1/Time is brain! But what time is it?
If you don’t know the time of stroke onset, are you able to deduce it from imaging?
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you date a #stroke on MR!
#medtwitter #meded #neurotwitter #neurology #neurorad #radres #radtwitter #radiology #FOAMed #FOAMrad
If you don’t know the time of stroke onset, are you able to deduce it from imaging?
Here’s a #tweetorial to help you date a #stroke on MR!
#medtwitter #meded #neurotwitter #neurology #neurorad #radres #radtwitter #radiology #FOAMed #FOAMrad
2/In up to 25% of acute stroke patients, the time of last known well is well, not known. Then it’s important to use the stroke’s MR imaging features to help date its timing. Is it hyperacute? Acute? Subacute? Or are the “stroke” symptoms from a seizure from their chronic infarct? 

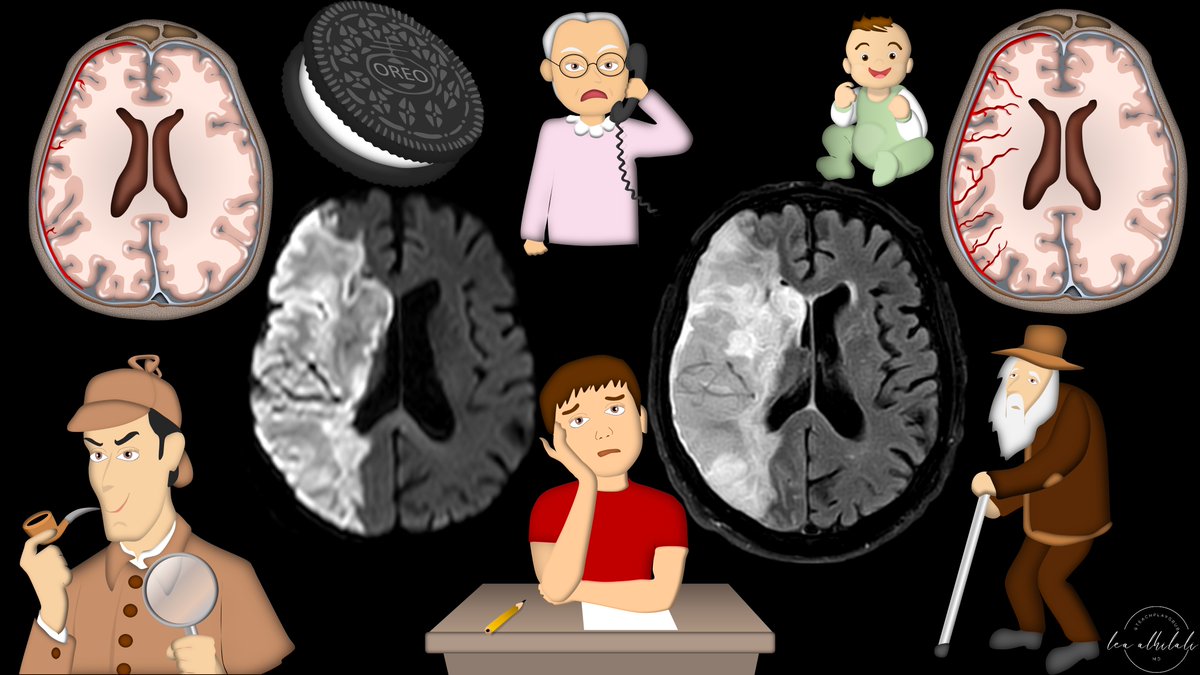
3/Strokes evolve, or grow old, the same way people evolve or grow old. The appearance of stroke on imaging mirrors the life stages of a person—you just have to change days for a stroke into years for a person. So 15 day old stroke has features of a 15 year old person, etc. 

4/Initially (less than 4-6 hrs), the only finding is restriction (brightness) on diffusion imaging (DWI). You can remember this bc in the first few months, a baby does nothing but be swaddled or restricted. So early/newly born stroke is like a baby, only restricted 

5/ Remember, all diffusion does is detect how difficult it is for water to move. Anything that makes the space around water crowded and difficult to move will be bright on diffusion imaging 

6/When cells run out of ATP, Na/K pump stops working & immediately water rushes in from osmotic pressure & the cells swell. The swollen cells fill the interstitium & restrict movement of water. This is why strokes are bright on DWI! This can happen early as 5 min or late as 3 hrs 

7/The other sign you see in this hyperacute phase is bright signal on vessels on FLAIR from slow flow. The twisting bright vessels look like ivy vines (like the moya moya ivy sign). You can remember this bc restricted babies this young are just like potted plants or potted ivy 

8/Next, at 4-6 hours, you see bright signal on FLAIR imaging. You can remember this bc after a few months, a baby starts to develop some personality or "flair". So after a few hours, the stroke gets some flair as well. So if you see FLAIR, stroke is old enough to have personality 

9/Why does a stroke become FLAIR bright? It’s the first sign of blood brain breakdown. Brain realizes the stroke is a problem & opens the doors to let in leukocytes to clean up. It’s like an out-of-control party—it’s a few hours before police are called for help—same w/the brain 

10/Even when the stroke has personality/FLAIR, it is still restricted/bright on DWI. You can remember this bc even after you form a personality & get some flair, you are still very restricted by your parents in your early months. 

11/So early hyperacute strokes only have DWI (<4.5 hr), but late hyperacute (>4.5 hr) have both FLAIR & DWI
This DWI/FLAIR mismatch is used to date very early strokes
If FLAIR is seen, the region is old enough to have personality, but if it doesn’t, it’s still swaddling young
This DWI/FLAIR mismatch is used to date very early strokes
If FLAIR is seen, the region is old enough to have personality, but if it doesn’t, it’s still swaddling young

12/But it’s not exact. Seeing FLAIR signal is used to date a stroke as >4.5 hours, but the actual time depends on the collateral status. With poor collaterals, it can be seen as early as 3 hrs, but w/good collaterals, it could be seen as late as 6. This is important to remember 

13/You can remember this by thinking of collaterals like siblings. The more siblings you have, the less attention you’re getting & so you’re probably going to develop a little on the later side & show off your personality/flair later. So lots of collaterals/siblings = late FLAIR 

14/Next stage in life is when you go off to school to “enhance” your education beyond just your parents/family at home. This can be early, i.e. preschool (at like 3yrs) but usually its kindergarten (5 yrs). So most strokes start to enhance at 5 days, but can be a bit earlier 

15/Now even when you are going off to school, you are still a little kid, so you are still very restricted by your parents. So at this age, a stroke is still restricted. Remember, if the enhancing infarct is DWI bright, you know it's at a young age in its schooling/enhancement 

16/It’s not until you’re about 10 that your parents give you a little independence (loosen restrictions), liking letting you go away by yourself to camp. Same w/strokes, at about 10 days restricted diffusion ends—so if there’s no restriction, kid’s gotta be older than about 10 

17/At about 15 is when you go through your rebellious phase. You start doing this like dyeing the tips of your hair. Same w/strokes—you start to see T1 bright signal along the tips of the cortex at about 15 days—called cortical laminar necrosis 

18/What causes cortical laminar necrosis? Middle cortical layer 3 is the most metabolically active & most vulnerable to infarct first. It then spills T1 bright protein & blood products. It’s like an Oreo—there’s many layers, but it’s the middle layer that’s eaten first! 

19/Enhancement ends from 15 to 40 days, very variable. It’s when you get tired of education/enhancement in life. For some it’s in their teens but others (doctors!) it’s not until later. But if you’re still in education/enhancement at age 50—it’s unusual & consider more imaging 

20/In the later stages of life, you may not have the tips of your hair dyed, but you do have them colored—w/gray hair! So cortical laminar necrosis can continue—many times up to 60 days or even longer—just like you can have salt & pepper tips right up until old age. 

21/Finally, the last stage is encephalomalacia—where you lose volume. And everyone knows that things start to go downhill after 40. Just like people lose volume & shrivel up as they age, so do strokes. Any stroke showing volume loss/encephalomalacia is always chronic 

22/So now you know how to date a stroke on imaging, by using it’s imaging features to see what stage of life it is at.
Now when a stroke w/unknown onset comes in, you’ll be ready—right in the nick of time!
Now when a stroke w/unknown onset comes in, you’ll be ready—right in the nick of time!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















