1/Feeling unarmed when it comes to evaluating cervical radiculopathy & foraminal narrowing on MR?
Here’s a #tweetorial that’ll take that weight off your shoulder & show you how to rate cervical foraminal stenosis!
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #radtwitter #neurorad #spine #radres
Here’s a #tweetorial that’ll take that weight off your shoulder & show you how to rate cervical foraminal stenosis!
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #radtwitter #neurorad #spine #radres

2/First, the anatomy. Nerve rootlets arise from the anterior & posterior horns, merging to form anterior (motor) & dorsal (sensory) nerves roots in the thecal sac.
These come together & the dorsal root has its dorsal root ganglion before the spinal nerve extends extravertebral
These come together & the dorsal root has its dorsal root ganglion before the spinal nerve extends extravertebral
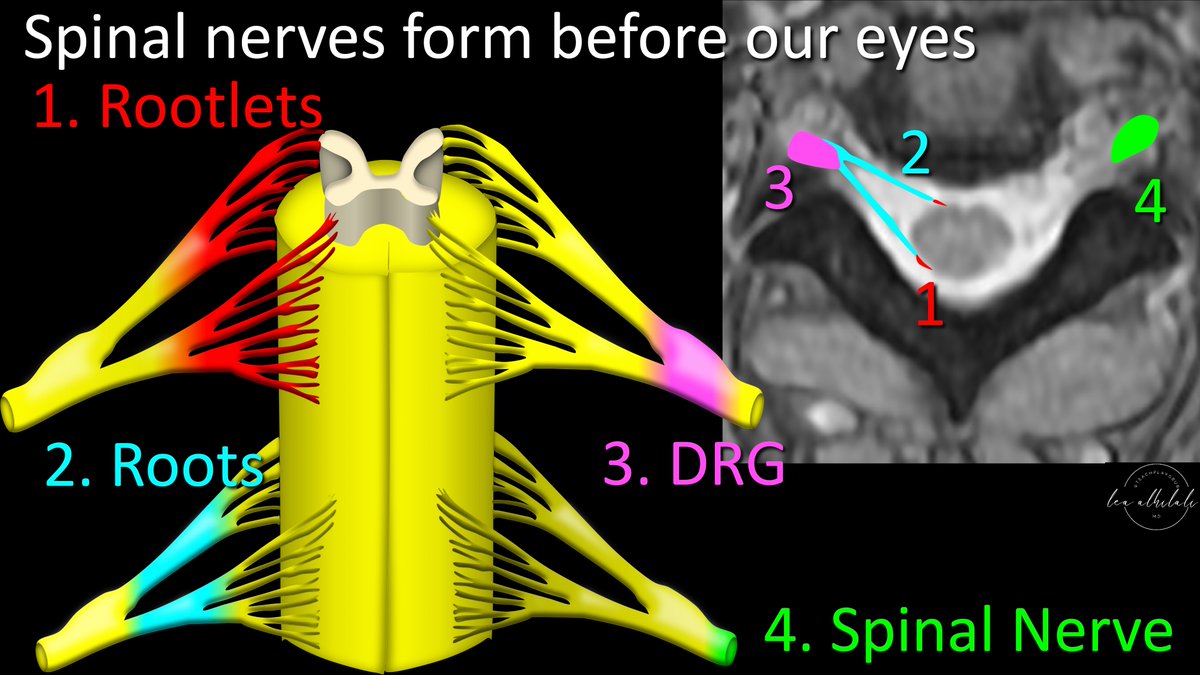
3/Think of it like a road system but carrying information/impulses instead of cars. Small roads (rootlets) merging to make larger roads (roots), before these finally merge together onto the big highway, which is the dorsal root ganglion and spinal nerve 

4/This highway of impulses & information must travel from the spinal cord inside the dura, to the rest of the body/arms in the extravertebral space.
The neural foramen is the doorway to pass from intradural to extra vertebral.
The neural foramen is the doorway to pass from intradural to extra vertebral.

5/Neural foramen is narrower than the intradural space/thecal sac or extravertebral region
It’s like our information highway must pass through a tollbooth—where the 8 lane highway narrows to 4. This can cause a bottleneck if there’s too much traffic before the road widens again
It’s like our information highway must pass through a tollbooth—where the 8 lane highway narrows to 4. This can cause a bottleneck if there’s too much traffic before the road widens again

6/Impingement may occur anywhere on the highway (medial/intradural, intermediate/foraminal, lateral/extravertebral). Medially, it’s mostly from uncovertebral joint/disc which sit in front of the anterior root. Weakness may occur; amyotrophy will not w/o cord flattening also 

7/At the other end (extravertebral), the nerve sits in the neural sulcus of the transverse process. It’s like an emergency exit slide from a plane—except it’s a nerve exiting a foramen not a plane. Posterior wall is the facet & hypertrophy here will hit the nerve in its slide 

8/Impingement medially & laterally are rare compared to foraminal impingement, as foramen is the bottleneck (tollbooth) of our road from spinal cord to arm
Neural foramen is made of disc/uncovertebral joint anteriorly & facet posteriorly. Hypertrophy of either will narrow it
Neural foramen is made of disc/uncovertebral joint anteriorly & facet posteriorly. Hypertrophy of either will narrow it

9/How do we image the foramen to detect stenosis/impingement?
Unlike the L-spine, we can’t do straight sagittals bc the foramina come at a 45 degree angle anteriorly—like when someone is reaching anteriorly to hug you
So true sagittals don’t show the foramen in cross-section
Unlike the L-spine, we can’t do straight sagittals bc the foramina come at a 45 degree angle anteriorly—like when someone is reaching anteriorly to hug you
So true sagittals don’t show the foramen in cross-section

10/Maybe oblique sagittals perpendicular to the foramen?
Sounds great, but if there’s curve/kyphosis/rotation, position of the foramen changes w/respect to the oblique sagittal, so it may not be perpendicular anymore. Neck is susceptible to imperfect positioning in the scanner
Sounds great, but if there’s curve/kyphosis/rotation, position of the foramen changes w/respect to the oblique sagittal, so it may not be perpendicular anymore. Neck is susceptible to imperfect positioning in the scanner

11/How about axials?
Unlike the lumbar, where foramina take off at sharp angles like a Xmas tree—cervical foramina are much more flat, like a totem pole, so they are almost entirely in the axial plane.
Axial plane is 90 degrees & cervical foramina angles are very close to that
Unlike the lumbar, where foramina take off at sharp angles like a Xmas tree—cervical foramina are much more flat, like a totem pole, so they are almost entirely in the axial plane.
Axial plane is 90 degrees & cervical foramina angles are very close to that

12/Axial images are actually good at evaluating cervical foramina.
Axial stenosis ratings have very good concordance w/oblique sagittal ratings (for experienced readers, not residents)--& using axials saves you 2 extra oblique sagittal acquisitions!
Axial stenosis ratings have very good concordance w/oblique sagittal ratings (for experienced readers, not residents)--& using axials saves you 2 extra oblique sagittal acquisitions!

13/So how do we rate foraminal narrowing in the axial plane?
Think of the nerve root like a hot dog, sitting between the two buns of the disc/uncovertebral joint & facet. The more you put in your hot dog, the more the hot dog itself is squished. Same w/the nerve root.
Think of the nerve root like a hot dog, sitting between the two buns of the disc/uncovertebral joint & facet. The more you put in your hot dog, the more the hot dog itself is squished. Same w/the nerve root.

14/Spurring & degenerative change are like the extra topping that push on the hot dog inside the buns. A small amount of toppings/degenerative change, leaves the hot dog space. But if you pile on fixings, then the hot dog is taken over.
Ask yourself--how is my hot dog doing?
Ask yourself--how is my hot dog doing?

15/So how much is too much?
Take inspiration from the carotid. W/carotid stenosis, narrowing the lumen >50% of the normal downstream lumen results in hemodynamic effects.
Same w/the foramen—narrowing it >50% of the downstream nerve causes significant symptoms
Take inspiration from the carotid. W/carotid stenosis, narrowing the lumen >50% of the normal downstream lumen results in hemodynamic effects.
Same w/the foramen—narrowing it >50% of the downstream nerve causes significant symptoms

16/So mild stenosis is like when there’s calficied plaque in the carotid wall that doesn’t narrow it at all.
Moderate stenosis is when the plaque narrows the lumen, but not >50%.
And finally, severe stenosis is when you narrow it >50% of the normal downstream lumen
Moderate stenosis is when the plaque narrows the lumen, but not >50%.
And finally, severe stenosis is when you narrow it >50% of the normal downstream lumen

17/But there isn’t a downstream foramen like there’s a downstream lumen for the carotid. So you use the diameter of the normal extravertebral nerve instead—b/c it’s rarely compressed.
Mild stenosis is like just a little ketchup & mustard on the bun but hot dog still has space.
Mild stenosis is like just a little ketchup & mustard on the bun but hot dog still has space.

18/Moderate stenosis is when you aren’t just putting on sauce, you are adding things that take up space, like relish. But there’s only so much relish one can put on, so it doesn’t take up more than half the bun. 

19/Severe stenosis is like a chili cheese dog, where the hot dog is smothered & it has no room in the bun away from the chili or cheese. Here the narrowing is greater than 50% 

20/This is the Kim classification & has strong correlation w/symptoms
I like it bc it doesn’t require calipers to estimate a >50% narrowing
It’s technically for axial T2 images, but it’s been applied to gradient images & even CT, although there’s not yet confirmatory evidence
I like it bc it doesn’t require calipers to estimate a >50% narrowing
It’s technically for axial T2 images, but it’s been applied to gradient images & even CT, although there’s not yet confirmatory evidence

21/You might say, 50% stenosis may be hemodynamically significant, but it’s not severe. Why is it severe in the foramen?
It’s bc hemodynamics is linear, where more stenosis = more effect. But pain is kind of binary—once there’s pain, it’s there, whether narrowing is 55% or 95%
It’s bc hemodynamics is linear, where more stenosis = more effect. But pain is kind of binary—once there’s pain, it’s there, whether narrowing is 55% or 95%

22/So now you know how to both image and assess stenosis in the cervical neural foramen.
Now hopefully rating cervical foraminal narrowing won’t be a pain in the neck!
Now hopefully rating cervical foraminal narrowing won’t be a pain in the neck!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















