assets. This increases the money supply, lowers long-term interest rates, and encourages lending and investment. Used when short-term rates are already near zero.
While quantitative easing is designed to stimulate the economy, the counterpart called quantitative tightening is a process through which central banks reverse the effects of QE by reducing the size of their balance sheets.
Now with the collapsing of bank the US started QE again. Riskier assets will do better as the money supply increases, for example, the QE in the pandemic years when the balance sheet went from $4T to $9T. 
In conclusion, understanding the history and mechanics of interest rates, as well as other monetary policy tools, can provide valuable context and help you make better informed decisions on your trades in response to economic trends and central bank actions.
I hope this thread has helped you understand the current high-interest rates, their implications on the economy and financial markets, and their potential future implications.
Please help me by linking ♥️ the first tweet and let me know what you'd like me to cover next! 👇
Please help me by linking ♥️ the first tweet and let me know what you'd like me to cover next! 👇
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh